Question Number 135986 by SOMEDAVONG last updated on 17/Mar/21
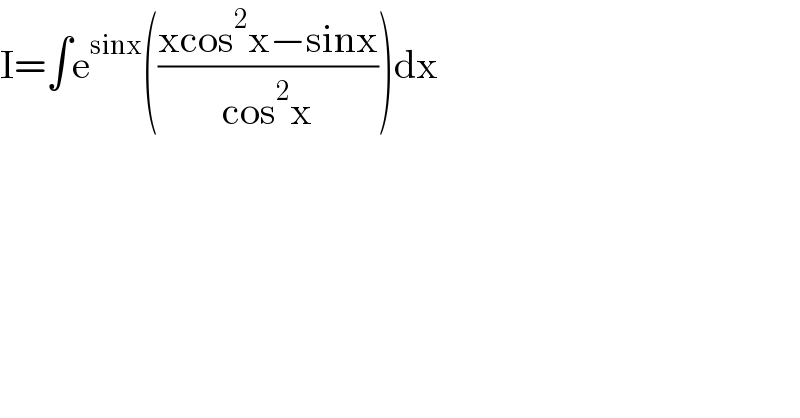
$$\mathrm{I}=\int\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{sinx}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{xcos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}−\mathrm{sinx}}{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}\right)\mathrm{dx} \\ $$
Answered by Olaf last updated on 17/Mar/21
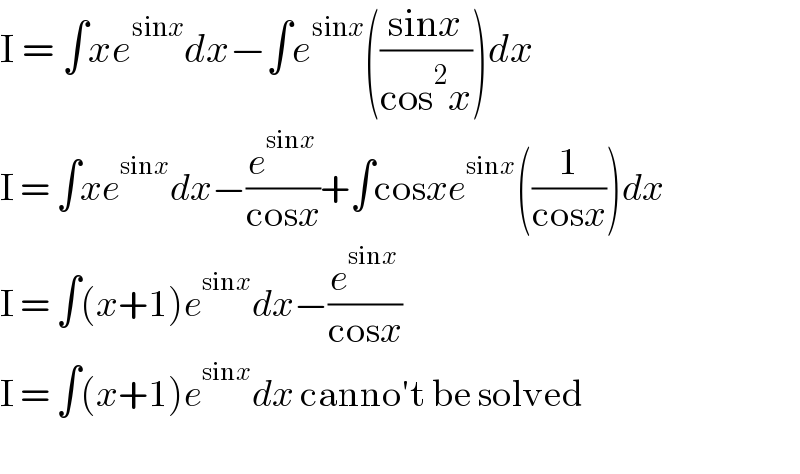
$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\int{xe}^{\mathrm{sin}{x}} {dx}−\int{e}^{\mathrm{sin}{x}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{sin}{x}}{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\int{xe}^{\mathrm{sin}{x}} {dx}−\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{sin}{x}} }{\mathrm{cos}{x}}+\int\mathrm{cos}{xe}^{\mathrm{sin}{x}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{cos}{x}}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\int\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right){e}^{\mathrm{sin}{x}} {dx}−\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{sin}{x}} }{\mathrm{cos}{x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\int\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right){e}^{\mathrm{sin}{x}} {dx}\:\mathrm{canno}'\mathrm{t}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{solved} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by SOMEDAVONG last updated on 17/Mar/21

$$\mathrm{Thanks}\:\mathrm{Teacher} \\ $$
