Question Number 933 by 123456 last updated on 29/Apr/15
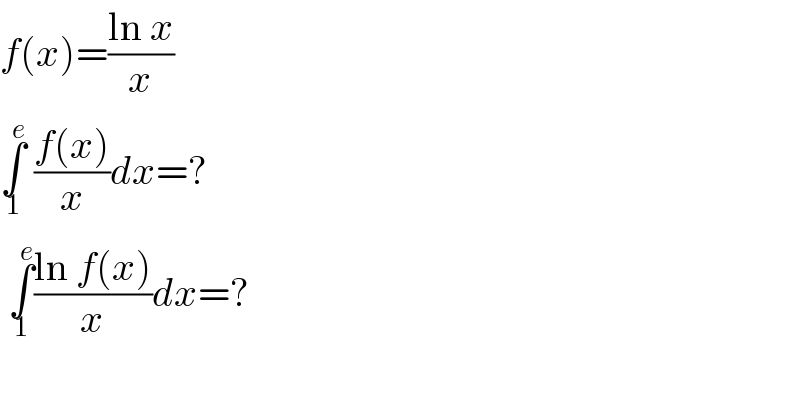
$${f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:{x}}{{x}} \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{e}} {\int}}\:\frac{{f}\left({x}\right)}{{x}}{dx}=? \\ $$$$\:\underset{\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{e}} {\int}}\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:{f}\left({x}\right)}{{x}}{dx}=? \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 30/Apr/15
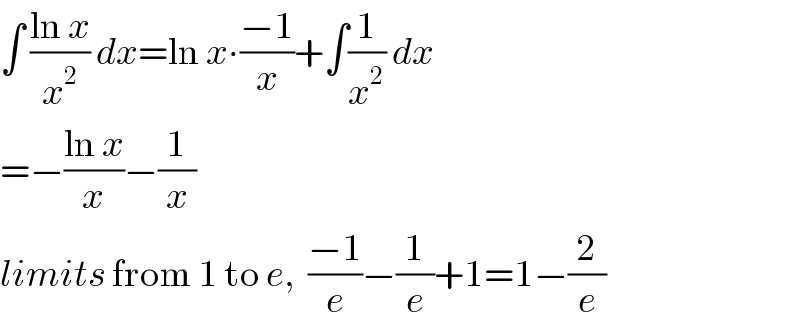
$$\int\:\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:{x}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx}=\mathrm{ln}\:{x}\centerdot\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{{x}}+\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:{x}}{{x}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}} \\ $$$${limits}\:\mathrm{from}\:\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{to}\:{e},\:\:\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{{e}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{e}}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{e}} \\ $$
