Question Number 66830 by Rio Michael last updated on 20/Aug/19
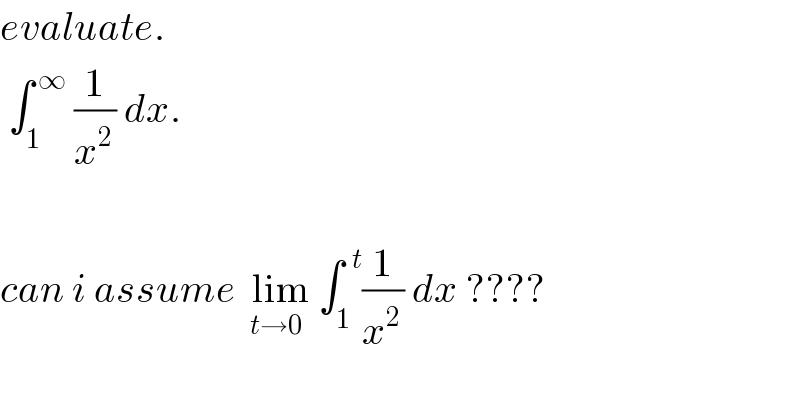
$${evaluate}. \\ $$$$\:\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\:\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}\:} }\:{dx}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${can}\:{i}\:{assume}\:\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\:\mathrm{lim}}\:\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\:\:{t}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}\:} }\:{dx}\:???? \\ $$
Commented by Tony Lin last updated on 20/Aug/19
![∫_1 ^∞ (1/x^2 )dx =lim_(t→∞) ∫_1 ^t (1/x^2 )dx =lim_(t→∞) [−(1/x)]_1 ^t =lim_(t→∞) (−(1/t)+1) =1](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q66843.png)
$$\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$$$=\underset{{t}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{{t}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$$$=\underset{{t}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right]_{\mathrm{1}} ^{{t}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{t}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}}+\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by Rio Michael last updated on 20/Aug/19

$${what}\:{if}\:{i}\:{have}\:\: \\ $$$$\:\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\:{dx} \\ $$
Commented by Tony Lin last updated on 21/Aug/19

$$\underset{{t}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{{t}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}{dx} \\ $$$$=\underset{{t}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}{ln}\mid{t}\mid \\ $$$$=+\infty \\ $$
Commented by Rio Michael last updated on 21/Aug/19

$${thanks} \\ $$
