Question Number 72813 by Learner-123 last updated on 03/Nov/19
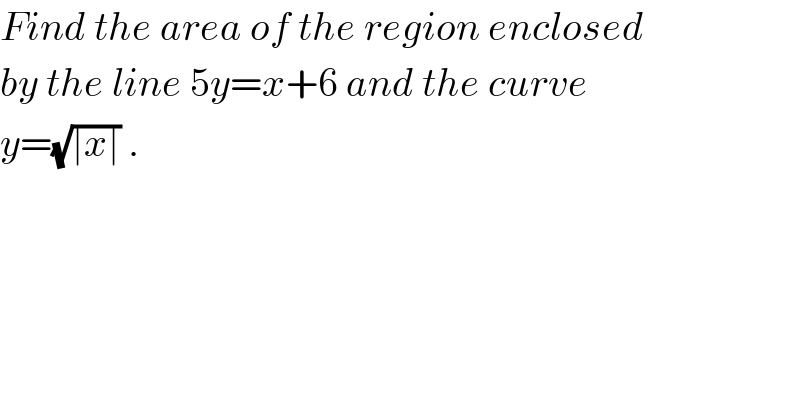
$${Find}\:{the}\:{area}\:{of}\:{the}\:{region}\:{enclosed} \\ $$$${by}\:{the}\:{line}\:\mathrm{5}{y}={x}+\mathrm{6}\:{and}\:{the}\:{curve} \\ $$$${y}=\sqrt{\mid{x}\mid}\:. \\ $$
Commented by ajfour last updated on 03/Nov/19
Commented by ajfour last updated on 03/Nov/19
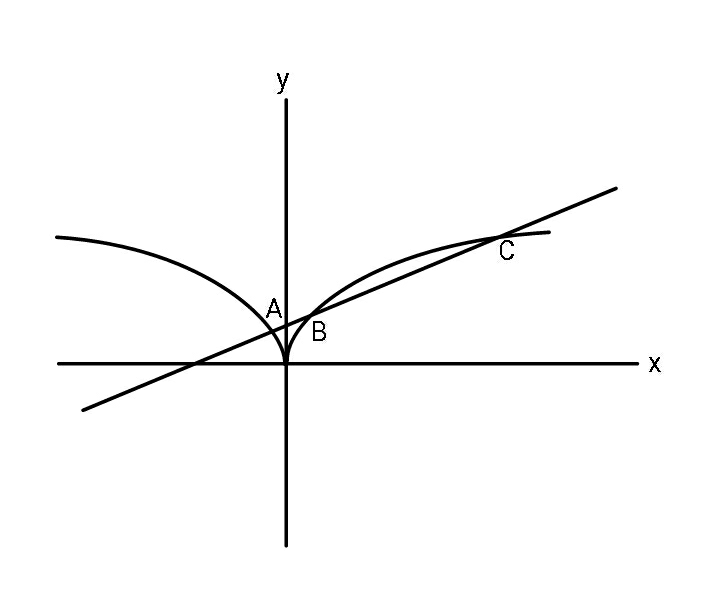
![5y=x+6 y=(√(∣x∣)) ⇒ for intersection points (x+6)^2 =25∣x∣ ⇒ x^2 +12x−25∣x∣+36=0 for x>0 x^2 −13x+36=0 x=((13)/2)±(√(((169)/4)−36)) = ((13)/2)±(5/2) x_B =4, x_C =9 for x<0 x^2 +37x+36=0 (x+36)(x+1)=0 x_A =−1 Area A=A_1 +A_2 +A_3 A_1 =∫_(−1) ^( 0) (((x+6)/5)−(√(−x)))dx =[((x^2 +12x)/(10))−(2/3)(−x)^(3/2) ]_(−1) ^0 = (2/3)+((11)/(10))=((53)/(30)) A_2 =∫_0 ^( 4) (((x+6)/5)−(√x))dx =[((x^2 +12x)/(10))−(2/3)x^(3/2) ]_0 ^4 = ((64)/(10))−((16)/3)=((16)/(15)) A_3 =∫_4 ^( 9) ((√x)−((x+6)/5))dx = (2/3)x^(3/2) −((x^2 +12x)/(10)) =(2/3)(27−8)−(1/(10))(81+108−16−48) =((38)/3)−((25)/2)=(1/6) A=((53)/(30))+((32)/(30))+(5/(30))= 3 sq. units.](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q72818.png)
$$\mathrm{5}{y}={x}+\mathrm{6} \\ $$$${y}=\sqrt{\mid{x}\mid} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{for}\:{intersection}\:{points} \\ $$$$\left({x}+\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{25}\mid{x}\mid \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{12}{x}−\mathrm{25}\mid{x}\mid+\mathrm{36}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${for}\:{x}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{13}{x}+\mathrm{36}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{13}}{\mathrm{2}}\pm\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{169}}{\mathrm{4}}−\mathrm{36}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{13}}{\mathrm{2}}\pm\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:{x}_{{B}} =\mathrm{4},\:\:{x}_{{C}} =\mathrm{9} \\ $$$${for}\:{x}<\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{37}{x}+\mathrm{36}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({x}+\mathrm{36}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}_{{A}} =−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${Area}\:{A}={A}_{\mathrm{1}} +{A}_{\mathrm{2}} +{A}_{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$${A}_{\mathrm{1}} =\int_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{\:\mathrm{0}} \left(\frac{{x}+\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{5}}−\sqrt{−{x}}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\left[\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{12}{x}}{\mathrm{10}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\left(−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{3}/\mathrm{2}} \right]_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{0}} \\ $$$$\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{11}}{\mathrm{10}}=\frac{\mathrm{53}}{\mathrm{30}} \\ $$$${A}_{\mathrm{2}} =\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\mathrm{4}} \left(\frac{{x}+\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{5}}−\sqrt{{x}}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:=\left[\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{12}{x}}{\mathrm{10}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}{x}^{\mathrm{3}/\mathrm{2}} \right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{64}}{\mathrm{10}}−\frac{\mathrm{16}}{\mathrm{3}}=\frac{\mathrm{16}}{\mathrm{15}} \\ $$$$\:{A}_{\mathrm{3}} =\int_{\mathrm{4}} ^{\:\mathrm{9}} \left(\sqrt{{x}}−\frac{{x}+\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{5}}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}{x}^{\mathrm{3}/\mathrm{2}} −\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{12}{x}}{\mathrm{10}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\left(\mathrm{27}−\mathrm{8}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{10}}\left(\mathrm{81}+\mathrm{108}−\mathrm{16}−\mathrm{48}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:=\frac{\mathrm{38}}{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$${A}=\frac{\mathrm{53}}{\mathrm{30}}+\frac{\mathrm{32}}{\mathrm{30}}+\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{30}}=\:\mathrm{3}\:{sq}.\:{units}. \\ $$
Commented by Learner-123 last updated on 03/Nov/19

$${thanks}\:{sir}. \\ $$
