Question Number 8728 by kuldeep singh raj last updated on 24/Oct/16
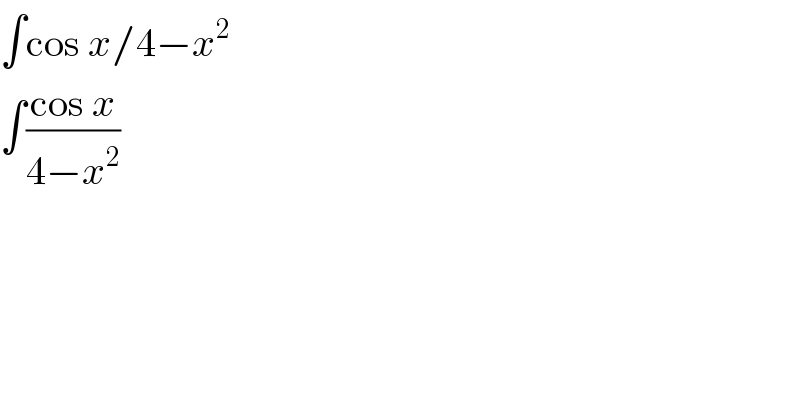
$$\int\mathrm{cos}\:{x}/\mathrm{4}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{\mathrm{4}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 24/Oct/16
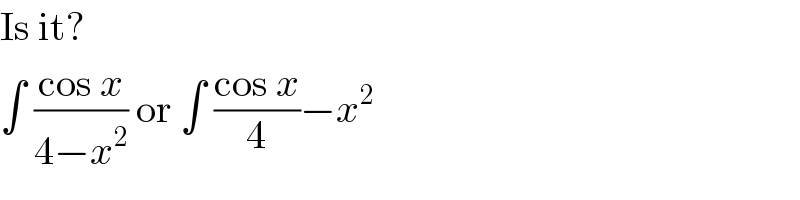
$$\mathrm{Is}\:\mathrm{it}? \\ $$$$\int\:\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{\mathrm{4}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\mathrm{or}\:\int\:\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{\mathrm{4}}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 25/Oct/16
![∫ ((cos x)/(4−x^2 )) =(1/4)[∫ ((cos x)/(2−x))dx+∫ ((cos x)/(2+x))dx] ∫ ((cos x)/(2−x))dx 2−x=u du=−dx =−∫((cos (2−u))/u)du =−∫((cos 2cos u+sin 2sin u)/u)du =−cos 2∫((cos u)/u)du−sin 2∫((sin u)/u)du =−cos 2∙Ci(u)−sin 2∙Si(u) =−cos 2Ci(2−x)−sin 2∙Si(2−x)+C Similarly ∫((cos x)/(2+x))dx; x+2=u, dx=du ∫((cos (u−2))/u)du=∫((cos 2cos u)/u)du+∫((sin 2sin u)/u)du =cos 2∙Ci(2+x)+sin 2∙Si(2+x)+C Hence ∫((cos x)/(4−x^2 ))dx=cos 2{Ci(2+x)−Ci(2−x)}+ sin 2{Si(x+2)−Si(2−x)}+C Note ∫((sin x)/x)dx=Si(x) ∫((cos x)/x)dx=Ci(x)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q8744.png)
$$\int\:\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{\mathrm{4}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left[\int\:\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{\mathrm{2}−{x}}{dx}+\int\:\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{\mathrm{2}+{x}}{dx}\right] \\ $$$$\int\:\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{\mathrm{2}−{x}}{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}−{x}={u} \\ $$$${du}=−{dx} \\ $$$$=−\int\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{2}−{u}\right)}{{u}}{du} \\ $$$$=−\int\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2cos}\:{u}+\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2sin}\:{u}}{{u}}{du} \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}\int\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{u}}{{u}}{du}−\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}\int\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:{u}}{{u}}{du} \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}\centerdot\mathrm{Ci}\left({u}\right)−\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}\centerdot\mathrm{Si}\left({u}\right) \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2Ci}\left(\mathrm{2}−{x}\right)−\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}\centerdot\mathrm{Si}\left(\mathrm{2}−{x}\right)+{C} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Similarly} \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{\mathrm{2}+{x}}{dx};\:{x}+\mathrm{2}={u},\:{dx}={du} \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:\left({u}−\mathrm{2}\right)}{{u}}{du}=\int\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2cos}\:{u}}{{u}}{du}+\int\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2sin}\:{u}}{{u}}{du} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}\centerdot\mathrm{Ci}\left(\mathrm{2}+{x}\right)+\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}\centerdot\mathrm{Si}\left(\mathrm{2}+{x}\right)+{C} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Hence} \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{\mathrm{4}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}=\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}\left\{\mathrm{Ci}\left(\mathrm{2}+{x}\right)−\mathrm{Ci}\left(\mathrm{2}−{x}\right)\right\}+ \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}\left\{\mathrm{Si}\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)−\mathrm{Si}\left(\mathrm{2}−{x}\right)\right\}+{C} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Note} \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}{{x}}\mathrm{d}{x}=\mathrm{Si}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{{x}}\mathrm{d}{x}=\mathrm{Ci}\left({x}\right) \\ $$
