Question Number 5692 by FilupSmith last updated on 24/May/16

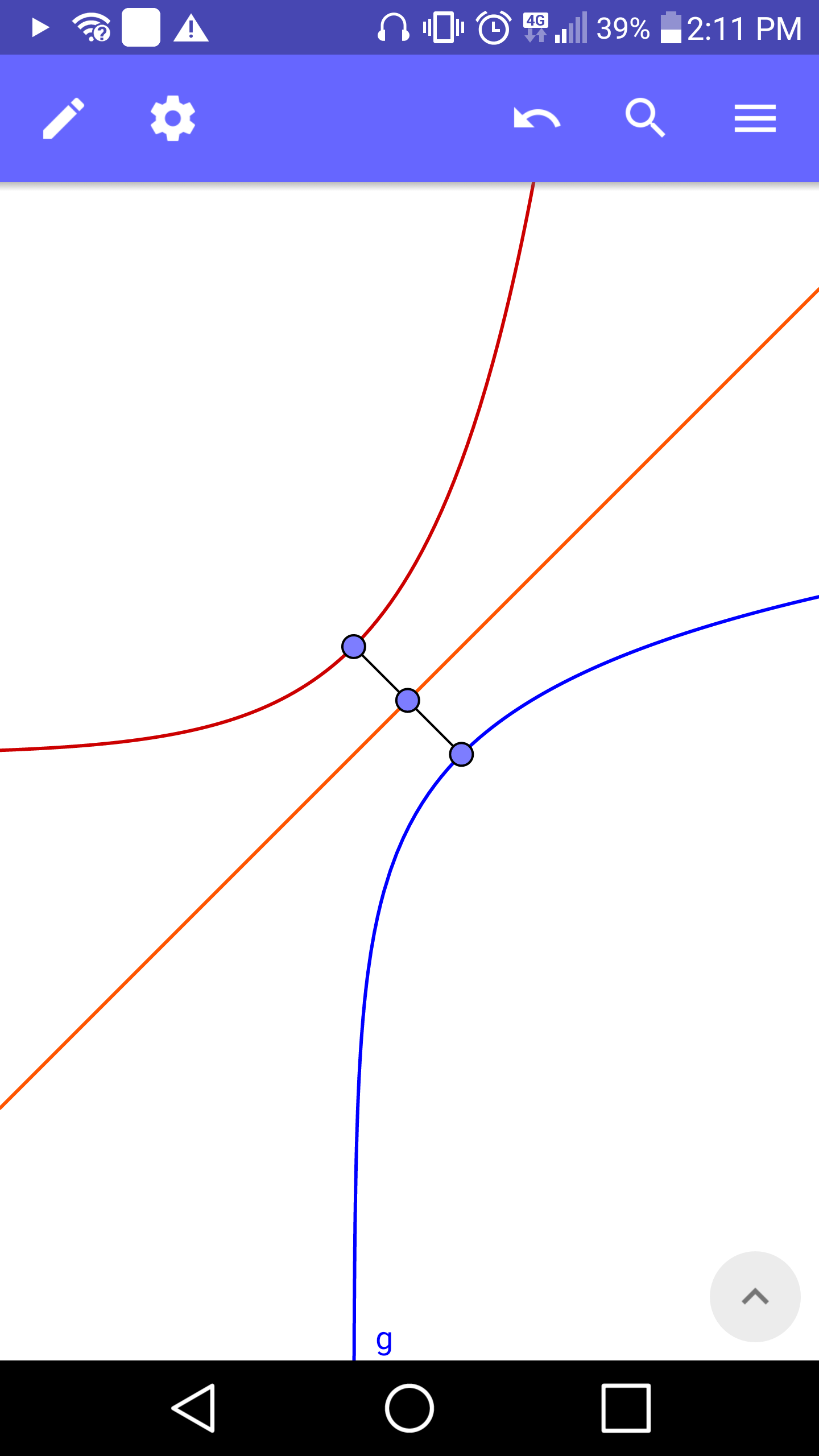
$${f}\left({x}\right)={e}^{{x}} \\ $$$${g}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{ln}\:{x} \\ $$$${h}\left({x}\right)={x} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}\:\mathrm{line}\:{L}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{perpendicular}\:\mathrm{to}\:{h}\left({x}\right)\:\mathrm{at}\:\mathrm{point} \\ $$$${P}\left({x},{y}\right)\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{extends}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{disects}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:\mathrm{and}\:{g}\left({x}\right). \\ $$$$\mathrm{The}\:\mathrm{length}\:\mathrm{of}\:{L}\:\mathrm{between}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:{and}\:{g}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{is}\:{r}.\:\mathrm{When}\:\mathrm{is}\:{r}\:\mathrm{minimum}? \\ $$
Commented by FilupSmith last updated on 24/May/16
Commented by Yozzii last updated on 25/May/16
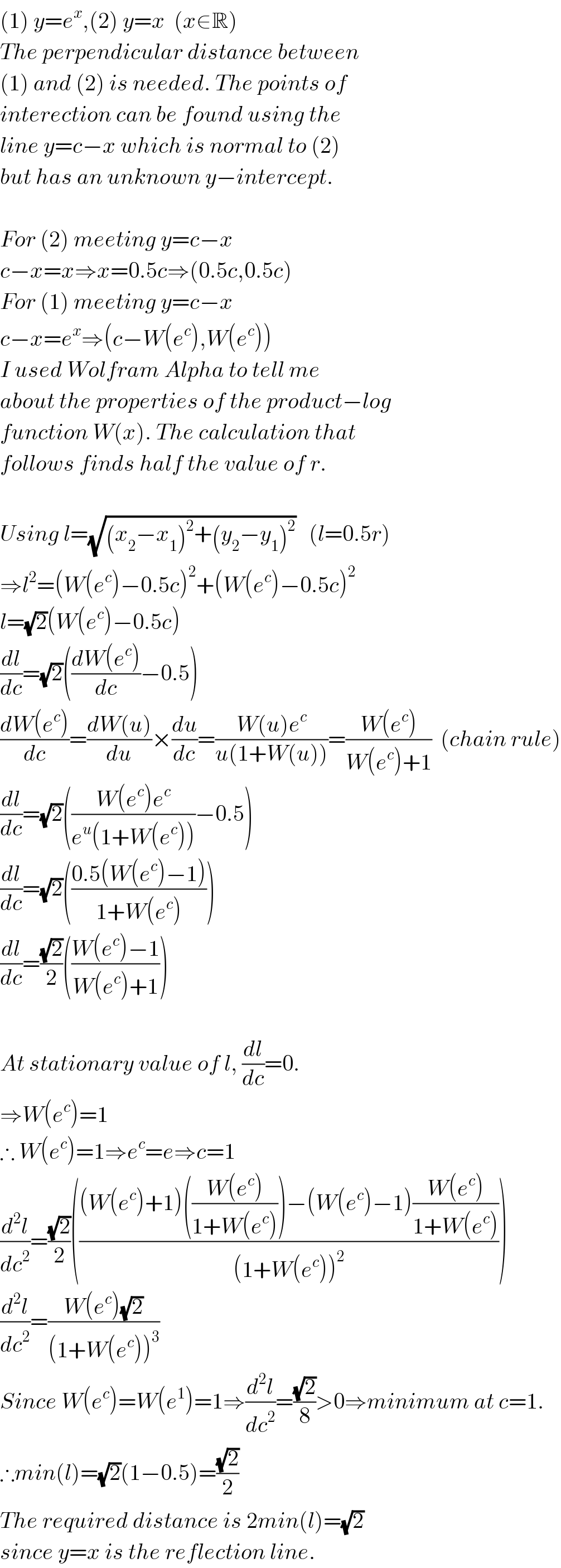
$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:{y}={e}^{{x}} ,\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:{y}={x}\:\:\left({x}\in\mathbb{R}\right) \\ $$$${The}\:{perpendicular}\:{distance}\:{between} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:{and}\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:{is}\:{needed}.\:{The}\:{points}\:{of} \\ $$$${interection}\:{can}\:{be}\:{found}\:{using}\:{the} \\ $$$${line}\:{y}={c}−{x}\:{which}\:{is}\:{normal}\:{to}\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${but}\:{has}\:{an}\:{unknown}\:{y}−{intercept}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${For}\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:{meeting}\:{y}={c}−{x} \\ $$$${c}−{x}={x}\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}{c}\Rightarrow\left(\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}{c},\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}{c}\right) \\ $$$${For}\:\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:{meeting}\:{y}={c}−{x} \\ $$$${c}−{x}={e}^{{x}} \Rightarrow\left({c}−{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right),{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)\right) \\ $$$${I}\:{used}\:{Wolfram}\:{Alpha}\:{to}\:{tell}\:{me} \\ $$$${about}\:{the}\:{properties}\:{of}\:{the}\:{product}−{log} \\ $$$${function}\:{W}\left({x}\right).\:{The}\:{calculation}\:{that} \\ $$$${follows}\:{finds}\:{half}\:{the}\:{value}\:{of}\:{r}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${Using}\:{l}=\sqrt{\left({x}_{\mathrm{2}} −{x}_{\mathrm{1}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({y}_{\mathrm{2}} −{y}_{\mathrm{1}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:\:\left({l}=\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}{r}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{l}^{\mathrm{2}} =\left({W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}{c}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}{c}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${l}=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\left({W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}{c}\right)\:\: \\ $$$$\frac{{dl}}{{dc}}=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\left(\frac{{dW}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)}{{dc}}−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}\right) \\ $$$$\frac{{dW}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)}{{dc}}=\frac{{dW}\left({u}\right)}{{du}}×\frac{{du}}{{dc}}=\frac{{W}\left({u}\right){e}^{{c}} }{{u}\left(\mathrm{1}+{W}\left({u}\right)\right)}=\frac{{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)}{{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)+\mathrm{1}}\:\:\left({chain}\:{rule}\right) \\ $$$$\frac{{dl}}{{dc}}=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\left(\frac{{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right){e}^{{c}} }{{e}^{{u}} \left(\mathrm{1}+{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)\right)}−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}\right) \\ $$$$\frac{{dl}}{{dc}}=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}\left({W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{1}+{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)}\right) \\ $$$$\frac{{dl}}{{dc}}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\frac{{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)−\mathrm{1}}{{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)+\mathrm{1}}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${At}\:{stationary}\:{value}\:{of}\:{l},\:\frac{{dl}}{{dc}}=\mathrm{0}. \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\therefore\:{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)=\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow{e}^{{c}} ={e}\Rightarrow{c}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {l}}{{dc}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\frac{\left({W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\frac{{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)}{\mathrm{1}+{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)}\right)−\left({W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)−\mathrm{1}\right)\frac{{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)}{\mathrm{1}+{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\right) \\ $$$$\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {l}}{{dc}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)\right)^{\mathrm{3}} } \\ $$$${Since}\:{W}\left({e}^{{c}} \right)={W}\left({e}^{\mathrm{1}} \right)=\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {l}}{{dc}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{8}}>\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow{minimum}\:{at}\:{c}=\mathrm{1}. \\ $$$$\therefore{min}\left({l}\right)=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}\right)=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${The}\:{required}\:{distance}\:{is}\:\mathrm{2}{min}\left({l}\right)=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${since}\:{y}={x}\:{is}\:{the}\:{reflection}\:{line}. \\ $$
