Question Number 50 by surabhi last updated on 25/Jan/15
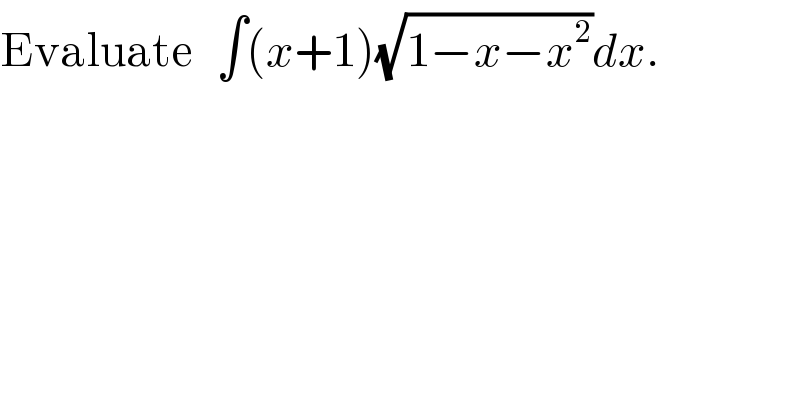
$$\mathrm{Evaluate}\:\:\:\int\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}. \\ $$
Commented by 123456 last updated on 13/Dec/14

$$\mathrm{tente}?\mathrm{completar}\:\mathrm{quadrados}\:\mathrm{e}\:\mathrm{fca}\:\mathrm{uma}\:\mathrm{substutuico} \\ $$
Answered by 123456 last updated on 13/Dec/14

$$\mathrm{hint}: \\ $$$$−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}+\mathrm{1}= \\ $$$$−\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}\right)+\mathrm{1}= \\ $$$$−\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×{x}\right)+\mathrm{1}= \\ $$$$−\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)+\mathrm{1}= \\ $$$$−\left({x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{4}}= \\ $$$$\frac{−\left(\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{from}\:\mathrm{here}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{use}\:\mathrm{trigonometric}\:\mathrm{substituition}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{references}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{answer}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{at}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{coments},\:\mathrm{good}\:\mathrm{luck}\::\mathrm{3} \\ $$
Commented by 123456 last updated on 13/Dec/14
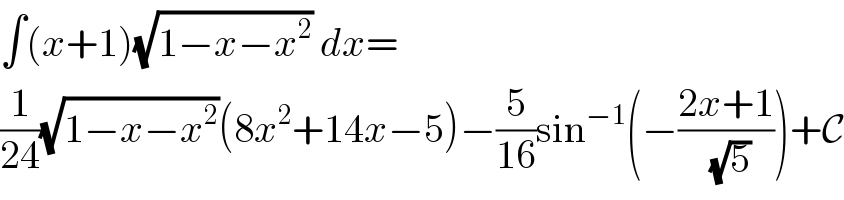
$$\int\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx}= \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{24}}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\left(\mathrm{8}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{14}{x}−\mathrm{5}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{16}}\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(−\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}\right)+\mathcal{C} \\ $$
