Question Number 132729 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 16/Feb/21
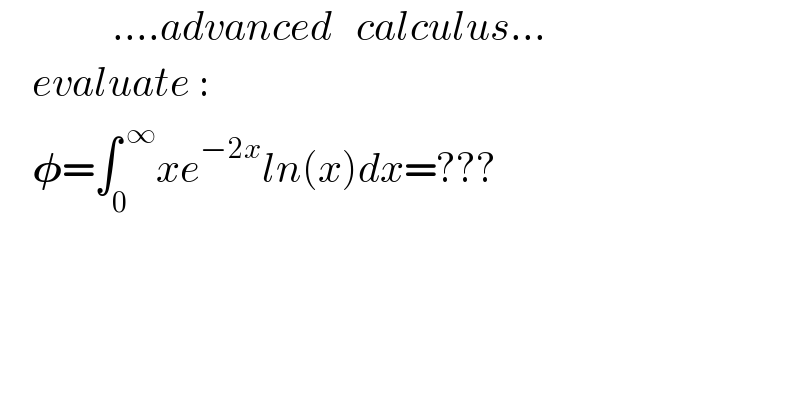
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:….{advanced}\:\:\:{calculus}… \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{evaluate}\:: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\boldsymbol{\phi}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\infty} {xe}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} {ln}\left({x}\right){dx}=??? \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Olaf last updated on 16/Feb/21
![φ = ∫_0 ^∞ xe^(−2x) lnxdx φ = ∫_0 ^∞ (xlnx−x)e^(−2x) dx+∫_0 ^∞ xe^(−2x) dx φ = [−(e^(−2x) /2)(xlnx−x)]_0 ^∞ +(1/2)∫_0 ^∞ lnxe^(−2x) dx +[−((1/2)x+(1/4))e^(−2x) ]_0 ^∞ φ = (1/2)∫_0 ^∞ lnxe^(−2x) dx+(1/4) φ = (1/2)(−(γ/2)−((ln2)/2))+(1/4) φ = (1/4)(1−γ−ln2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q132731.png)
$$\phi\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {xe}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} \mathrm{ln}{xdx} \\ $$$$\phi\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left({x}\mathrm{ln}{x}−{x}\right){e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} {dx}+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {xe}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} {dx} \\ $$$$\phi\:=\:\left[−\frac{{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}\left({x}\mathrm{ln}{x}−{x}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \mathrm{ln}{xe}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} {dx} \\ $$$$+\left[−\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\right){e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} \right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \\ $$$$\phi\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \mathrm{ln}{xe}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} {dx}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\phi\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(−\frac{\gamma}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{ln2}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\phi\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left(\mathrm{1}−\gamma−\mathrm{ln2}\right) \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 16/Feb/21
$${tayeballah}\:{mr}\:{olaf}… \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 16/Feb/21
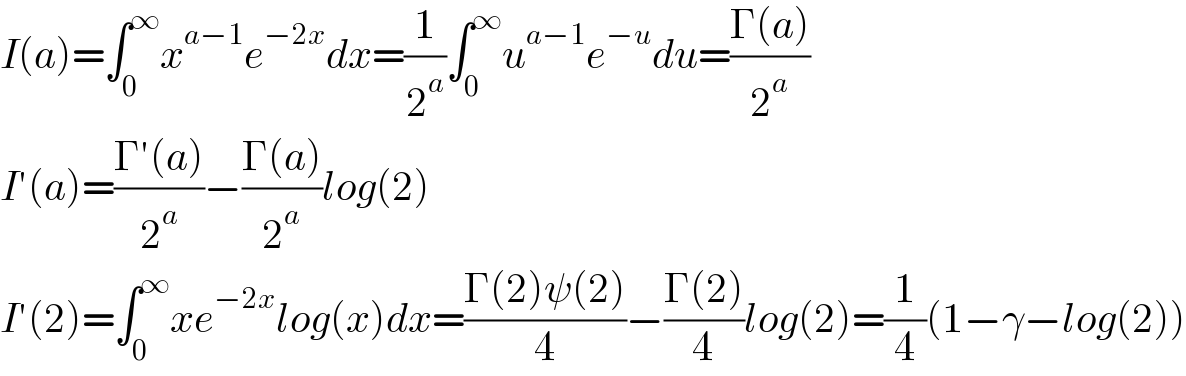
$${I}\left({a}\right)=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {x}^{{a}−\mathrm{1}} {e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} {dx}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{{a}} }\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {u}^{{a}−\mathrm{1}} {e}^{−{u}} {du}=\frac{\Gamma\left({a}\right)}{\mathrm{2}^{{a}} } \\ $$$${I}'\left({a}\right)=\frac{\Gamma'\left({a}\right)}{\mathrm{2}^{{a}} }−\frac{\Gamma\left({a}\right)}{\mathrm{2}^{{a}} }{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${I}'\left(\mathrm{2}\right)=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {xe}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} {log}\left({x}\right){dx}=\frac{\Gamma\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\psi\left(\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{4}}−\frac{\Gamma\left(\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{4}}{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left(\mathrm{1}−\gamma−{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right) \\ $$
Answered by mnjuly1970 last updated on 16/Feb/21

