Question Number 601 by 123456 last updated on 08/Feb/15

$$\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{+\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{1}}{dx} \\ $$
Answered by prakash jain last updated on 08/Feb/15
![∫_0 ^1 ((x+1)/(x^2 +x+1)) dx =∫_0 ^1 (1/2)∙((2x+1)/(x^2 +x+1))dx+(1/2)∫_0 ^1 (1/(x^2 +x+1))dx =[(1/2)ln (x^2 +x+1)]_0 ^1 +(1/2)∫_0 ^1 (1/((x+(1/2))^2 +(((√3)/2))^2 ))dx =(1/2)ln 3+(1/2)[(2/( (√3)))tan^(−1) ((x+(1/2))/((√3)/2))]_0 ^1 =(1/2)ln 3+(1/( (√3)))[tan^(−1) (√3)−tan^(−1) (1/( (√3)))] =(1/2)ln 3+(1/( (√3)))((π/3)−(π/6)) =(1/2)ln 3+(π/(6(√3)))](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q602.png)
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}}\:{dx} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\centerdot\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}}{dx}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}}{dx} \\ $$$$=\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{ln}\:\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{3}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \frac{{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}}{\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}}}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{3}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\left[\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \sqrt{\mathrm{3}}−\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\right] \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{3}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{6}}\right) \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{3}+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{6}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 08/Feb/15
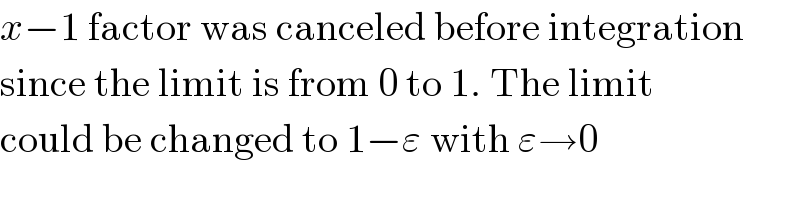
$${x}−\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{factor}\:\mathrm{was}\:\mathrm{canceled}\:\mathrm{before}\:\mathrm{integration} \\ $$$$\mathrm{since}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{limit}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{from}\:\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{1}.\:\mathrm{The}\:\mathrm{limit} \\ $$$$\mathrm{could}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{changed}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{1}−\varepsilon\:\mathrm{with}\:\varepsilon\rightarrow\mathrm{0} \\ $$
