Question Number 5343 by sanusihammed last updated on 09/May/16
![[((1−x^(−1) −6x^(−2) )/(1−5x^(−1) −24x^(−2) ))]^x Limit x → ∞ please help.](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q5343.png)
$$\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{−\mathrm{1}} −\mathrm{6}{x}^{−\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{5}{x}^{−\mathrm{1}} −\mathrm{24}{x}^{−\mathrm{2}} }\right]^{{x}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${Limit}\:{x}\:\rightarrow\:\infty \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${please}\:{help}. \\ $$
Commented by Yozzii last updated on 09/May/16
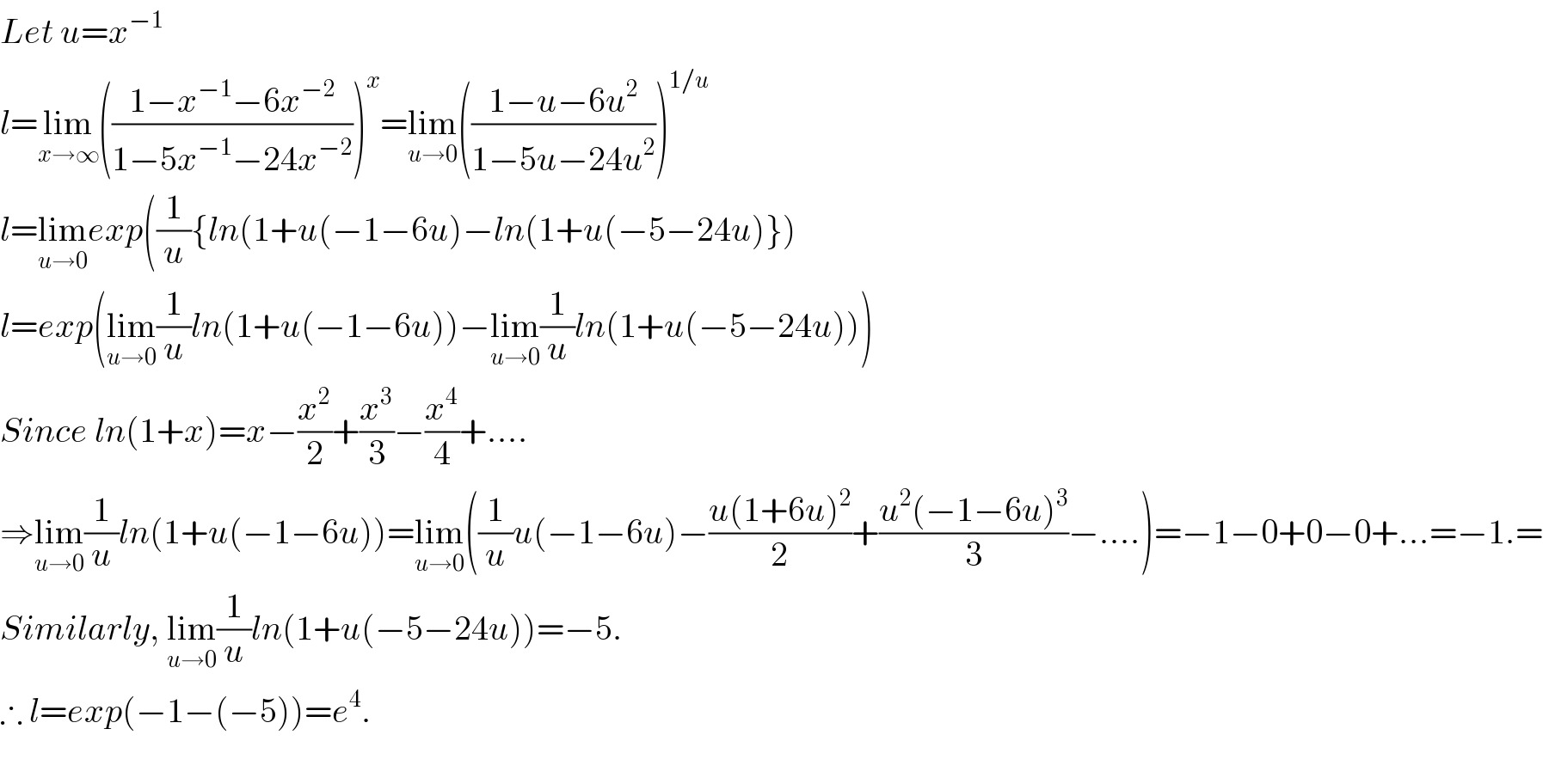
$${Let}\:{u}={x}^{−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${l}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{−\mathrm{1}} −\mathrm{6}{x}^{−\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{5}{x}^{−\mathrm{1}} −\mathrm{24}{x}^{−\mathrm{2}} }\right)^{{x}} =\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}−{u}−\mathrm{6}{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{5}{u}−\mathrm{24}{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)^{\mathrm{1}/{u}} \\ $$$${l}=\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}{exp}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}\left\{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\left(−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{6}{u}\right)−{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\left(−\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{24}{u}\right)\right\}\right)\right.\right. \\ $$$${l}={exp}\left(\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\left(−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{6}{u}\right)\right)−\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\left(−\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{24}{u}\right)\right)\right) \\ $$$${Since}\:{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)={x}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{4}}+…. \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\left(−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{6}{u}\right)\right)=\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}{u}\left(−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{6}{u}\right)−\frac{{u}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{6}{u}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{6}{u}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}−….\right)=−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{0}+\mathrm{0}−\mathrm{0}+…=−\mathrm{1}.= \\ $$$${Similarly},\:\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\left(−\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{24}{u}\right)\right)=−\mathrm{5}. \\ $$$$\therefore\:{l}={exp}\left(−\mathrm{1}−\left(−\mathrm{5}\right)\right)={e}^{\mathrm{4}} . \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by sanusihammed last updated on 09/May/16

$${Thanks}\:{so}\:{much} \\ $$
