Question Number 65690 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 02/Aug/19
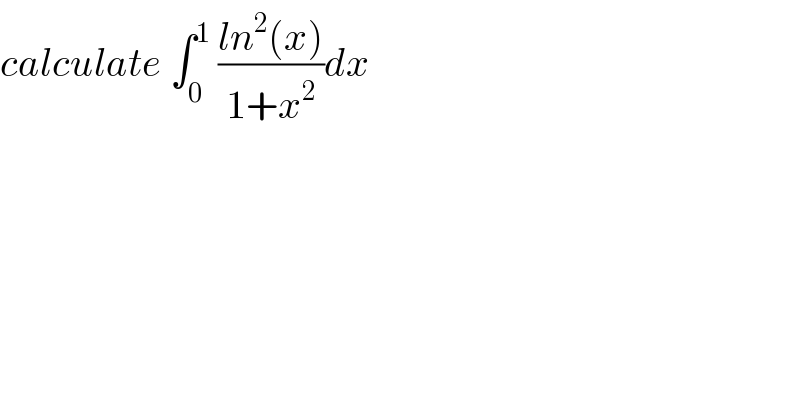
$${calculate}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}\right)}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 02/Aug/19
![let A =∫_0 ^1 ((ln^2 x)/(1+x^2 ))dx changement lnx =−t give x =e^(−t) ⇒ A = −∫_0 ^(+∞) (t^2 /(1+e^(−2t) ))(−e^(−t) )dt = ∫_0 ^∞ ((t^2 e^(−t) )/(1+e^(−2t) ))dt A =∫_0 ^∞ t^2 e^(−t) (Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (−1)^n e^(−2nt) )dt =Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (−1)^n ∫_0 ^∞ t^2 e^(−(2n+1)t) dt=Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (−1)^n A_n A_n =_((2n+1)t =u) ∫_0 ^∞ (u^2 /((2n+1)^2 )) e^(−u) (du/(2n+1)) =(1/((2n+1)^3 ))∫_0 ^∞ u^2 e^(−u) du by parts ∫_0 ^∞ u^2 e^(−u) du =[−u^2 e^(−u) ]_0 ^(+∞) −∫_0 ^∞ 2u(−e^(−u) )du =2 ∫_0 ^∞ u e^(−u) du =2{[−ue^(−u) ]_0 ^(+∞) −∫_0 ^∞ (−e^(−u) )du} =2∫_0 ^∞ e^(−u) du =2[−e^(−u) ]_0 ^(+∞) =2 ⇒A_n =(2/((2n+1)^3 )) ⇒ A =2Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (((−1)^n )/((2n+1)^3 )) be continued....](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q65715.png)
$${let}\:{A}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{ln}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}\:\:{changement}\:{lnx}\:=−{t}\:{give}\:{x}\:={e}^{−{t}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${A}\:=\:−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} }\left(−{e}^{−{t}} \right){dt}\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{t}} }{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} }{dt} \\ $$$${A}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{e}^{−{t}} \left(\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} {e}^{−\mathrm{2}{nt}} \right){dt} \\ $$$$=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{e}^{−\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right){t}} {dt}=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \:{A}_{{n}} \\ $$$${A}_{{n}} =_{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right){t}\:={u}} \:\:\:\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{e}^{−{u}} \frac{{du}}{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{u}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{u}} {du} \\ $$$${by}\:{parts}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{u}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{u}} \:{du}\:=\left[−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{e}^{−{u}} \right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} −\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{2}{u}\left(−{e}^{−{u}} \right){du} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{u}\:{e}^{−{u}} {du}\:=\mathrm{2}\left\{\left[−{ue}^{−{u}} \right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} −\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\left(−{e}^{−{u}} \right){du}\right\} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{e}^{−{u}} \:{du}\:=\mathrm{2}\left[−{e}^{−{u}} \right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} \:=\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow{A}_{{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${A}\:=\mathrm{2}\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }\:\:\:{be}\:{continued}…. \\ $$
Commented by ~ À ® @ 237 ~ last updated on 04/Aug/19
![Let named I that integral.when changing u=(1/x) dx=((−du)/u^2 ) I=∫_1 ^∞ ((ln^2 (u))/(1+u^2 ))du and then ∫_0 ^∞ ((ln^2 (u))/(1+u^2 ))du=2I 1+u^2 =(u−i)(u+i) With the residus theorem 2I=2iπRes(f. i) with f(x)=((ln^2 (x))/(1+x^2 )) Res(f. i)=lim_(z−>i) ((ln^2 (z))/(z+i))=(([ln(e^(i(π/2)) )]^2 )/(2i))=(((−π^2 )/4)/(2i))=((−π^2 )/(8i)) Then 2I=((−π^3 )/4) so finally I= ((−π^3 )/8)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q65814.png)
$${Let}\:{named}\:{I}\:{that}\:{integral}.{when}\:{changing}\:{u}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\:\:\:\:{dx}=\frac{−{du}}{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:\:\: \\ $$$${I}=\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({u}\right)}{\mathrm{1}+{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }{du}\:\:\:{and}\:{then}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{{ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({u}\right)}{\mathrm{1}+{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }{du}=\mathrm{2}{I} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}+{u}^{\mathrm{2}} =\left({u}−{i}\right)\left({u}+{i}\right) \\ $$$${With}\:{the}\:{residus}\:{theorem}\:\mathrm{2}{I}=\mathrm{2}{i}\pi{Res}\left({f}.\:\:{i}\right)\:\:{with}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{{ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}\right)}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${Res}\left({f}.\:\:{i}\right)={lim}_{{z}−>{i}} \:\:\frac{{ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({z}\right)}{{z}+{i}}=\frac{\left[{ln}\left({e}^{{i}\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \right)\right]^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}{i}}=\frac{\frac{−\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}}}{\mathrm{2}{i}}=\frac{−\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{8}{i}} \\ $$$${Then}\:\:\mathrm{2}{I}=\frac{−\pi^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$${so}\:{finally}\:\:\:{I}=\:\frac{−\pi^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$
