Question Number 137926 by brayan last updated on 08/Apr/21
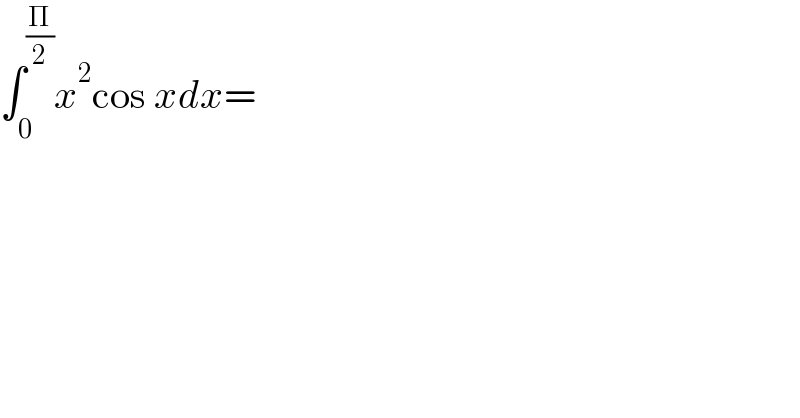
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\Pi}{\mathrm{2}}} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}\:{xdx}= \\ $$
Answered by Ñï= last updated on 08/Apr/21
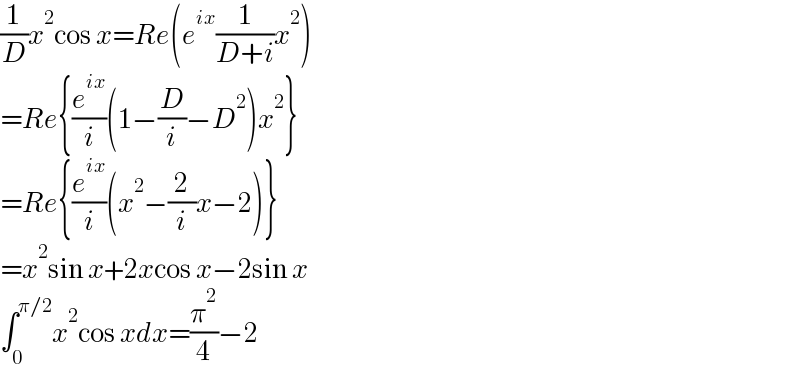
$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{D}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}\:{x}={Re}\left({e}^{{ix}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{{D}+{i}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$={Re}\left\{\frac{{e}^{{ix}} }{{i}}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{{D}}{{i}}−{D}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right\} \\ $$$$={Re}\left\{\frac{{e}^{{ix}} }{{i}}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{i}}{x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\right\} \\ $$$$={x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}+\mathrm{2}{x}\mathrm{cos}\:{x}−\mathrm{2sin}\:{x} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}\:{xdx}=\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}}−\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 08/Apr/21
![∫x^2 cos x dx =x^2 sin x−2∫x sin x dx =x^2 sin x−2[−x cos x+∫cos x dx] =x^2 sin x−2[−x cos x+sin x]+C =x^2 sin x+2x cos x−2 sin x+C ∫_0 ^(π/2) =(π^2 /4)−2](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q137929.png)
$$\int{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:{dx} \\ $$$$={x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}−\mathrm{2}\int{x}\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:{dx} \\ $$$$={x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}−\mathrm{2}\left[−{x}\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}+\int\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:{dx}\right] \\ $$$$={x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}−\mathrm{2}\left[−{x}\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}+\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\right]+{C} \\ $$$$={x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}+\mathrm{2}{x}\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}−\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}+{C} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} =\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}}−\mathrm{2} \\ $$
