Question Number 140614 by bramlexs22 last updated on 10/May/21
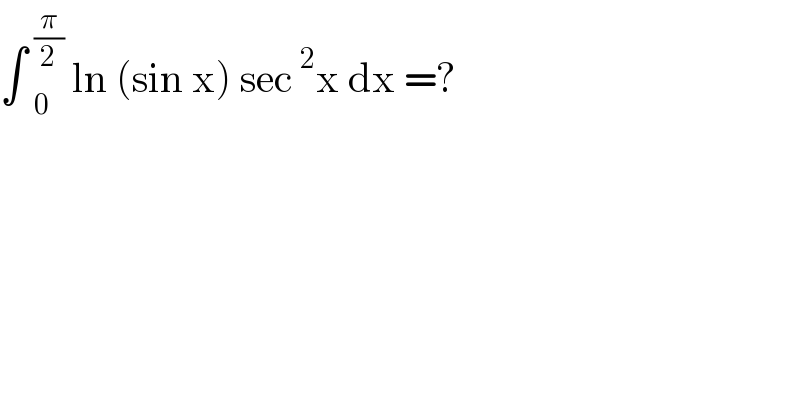
$$\int\:_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{x}\right)\:\mathrm{sec}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{dx}\:=?\: \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by bemath last updated on 10/May/21

Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 10/May/21
![∫_0 ^(π/2) log(sinx)sec^2 xdx =[log(sinx)tanx]_0 ^(π/2) −∫_0 ^(π/2) tanx.((cosx)/(sinx))dx =0−(π/2)=−(π/2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q140622.png)
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} {log}\left({sinx}\right){sec}^{\mathrm{2}} {xdx} \\ $$$$=\left[{log}\left({sinx}\right){tanx}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} −\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} {tanx}.\frac{{cosx}}{{sinx}}{dx} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{0}−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}=−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
