Question Number 143184 by bramlexs22 last updated on 11/Jun/21
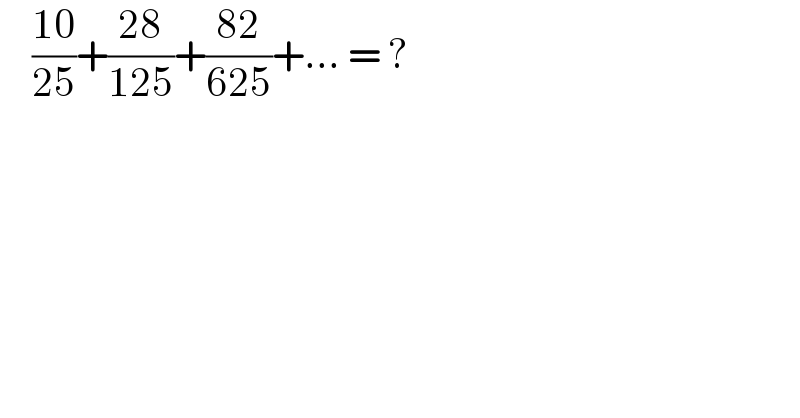
$$\:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{25}}+\frac{\mathrm{28}}{\mathrm{125}}+\frac{\mathrm{82}}{\mathrm{625}}+…\:=\:? \\ $$
Answered by Canebulok last updated on 11/Jun/21
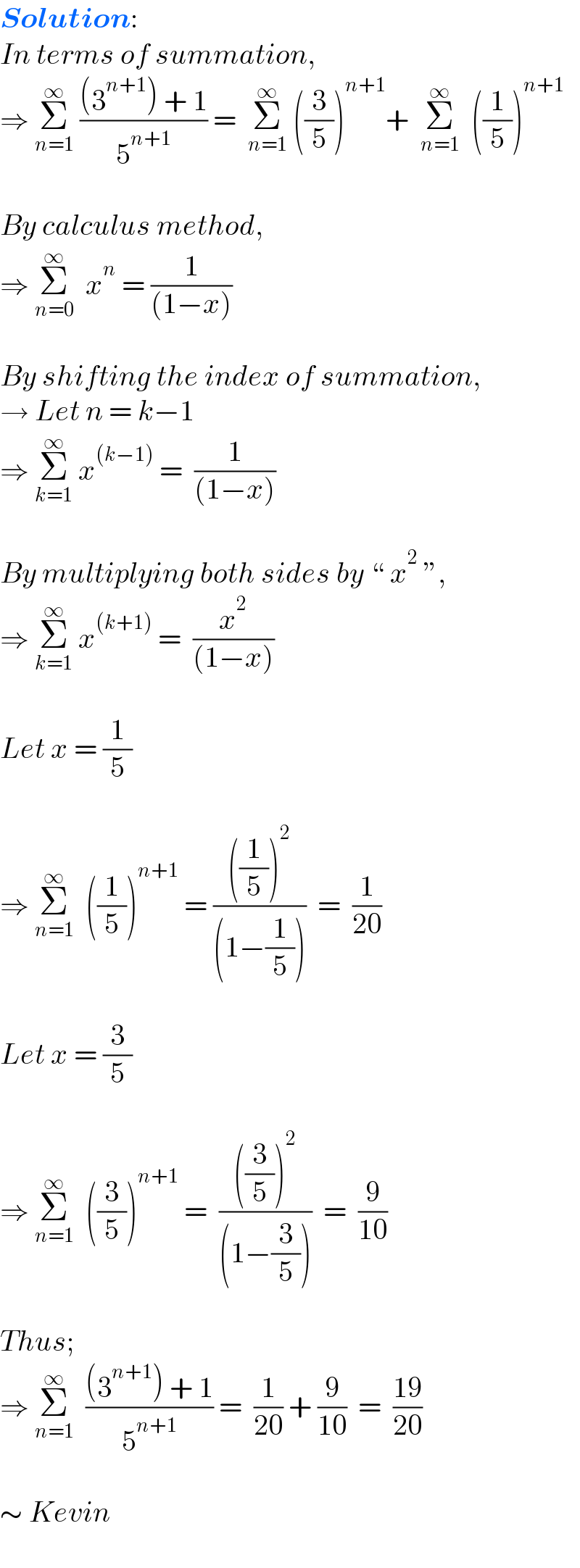
$$\boldsymbol{{Solution}}: \\ $$$${In}\:{terms}\:{of}\:{summation}, \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:\frac{\left(\mathrm{3}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \right)\:+\:\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }\:=\:\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{5}}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} +\:\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \: \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$${By}\:{calculus}\:{method}, \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:\:{x}^{{n}} \:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$${By}\:{shifting}\:{the}\:{index}\:{of}\:{summation}, \\ $$$$\rightarrow\:{Let}\:{n}\:=\:{k}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:{x}^{\left({k}−\mathrm{1}\right)} \:=\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$${By}\:{multiplying}\:{both}\:{sides}\:{by}\:“\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:'', \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:{x}^{\left({k}+\mathrm{1}\right)} \:=\:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$${Let}\:{x}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \:=\:\frac{\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\right)}\:\:=\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{20}} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$${Let}\:{x}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{5}}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \:=\:\:\frac{\left(\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{5}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{5}}\right)}\:\:=\:\:\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{10}} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$${Thus}; \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:\:\frac{\left(\mathrm{3}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \right)\:+\:\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }\:=\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{20}}\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{10}}\:\:=\:\:\frac{\mathrm{19}}{\mathrm{20}} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$$\sim\:{Kevin} \\ $$
