Question Number 74411 by peter frank last updated on 24/Nov/19

$${A}\:{rocket}\:{vertically}\:{from} \\ $$$${the}\:{surface}\:{of}\:{the}\:{earth} \\ $$$${with}\:{an}\:{initil}\:{velocity}\left({v}_{{o}} \right) \\ $$$${show}\:{that}\:{its}\:{velocity}\:{v} \\ $$$${at}\:{height}\:{h}\:{is}\:{given}\:{by} \\ $$$${v}_{{o}} ^{\mathrm{2}} −{v}^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{2}{gh}}{\mathrm{1}+\frac{{h}}{{R}}} \\ $$$${where}\:{R}\:{is}\:{radius}\:{of}\:{earth} \\ $$$${and}\:\:{g}\:{is}\:{the}\:{acceleration} \\ $$$${due}\:{to}\:{gravity}\:{at}\:{the}\:{earth} \\ $$$${surface} \\ $$
Answered by ajfour last updated on 24/Nov/19
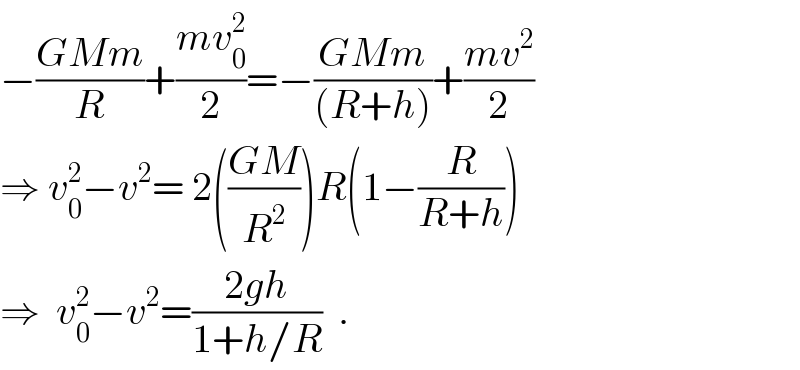
$$−\frac{{GMm}}{{R}}+\frac{{mv}_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}=−\frac{{GMm}}{\left({R}+{h}\right)}+\frac{{mv}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{v}_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} −{v}^{\mathrm{2}} =\:\mathrm{2}\left(\frac{{GM}}{{R}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right){R}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{{R}}{{R}+{h}}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\:{v}_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} −{v}^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{2}{gh}}{\mathrm{1}+{h}/{R}}\:\:. \\ $$
Commented by peter frank last updated on 24/Nov/19

$${thank}\:{you} \\ $$
