Question Number 135493 by EDWIN88 last updated on 13/Mar/21
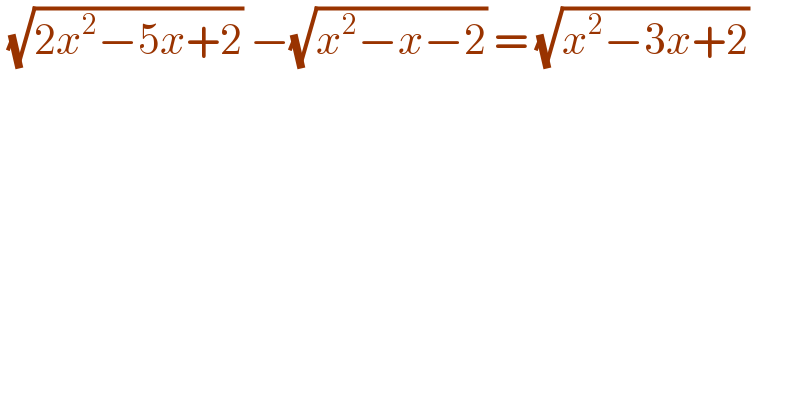
$$\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}{x}+\mathrm{2}}\:−\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}−\mathrm{2}}\:=\:\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by john_santu last updated on 13/Mar/21
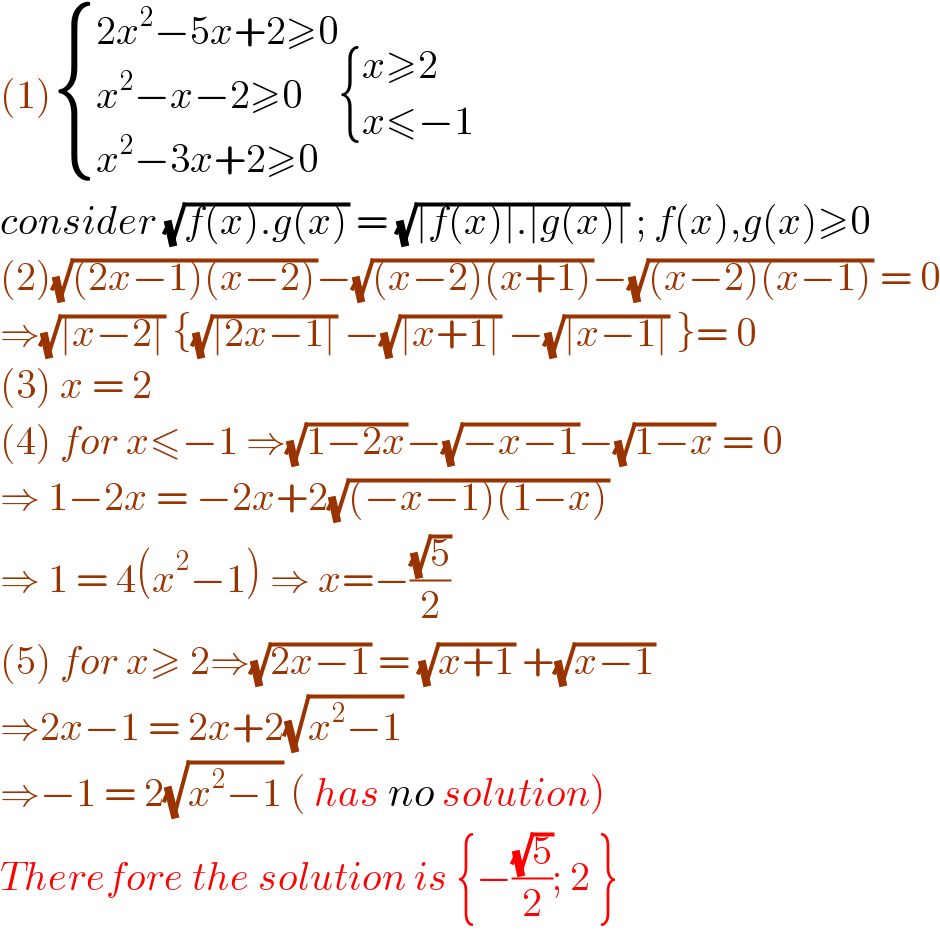
$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\begin{cases}{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}{x}+\mathrm{2}\geqslant\mathrm{0}}\\{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}−\mathrm{2}\geqslant\mathrm{0}}\\{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{2}\geqslant\mathrm{0}}\end{cases}\begin{cases}{{x}\geqslant\mathrm{2}}\\{{x}\leqslant−\mathrm{1}}\end{cases} \\ $$$${consider}\:\sqrt{{f}\left({x}\right).{g}\left({x}\right)}\:=\:\sqrt{\mid{f}\left({x}\right)\mid.\mid{g}\left({x}\right)\mid}\:;\:{f}\left({x}\right),{g}\left({x}\right)\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\sqrt{\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)}−\sqrt{\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)}−\sqrt{\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\sqrt{\mid{x}−\mathrm{2}\mid}\:\left\{\sqrt{\mid\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\mid}\:−\sqrt{\mid{x}+\mathrm{1}\mid}\:−\sqrt{\mid{x}−\mathrm{1}\mid}\:\right\}=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{3}\right)\:{x}\:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{4}\right)\:{for}\:{x}\leqslant−\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2}{x}}−\sqrt{−{x}−\mathrm{1}}−\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2}{x}\:=\:−\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\left(−{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{1}\:=\:\mathrm{4}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right)\:\Rightarrow\:{x}=−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{5}\right)\:{for}\:{x}\geqslant\:\mathrm{2}\Rightarrow\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:=\:\sqrt{{x}+\mathrm{1}}\:+\sqrt{{x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\:=\:\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow−\mathrm{1}\:=\:\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}\:\left(\:{has}\:{no}\:{solution}\right) \\ $$$${Therefore}\:{the}\:{solution}\:{is}\:\left\{−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}};\:\mathrm{2}\:\right\} \\ $$
