Question Number 131957 by rs4089 last updated on 10/Feb/21
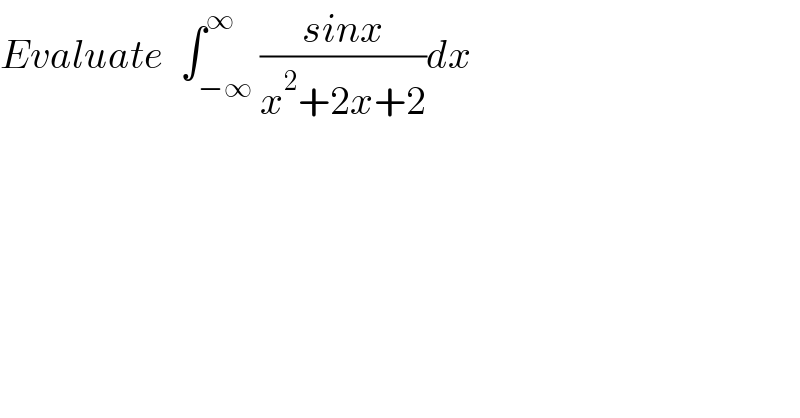
$${Evaluate}\:\:\int_{−\infty} ^{\infty} \frac{{sinx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}}{dx} \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 10/Feb/21

$$\int_{−\infty} ^{\infty} \frac{{sinx}}{\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}+\mathrm{1}={u} \\ $$$$=\int_{−\infty} ^{\infty} \frac{{sinu}\:{cos}\mathrm{1}−{sin}\mathrm{1}{cosu}}{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}{du} \\ $$$$={cos}\mathrm{1}\int_{−\infty} ^{\infty} \frac{{sinu}}{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}−{sin}\mathrm{1}\int_{−\infty} ^{\infty} \frac{{cosu}}{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}{du} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{0}−\frac{\pi}{{e}}{sin}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=−\frac{\pi}{{e}}{sin}\left(\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 10/Feb/21

$${very}\:{nice}\:{mr}\:{payan}… \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 10/Feb/21

$$\mathrm{let}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\lambda\right)=\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{sin}\left(\lambda\mathrm{x}\right)}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{dx}\:\mathrm{with}\lambda>\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{f}\left(\lambda\right)=\mathrm{Im}\left(\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i}\lambda\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{dx}\right) \\ $$$$\Phi\left(\mathrm{z}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i}\lambda\mathrm{z}} }{\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{2z}+\mathrm{2}}\:\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{2z}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow\left(\mathrm{z}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{z}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =−\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{z}+\mathrm{1}=\overset{−} {+}\mathrm{i}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{z}\:=−\mathrm{1}\overset{−} {+}\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{si}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{poles}\:\mathrm{of}\:\Phi\:\mathrm{are}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{z}_{\mathrm{1}} =−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{z}_{\mathrm{2}} =−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{i} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{R}} \Phi\left(\mathrm{z}\right)\mathrm{dz}\:=\mathrm{2i}\pi\mathrm{Res}\left(\Phi,\mathrm{z}_{\mathrm{1}} \right)=\mathrm{2i}\pi\:.\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i}\lambda\mathrm{z}_{\mathrm{1}} } }{\mathrm{2i}}\:=\pi\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i}\lambda\left(−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{i}\right)} \\ $$$$=\pi\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{i}\lambda−\lambda} \:=\pi\mathrm{e}^{−\lambda} \left\{\mathrm{cos}\left(\lambda\right)−\mathrm{isin}\left(\lambda\right)\right\}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{f}\left(\lambda\right)=−\pi\mathrm{e}^{−\lambda} \:\mathrm{sin}\left(\lambda\right) \\ $$$$\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{sinx}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{dx}\:=\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{e}}\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$
