Question Number 6113 by enigmeyou last updated on 14/Jun/16
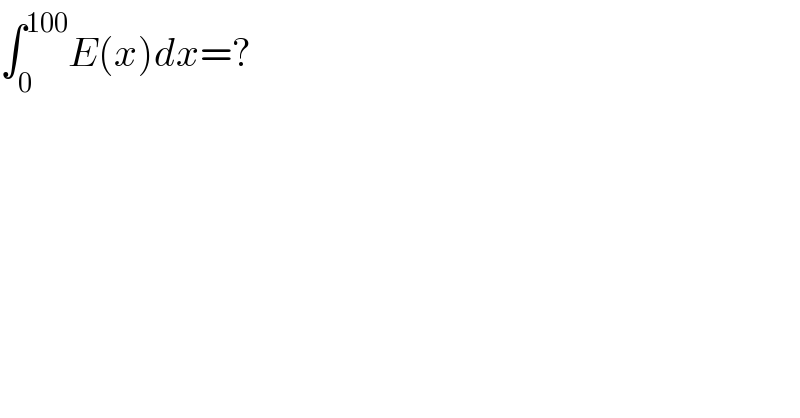
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{100}} {E}\left({x}\right){dx}=? \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by 123456 last updated on 14/Jun/16

$$\mathrm{what}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{E}\left({x}\right)? \\ $$
Commented by FilupSmith last updated on 15/Jun/16

$$\mathrm{Floor}\:\mathrm{func}. \\ $$$$\int_{{a}} ^{\:{b}} \lfloor{x}\rfloor{dx},\:\:\:{a},{b}\in\mathbb{Z}\:=\:{rectangle}\:={base}×{height} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{height}} \\ $$$${a}\leqslant{x}<{a}+\mathrm{1}\:\:\Rightarrow\:\:\lfloor{x}\rfloor=\:{a} \\ $$$${a}+\mathrm{1}\leqslant{x}<{a}+\mathrm{2}\:\:\Rightarrow\:\:\lfloor{x}\rfloor=\:{a}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$… \\ $$$${b}−\mathrm{1}\leqslant{x}<{b}\:\:\Rightarrow\:\:\lfloor{x}\rfloor\:=\:{b}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{base}}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\int_{{a}} ^{\:{b}} \lfloor{x}\rfloor{dx}={a}+\left({a}+\mathrm{1}\right)+…+\left({b}−\mathrm{2}\right)+\left({b}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$${first}\:{term}={a} \\ $$$${last}\:{term}\:=\:{b}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\therefore\:\int_{{a}} ^{\:{b}} \lfloor{x}\rfloor{dx}\:=\:\frac{\left({b}−\mathrm{1}\right)−{a}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({a}+{b}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$??? \\ $$
Commented by enigmeyou last updated on 15/Jun/16

