Question Number 7157 by Tawakalitu. last updated on 13/Aug/16
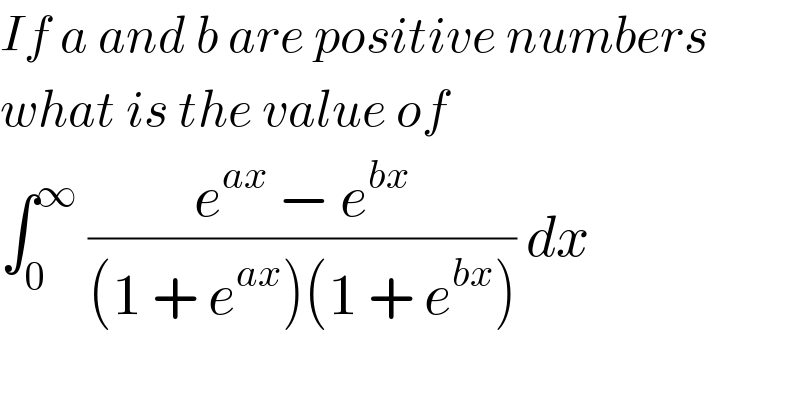
$${If}\:{a}\:{and}\:{b}\:{are}\:{positive}\:{numbers} \\ $$$${what}\:{is}\:{the}\:{value}\:{of}\: \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{e}^{{ax}} \:−\:{e}^{{bx}} }{\left(\mathrm{1}\:+\:{e}^{{ax}} \right)\left(\mathrm{1}\:+\:{e}^{{bx}} \right)}\:{dx}\: \\ $$
Answered by Yozzia last updated on 14/Aug/16
![(1/(1+e^(bx) ))−(1/(1+e^(ax) ))=((e^(ax) −e^(bx) )/((1+e^(ax) )(1+e^(bx) ))) (a,b>0) I=∫_0 ^∞ ((e^(ax) −e^(bx) )/((1+e^(ax) )(1+e^(bx) )))dx=∫_0 ^∞ [(1/(1+e^(bx) ))−(1/(1+e^(ax) ))]dx I=lim_(m→∞) [∫_0 ^m (1/(1+e^(bx) ))dx−∫_0 ^m (1/(1+e^(ax) ))dx] u=e^(bx) ⇒du=be^(bx) dx⇒dx=(1/(bu))du ∫(1/(bu(1+u)))du=(1/b)∫((1/u)−(1/(1+u)))du =(1/b)ln(u/(1+u))=(1/b)ln(1/(1+u^(−1) ))=(1/b)ln(1/(1+e^(−bx) )) ∴I=lim_(m→∞) [(1/b)ln((1/(1+e^(−bx) )))−(1/a)ln((1/(1+e^(−ax) )))]_0 ^m I=lim_(m→∞) [(1/b)ln(1/(1+e^(−bm) ))−(1/a)ln(1/(1+e^(−am) ))−(1/b)ln(1/(1+1))+(1/a)ln(1/(1+1))] Since a,b>0, I=(1/b)ln(1/(1+e^(−∞) ))−(1/a)ln(1/(1+e^(−∞) ))+(ln(1/2))((1/a)−(1/b)) I=(1/b)ln(1/(1+0))−(1/a)ln(1/(1+0))+(((a−b)ln2)/(ab)) ∫_0 ^∞ ((e^(ax) −e^(bx) )/((1+e^(ax) )(1+e^(bx) )))dx=(((a−b)ln2)/(ab))](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q7158.png)
$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{bx}} }−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{ax}} }=\frac{{e}^{{ax}} −{e}^{{bx}} }{\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{ax}} \right)\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{bx}} \right)}\:\:\:\left({a},{b}>\mathrm{0}\right) \\ $$$${I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{{e}^{{ax}} −{e}^{{bx}} }{\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{ax}} \right)\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{bx}} \right)}{dx}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{bx}} }−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{ax}} }\right]{dx} \\ $$$${I}=\underset{{m}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{m}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{bx}} }{dx}−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{m}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{ax}} }{dx}\right] \\ $$$${u}={e}^{{bx}} \Rightarrow{du}={be}^{{bx}} {dx}\Rightarrow{dx}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{bu}}{du} \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{bu}\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\right)}{du}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{b}}\int\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{u}}\right){du} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{b}}{ln}\frac{{u}}{\mathrm{1}+{u}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{b}}{ln}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{u}^{−\mathrm{1}} }=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{b}}{ln}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−{bx}} } \\ $$$$\therefore{I}=\underset{{m}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{b}}{ln}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−{bx}} }\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{a}}{ln}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−{ax}} }\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{m}} \\ $$$${I}=\underset{{m}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{b}}{ln}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−{bm}} }−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{a}}{ln}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−{am}} }−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{b}}{ln}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{a}}{ln}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}}\right] \\ $$$${Since}\:{a},{b}>\mathrm{0},\:{I}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{b}}{ln}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−\infty} }−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{a}}{ln}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−\infty} }+\left({ln}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{a}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{b}}\right) \\ $$$${I}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{b}}{ln}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{0}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{a}}{ln}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{0}}+\frac{\left({a}−{b}\right){ln}\mathrm{2}}{{ab}} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{{e}^{{ax}} −{e}^{{bx}} }{\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{ax}} \right)\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{bx}} \right)}{dx}=\frac{\left({a}−{b}\right){ln}\mathrm{2}}{{ab}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Tawakalitu. last updated on 14/Aug/16
$${Thanks}\:{so}\:{much}\:{sir} \\ $$
