Question Number 10790 by Nur450737 last updated on 25/Feb/17
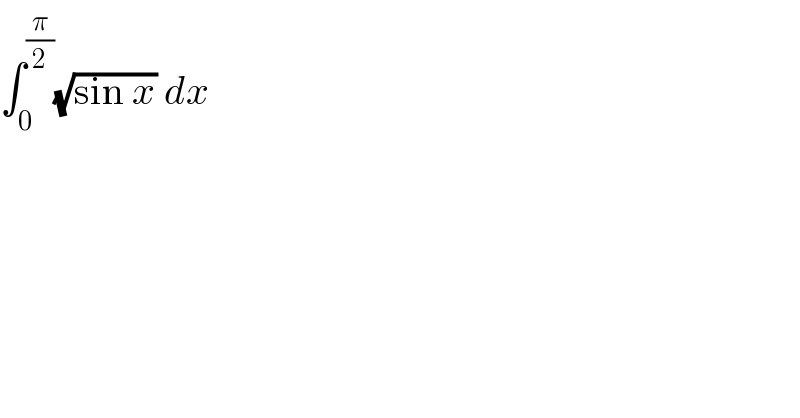
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \sqrt{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}\:{dx} \\ $$
Answered by bahmanfeshki last updated on 26/Feb/17
![(√(sin x))=t t^2 =sin x⇒cos x=(√(1−t^2 )) 2t dt=cos x dx⇒dx=((2t)/( (√(1−t^2 ))))dt ∫_0 ^1 ((2t^2 )/( (√(1−t^2 ))))dt=∫_0 ^(π/2) 2sin^2 vdv=[v−((sin 2v)/2)]_0 ^(π/2) =(π/2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q10823.png)
$$\sqrt{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}={t} \\ $$$${t}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\Rightarrow\mathrm{cos}\:{x}=\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{t}\:{dt}=\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:{dx}\Rightarrow{dx}=\frac{\mathrm{2}{t}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{dt} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\mathrm{2}{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{dt}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \mathrm{2sin}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {vdv}=\left[{v}−\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{v}}{\mathrm{2}}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} =\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
