Question Number 789 by 123456 last updated on 14/Mar/15

$$\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\underset{{x}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {\overset{\sqrt{{x}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }} {\int}}\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dydx}=? \\ $$$$\int\underset{\mathrm{B}} {\int}\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dxdy}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{B}=\left\{\left({x},{y}\right)\in\mathbb{R}^{\mathrm{2}} :{y}\geqslant{x}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \wedge{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}\leqslant\mathrm{0}\right\} \\ $$$$\int\underset{\mathrm{B}^{\ast} } {\int}\rho^{\mathrm{2}} {d}\rho{d}\theta\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{B}^{\ast} =??? \\ $$
Commented by 123456 last updated on 13/Mar/15
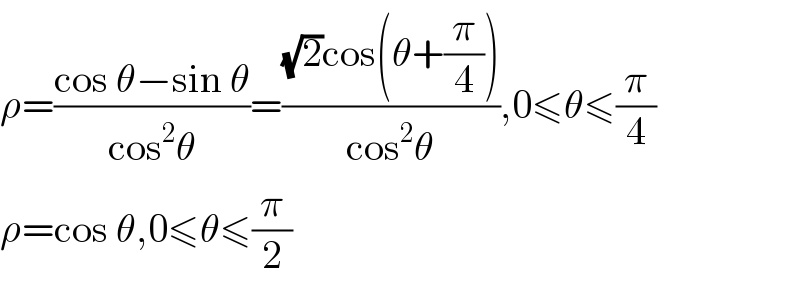
$$\rho=\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:\theta−\mathrm{sin}\:\theta}{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \theta}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{cos}\left(\theta+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right)}{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \theta},\mathrm{0}\leqslant\theta\leqslant\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\rho=\mathrm{cos}\:\theta,\mathrm{0}\leqslant\theta\leqslant\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 14/Mar/15

$${x}={u}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\Rightarrow{du}={dx} \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{0},{u}=−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5},\:{x}=\mathrm{1},{u}=\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5} \\ $$$${x}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} =\left({u}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)−\left({u}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Upper}\:\mathrm{limit}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{circle}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{radius}\:\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{lower}\:\mathrm{limits}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{parabola} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${u}=\rho\mathrm{cos}\:\theta,\:{y}=\rho\mathrm{sin}\:\theta \\ $$$$\rho^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \theta+\rho\mathrm{sin}\:\theta−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{solving}\:\mathrm{quadratic}\:\rho=\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}\:\theta}{\mathrm{2cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \theta} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Limits}\:\mathrm{on}\:\theta,\:\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{to}\:\pi \\ $$$$\mathrm{Limits}\:\mathrm{on}\:\rho,\:\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}\:\theta}{\mathrm{2cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \theta}\:\mathrm{to}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{or}\:\mathrm{Limits}\:\mathrm{of}\:\rho\:\mathrm{from}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}\:\theta\right)}\:\mathrm{to}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by prakash jain last updated on 14/Mar/15

$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\pi} \:\int_{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}\:\theta\right)}} ^{\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} \sqrt{\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\rho\mathrm{cos}\:\theta\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(\rho\mathrm{sin}\:\theta\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\rho{d}\rho{d}\theta \\ $$
