Question Number 133776 by bramlexs22 last updated on 24/Feb/21
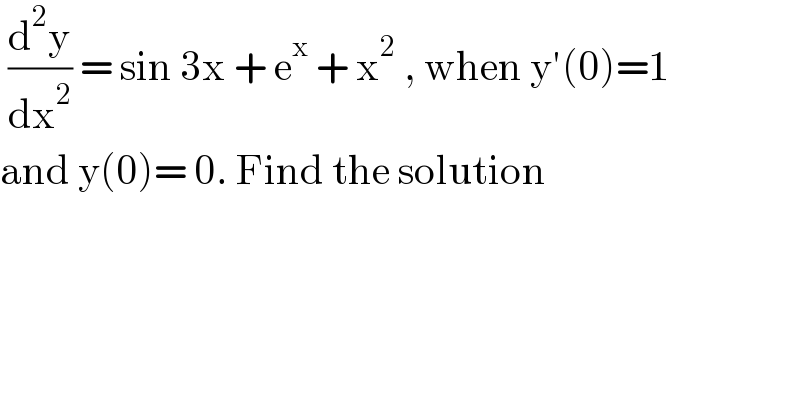
$$\:\frac{\mathrm{d}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{3x}\:+\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:,\:\mathrm{when}\:\mathrm{y}'\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{y}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\:\mathrm{0}.\:\mathrm{Find}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$
Answered by bobhans last updated on 24/Feb/21
![(d/dx) [ (dy/dx) ] = sin 3x+e^x +x^2 d[(dy/dx)] = (sin 3x+e^x +x^2 ) dx ∫ d[(dy/dx) ] = ∫ (sin 3x+e^x +x^2 )dx ⇒(dy/dx) = −(1/3)cos 3x+e^x +(1/3)x^3 +C_1 y′(0) = −(1/3)+1+C_1 =1 ; C_1 =(1/3) ∫ dy = ∫ (−(1/3)cos 3x+e^x +(1/3)x^3 +(1/3))dx y=−(1/9)sin 3x+e^x +(1/(12))x^4 +(1/3)x+C_2 y(0)=1+C_2 =0 ⇒C_2 =−1 ∴y=−((sin 3x)/9)+e^x +((x^4 +4x−12)/(12))](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q133779.png)
$$\:\frac{{d}}{{dx}}\:\left[\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:\right]\:=\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{3}{x}+{e}^{{x}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:{d}\left[\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\right]\:=\:\left(\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{3}{x}+{e}^{{x}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:{dx} \\ $$$$\int\:{d}\left[\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:\right]\:=\:\int\:\left(\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{3}{x}+{e}^{{x}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){dx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{3}{x}+{e}^{{x}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{C}_{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${y}'\left(\mathrm{0}\right)\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\mathrm{1}+{C}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{1}\:;\:{C}_{\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\int\:{dy}\:=\:\int\:\left(−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{3}{x}+{e}^{{x}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right){dx} \\ $$$${y}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{9}}\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{3}{x}+{e}^{{x}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{12}}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}{x}+{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${y}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{1}+{C}_{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow{C}_{\mathrm{2}} =−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\therefore{y}=−\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{3}{x}}{\mathrm{9}}+{e}^{{x}} +\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{12}}{\mathrm{12}} \\ $$
