Question Number 799 by 123456 last updated on 15/Mar/15

$$\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi} {\int}}\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\right){dx}\:{converge}? \\ $$
Answered by prakash jain last updated on 15/Mar/15
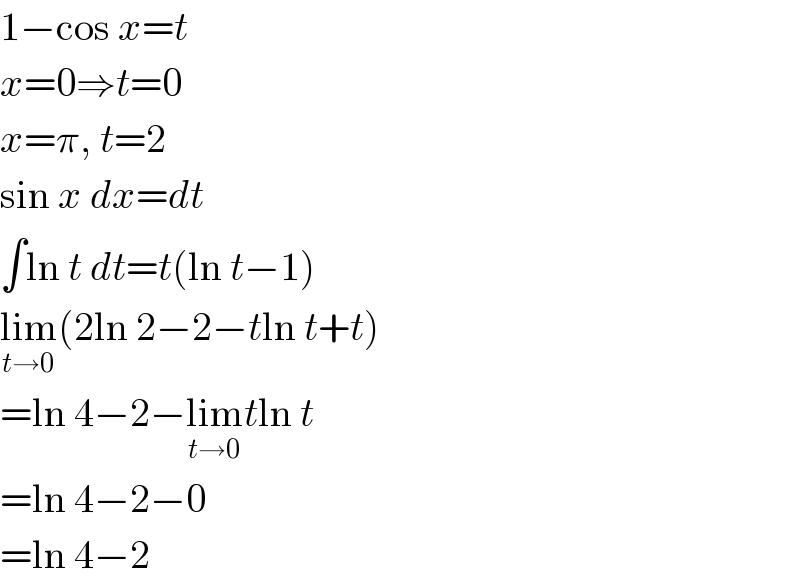
$$\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:{x}={t} \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow{t}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}=\pi,\:{t}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:{dx}={dt} \\ $$$$\int\mathrm{ln}\:{t}\:{dt}={t}\left(\mathrm{ln}\:{t}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{2ln}\:\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{2}−{t}\mathrm{ln}\:{t}+{t}\right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{2}−\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}{t}\mathrm{ln}\:{t} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{2} \\ $$
