Question Number 71314 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 13/Oct/19
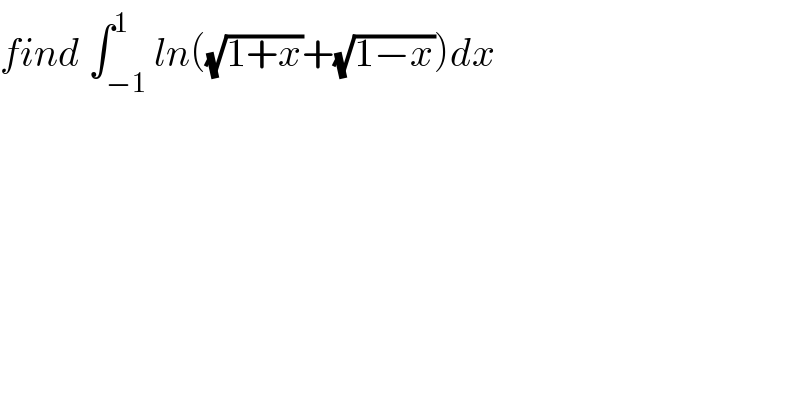
$${find}\:\int_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {ln}\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}}\right){dx} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 13/Oct/19
![let I=∫_(−1) ^1 ln((√(1+x))+(√(1−x)))dx ⇒I=2∫_0 ^1 ln((√(1+x))+(√(1−x)))dx (function even) I=_(x=cos(2t)) 2∫_(π/4) ^0 ln((√(1+cos(2t)))+(√(1−cos(2t))))(−2)sin(2t)dt =4 ∫_0 ^(π/4) ln((√2)cost +(√2)sint)sin(2t)dt =4∫_0 ^(π/4) ln((√2)((√2)cos(t−(π/4)))sin(2t)dt =4 ∫_0 ^(π/4) {ln(2)+ln(cos((π/4)−t)}sin(2t)dt =4ln(2)∫_0 ^(π/4) sin(2t)dt +4 ∫_0 ^(π/4) ln(cos((π/4)−t))sin(2t)dt =4ln(2)[−(1/2)cos(2t)]_0 ^(π/4) +4 ∫_0 ^(π/4) sin(2t)ln(cos((π/4)−t))dt =2ln(2) +4 ∫_0 ^(π/4) sin(2t)ln(cos((π/4)−t))dt changement (π/4)−t=u givd ∫_0 ^(π/4) sin(2t)ln(cos((π/4)−t))dt =−∫_0 ^(π/4) sin(2((π/4)−u))ln(cosu)(−du) =∫_0 ^(π/4) sin((π/2)−2u)ln(cosu)du =∫_0 ^(π/4) cos(2u) ln(cosu)du by parts f^′ =cos(2u) and g =ln(cosu) ⇎ ∫_0 ^(π/4) cos(2u)ln(cosu)du =[(1/2)sin(2u)ln(cosu)]_0 ^(π/4) −∫_0 ^(π/4) (1/2)sin(2u)(((−sinu)/(cosu)))du=(1/2)ln((1/( (√2))))+(1/2) ∫_0 ^(π/4) ((sin(u)(2sinu cosu))/(cosu))du =−(1/2)ln((√2)) +∫_0 ^(π/4) sin^2 u du =−(1/4)ln(2)+(1/2)∫_0 ^(π/4) (1−cos(2u))du =−(1/4)ln(2)+(π/8)−(1/4)[sin(2u)]_0 ^(π/4) =−(1/4)ln(2)+(π/8)−(1/4) ⇒ I =2ln(2)−ln(2)+(π/2) −1 =ln(2)+(π/2) −1](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q71345.png)
$${let}\:{I}=\int_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {ln}\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}}\right){dx}\:\Rightarrow{I}=\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {ln}\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\left({function}\:{even}\right) \\ $$$${I}=_{{x}={cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right)} \:\:\mathrm{2}\int_{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} ^{\mathrm{0}} {ln}\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right)}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right)}\right)\left(−\mathrm{2}\right){sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right){dt} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{4}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} {ln}\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}{cost}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}{sint}\right){sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right){dt} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{4}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} {ln}\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}{cos}\left({t}−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right)\right){sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right){dt}\right. \\ $$$$=\mathrm{4}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} \left\{{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+{ln}\left({cos}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}−{t}\right)\right\}{sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right){dt}\right. \\ $$$$=\mathrm{4}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} {sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right){dt}\:+\mathrm{4}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} {ln}\left({cos}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}−{t}\right)\right){sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right){dt} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{4}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\left[−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} \:+\mathrm{4}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} {sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right){ln}\left({cos}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}−{t}\right)\right){dt} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:+\mathrm{4}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} {sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right){ln}\left({cos}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}−{t}\right)\right){dt}\:{changement}\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}−{t}={u}\:{givd} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} \:{sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right){ln}\left({cos}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}−{t}\right)\right){dt}\:=−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} {sin}\left(\mathrm{2}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}−{u}\right)\right){ln}\left({cosu}\right)\left(−{du}\right) \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} \:{sin}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{2}{u}\right){ln}\left({cosu}\right){du}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} {cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{u}\right)\:{ln}\left({cosu}\right){du} \\ $$$${by}\:{parts}\:{f}^{'} ={cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{u}\right)\:{and}\:{g}\:={ln}\left({cosu}\right)\:\nLeftrightarrow \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} \:{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{u}\right){ln}\left({cosu}\right){du}\:=\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{u}\right){ln}\left({cosu}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} \\ $$$$−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{u}\right)\left(\frac{−{sinu}}{{cosu}}\right){du}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} \:\frac{{sin}\left({u}\right)\left(\mathrm{2}{sinu}\:{cosu}\right)}{{cosu}}{du} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)\:+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} \:{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {u}\:{du} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} \left(\mathrm{1}−{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{u}\right)\right){du} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{8}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left[{sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{u}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{8}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${I}\:=\mathrm{2}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:−\mathrm{1}\:={ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:−\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Answered by mind is power last updated on 13/Oct/19

