Question Number 66562 by Rio Michael last updated on 17/Aug/19
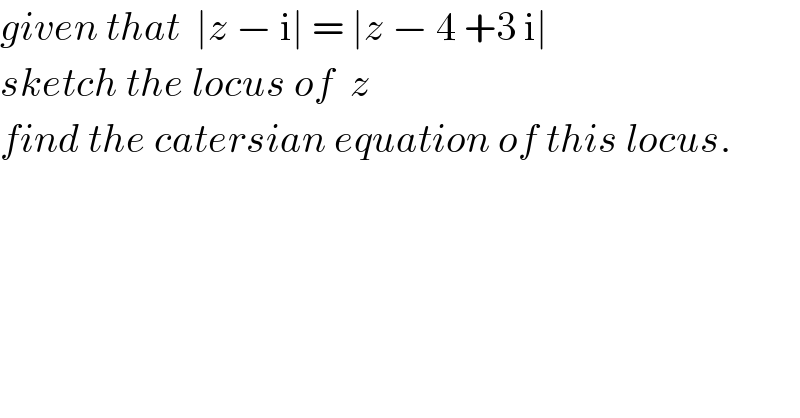
$${given}\:{that}\:\:\mid{z}\:−\:\mathrm{i}\mid\:=\:\mid{z}\:−\:\mathrm{4}\:+\mathrm{3}\:\mathrm{i}\mid \\ $$$${sketch}\:{the}\:{locus}\:{of}\:\:{z} \\ $$$${find}\:{the}\:{catersian}\:{equation}\:{of}\:{this}\:{locus}. \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 17/Aug/19
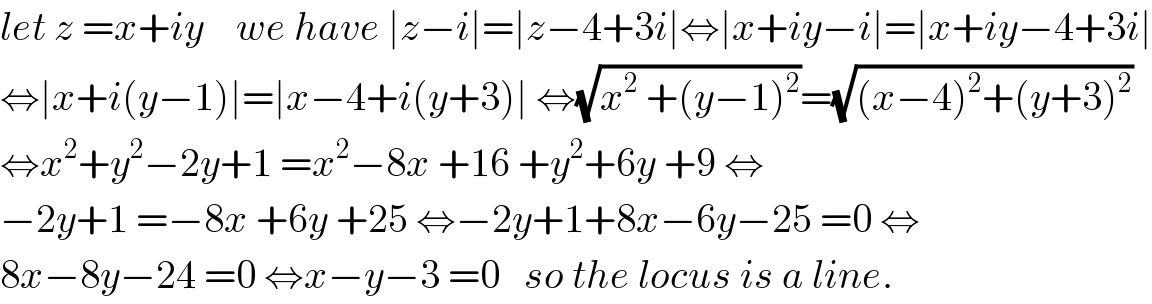
$${let}\:{z}\:={x}+{iy}\:\:\:\:{we}\:{have}\:\mid{z}−{i}\mid=\mid{z}−\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{3}{i}\mid\Leftrightarrow\mid{x}+{iy}−{i}\mid=\mid{x}+{iy}−\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{3}{i}\mid \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\mid{x}+{i}\left({y}−\mathrm{1}\right)\mid=\mid{x}−\mathrm{4}+{i}\left({y}+\mathrm{3}\right)\mid\:\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\left({y}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }=\sqrt{\left({x}−\mathrm{4}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({y}+\mathrm{3}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{y}+\mathrm{1}\:={x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{8}{x}\:+\mathrm{16}\:+{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{6}{y}\:+\mathrm{9}\:\Leftrightarrow \\ $$$$−\mathrm{2}{y}+\mathrm{1}\:=−\mathrm{8}{x}\:+\mathrm{6}{y}\:+\mathrm{25}\:\Leftrightarrow−\mathrm{2}{y}+\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{8}{x}−\mathrm{6}{y}−\mathrm{25}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\Leftrightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{8}{x}−\mathrm{8}{y}−\mathrm{24}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\Leftrightarrow{x}−{y}−\mathrm{3}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\:\:{so}\:{the}\:{locus}\:{is}\:{a}\:{line}. \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 17/Aug/19

$$\mid{z}\:−\:\mathrm{i}\mid\:=\:\mid{z}\:−\:\mathrm{4}\:+\mathrm{3}\:\mathrm{i}\mid\:{means} \\ $$$${the}\:{distance}\:{from}\:{the}\:{variable}\:{point} \\ $$$${P}\left({x},{y}\right)\:{to}\:{the}\:{point}\:{A}\left(\mathrm{0},\mathrm{1}\right)\:{is}\:{equal} \\ $$$${to}\:{the}\:{distance}\:{from}\:{P}\:\:{to}\:{the}\:{point} \\ $$$${B}\left(\mathrm{4},−\mathrm{3}\right).\:{the}\:{locus}\:{of}\:{point}\:{P}\:{is} \\ $$$${therefore}\:{the}\:{perpendicular}\:{bisector} \\ $$$${of}\:{AB},\:{i}.{e}.\:{the}\:{locus}\:{is}\:{a}\:{line}. \\ $$$${z}={x}+{yi} \\ $$$$\mid{z}−{i}\mid=\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({y}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\mid{z}−\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{3}{i}\mid=\sqrt{\left({x}−\mathrm{4}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({y}+\mathrm{3}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({y}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\left({x}−\mathrm{4}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({y}+\mathrm{3}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{y}={x}−\mathrm{3}\:\leftarrow\:{eqn}.\:{of}\:{locus} \\ $$
Commented by Rio Michael last updated on 17/Aug/19
$${thanks}\:{so}\:{much}\:{sir} \\ $$
