Question Number 131810 by Fikret last updated on 08/Feb/21
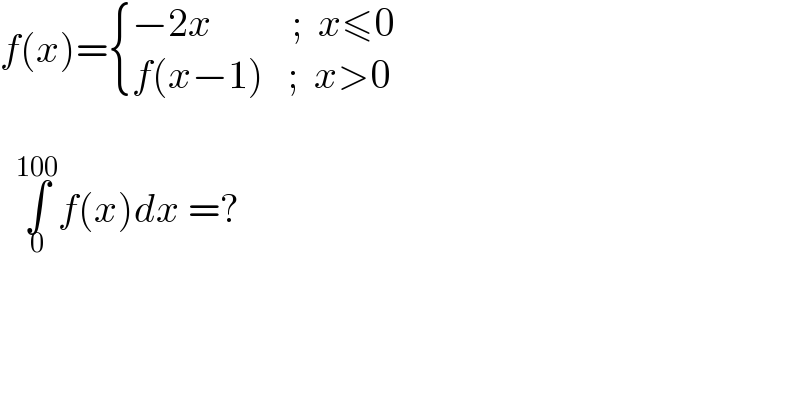
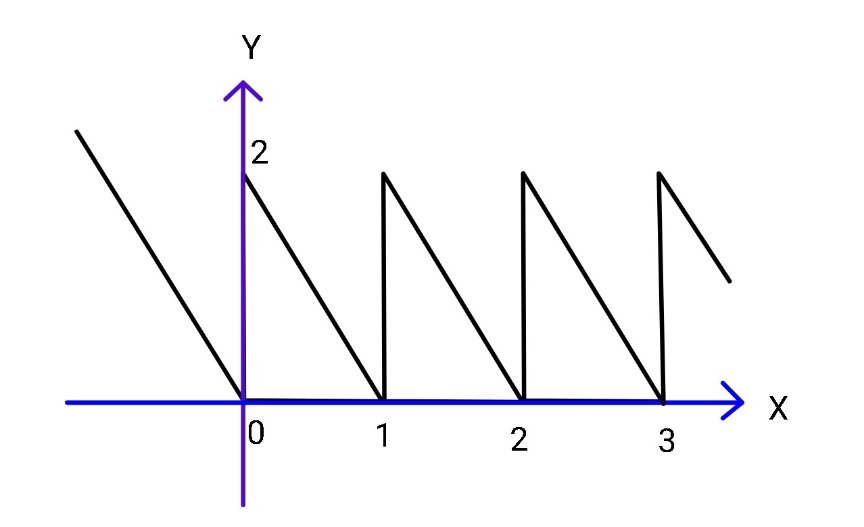
$${f}\left({x}\right)=\begin{cases}{−\mathrm{2}{x}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:;\:\:{x}\leqslant\mathrm{0}}\\{{f}\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\:\:\:;\:\:{x}>\mathrm{0}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\:\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{100}} {\int}}{f}\left({x}\right){dx}\:=? \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 09/Feb/21
![∫_0 ^(100) f(x)dx =Σ_(k=0) ^(99) ∫_k ^(k+1) f(x)dx =100∫_(−1) ^0 f(x)dx =100∫_(−1) ^0 (−2x)dx =100[−x^2 ]_(−1) ^0 =100](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q131817.png)
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{100}} {f}\left({x}\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\underset{{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{99}} {\sum}}\int_{{k}} ^{{k}+\mathrm{1}} {f}\left({x}\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{100}\int_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{0}} {f}\left({x}\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{100}\int_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{0}} \left(−\mathrm{2}{x}\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{100}\left[−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right]_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{0}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{100} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 09/Feb/21