$$\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{2a}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{dx}=−\mathrm{2sin}\left(\mathrm{2a}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{2cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{a}\right):\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{2sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{a}\right) \\ $$$$\int_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{x}}\right)\mathrm{dx}=\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{a}\right)\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{a}\right)\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{2a}\right)\mathrm{da} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{a}\right)+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{a}\right)\right)\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{2a}\right)\mathrm{da}=\left[\frac{−\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{2a}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{ln}\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{a}\right)+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{a}\right)\right)\int\frac{\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{2a}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}.\frac{\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{a}\right)−\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{a}\right)}{\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{a}\right)+\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{a}\right)}\mathrm{da}\:\right. \\ $$$$=\mathrm{ln}\left(\sqrt{\left.\mathrm{2}\right)}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\left(\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{a}\right)−\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{a}\right)\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{da}\right. \\ $$$$=\mathrm{ln}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{2a}\right)\mathrm{da} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{ln}\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}=\mathrm{2ln}\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 13/Oct/19
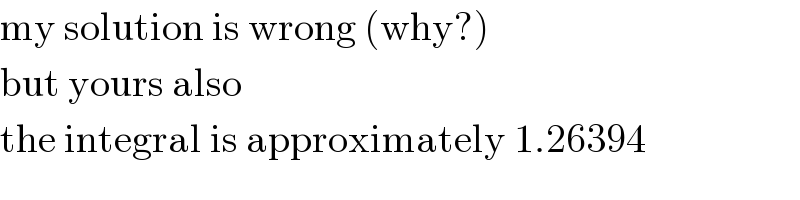
$$\mathrm{my}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{wrong}\:\left(\mathrm{why}?\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{yours}\:\mathrm{also} \\ $$$$\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{integral}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{approximately}\:\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{26394} \\ $$
Commented by mind is power last updated on 13/Oct/19

$$\mathrm{my}\:\mathrm{answer}\:\ast\mathrm{2}\: \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 13/Oct/19

$${thanks}\:{sir}. \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 13/Oct/19

$$…\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{had}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{sign}\:\mathrm{error}… \\ $$
Answered by MJS last updated on 13/Oct/19
![I=∫ln ((√(1+x))+(√(1−x))) dx= by parts ∫u′v=uv−∫uv′ u′=1 → u=x v=ln ((√(1+x))+(√(1−x))) → v′=((1−x^2 −(√(1−x^2 )))/(2x(1−x^2 ))) =x ln ((√(1+x))+(√(1−x))) −(1/2)∫((1−x^2 −(√(1−x^2 )))/(1−x^2 ))dx −(1/2)∫((1−x^2 −(√(1−x^2 )))/(1−x^2 ))dx= [t=arcsin x → dx=(√(1−x^2 ))dt] =(1/2)∫cos t dt −(1/2)∫dt= =(1/2)sin t −(t/2)=−(x/2)+(1/2)arcsin x ⇒ I=x ln ((√(1+x))+(√(1−x))) −(x/2)+(1/2)arcsin x +C](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q71333.png)
$${I}=\int\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}}\right)\:{dx}= \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{parts} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\int{u}'{v}={uv}−\int{uv}' \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{u}'=\mathrm{1}\:\rightarrow\:{u}={x} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{v}=\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}}\right)\:\rightarrow\:{v}'=\frac{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{\mathrm{2}{x}\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)} \\ $$$$={x}\:\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}}\right)\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\frac{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$$$−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\frac{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}= \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\left[{t}=\mathrm{arcsin}\:{x}\:\rightarrow\:{dx}=\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dt}\right] \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\mathrm{cos}\:{t}\:{dt}\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int{dt}= \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{sin}\:{t}\:−\frac{{t}}{\mathrm{2}}=−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{arcsin}\:{x} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{I}={x}\:\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}}\right)\:−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{arcsin}\:{x}\:+{C} \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 13/Oct/19
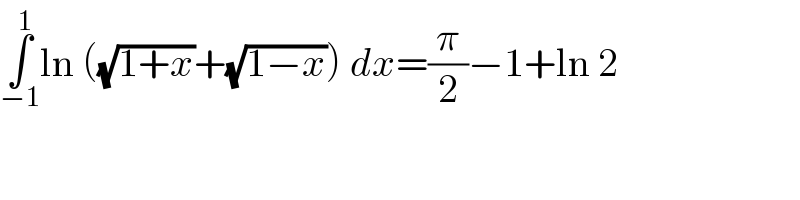
$$\underset{−\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}}\right)\:{dx}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$