$${the}\:{floor}\:{and}\:{ceiling}\:{function} \\ $$
Commented by FilupSmith last updated on 15/Jun/16
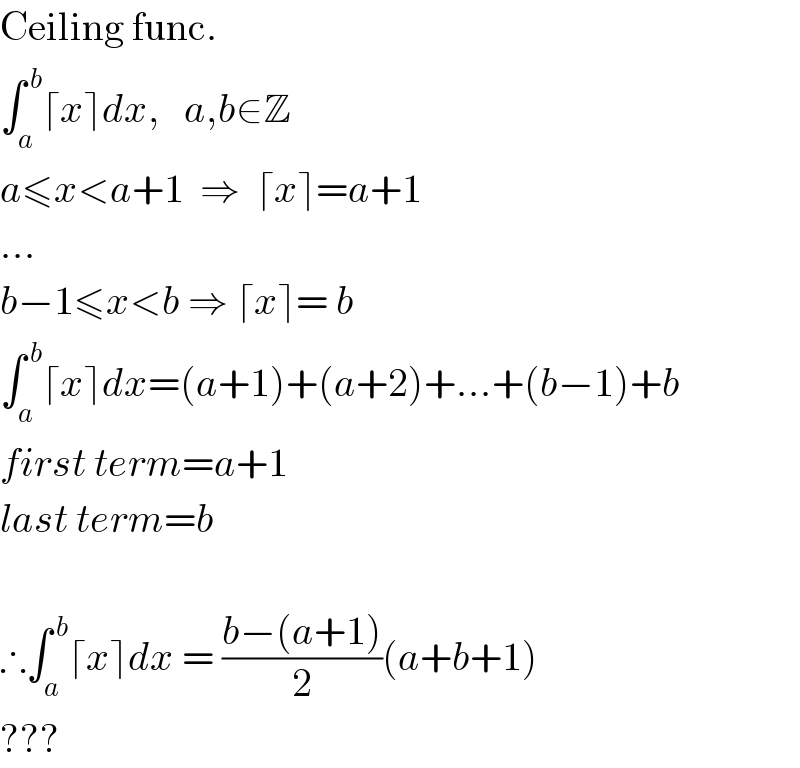
$$\mathrm{Ceiling}\:\mathrm{func}. \\ $$$$\int_{{a}} ^{\:{b}} \lceil{x}\rceil{dx},\:\:\:{a},{b}\in\mathbb{Z} \\ $$$${a}\leqslant{x}<{a}+\mathrm{1}\:\:\Rightarrow\:\:\lceil{x}\rceil={a}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$… \\ $$$${b}−\mathrm{1}\leqslant{x}<{b}\:\Rightarrow\:\lceil{x}\rceil=\:{b} \\ $$$$\int_{{a}} ^{\:{b}} \lceil{x}\rceil{dx}=\left({a}+\mathrm{1}\right)+\left({a}+\mathrm{2}\right)+…+\left({b}−\mathrm{1}\right)+{b} \\ $$$${first}\:{term}={a}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${last}\:{term}={b} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\therefore\int_{{a}} ^{\:{b}} \lceil{x}\rceil{dx}\:=\:\frac{{b}−\left({a}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\left({a}+{b}+\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$??? \\ $$
Answered by petmill last updated on 15/Jun/16
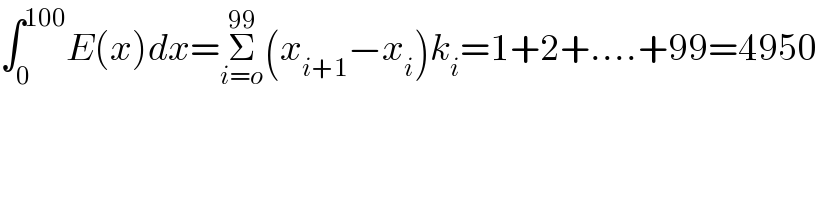
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{100}} {E}\left({x}\right){dx}=\underset{{i}={o}} {\overset{\mathrm{99}} {\sum}}\left({x}_{{i}+\mathrm{1}} −{x}_{{i}} \right){k}_{{i}} =\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}+….+\mathrm{99}=\mathrm{4950} \\ $$
Commented by enigmeyou last updated on 15/Jun/16
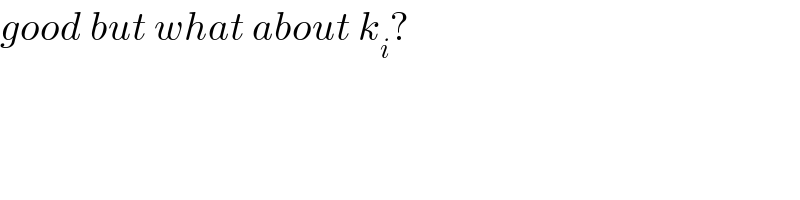
$${good}\:{but}\:{what}\:{about}\:{k}_{{i}} ? \\ $$
