Question Number 139288 by 7770 last updated on 25/Apr/21
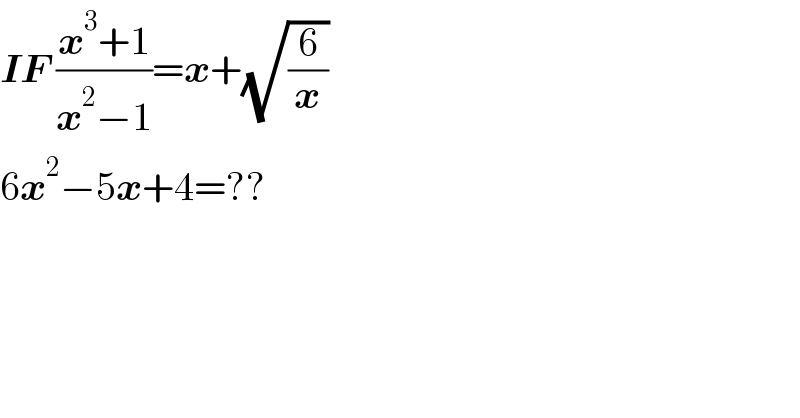
$$\boldsymbol{{IF}}\:\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{1}}{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}=\boldsymbol{{x}}+\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{\boldsymbol{{x}}}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{6}\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}\boldsymbol{{x}}+\mathrm{4}=?? \\ $$
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 25/Apr/21
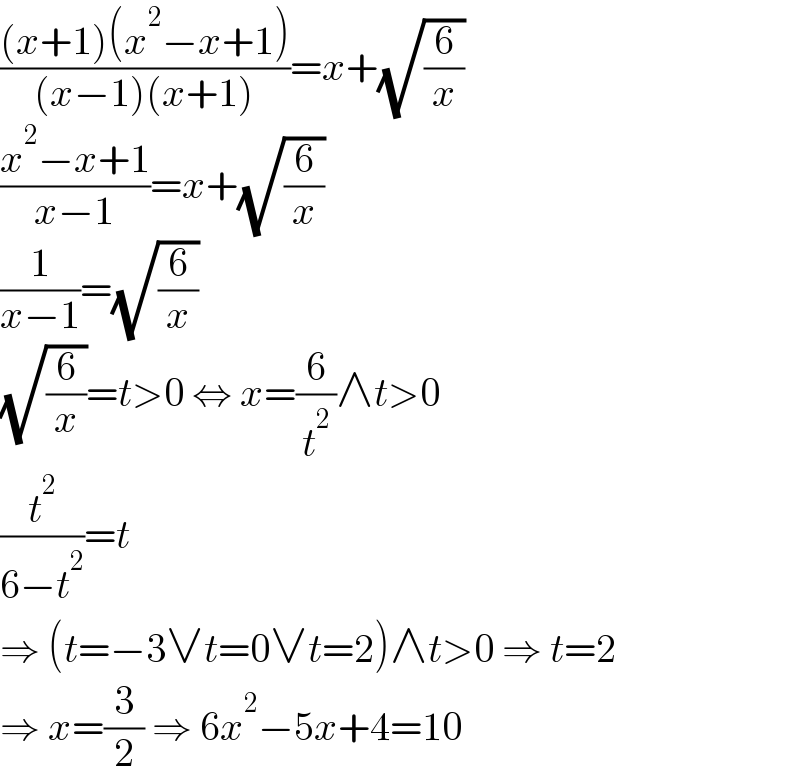
$$\frac{\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)}={x}+\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}}} \\ $$$$\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}={x}+\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}=\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}}} \\ $$$$\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}}}={t}>\mathrm{0}\:\Leftrightarrow\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\wedge{t}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{6}−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }={t} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\left({t}=−\mathrm{3}\vee{t}=\mathrm{0}\vee{t}=\mathrm{2}\right)\wedge{t}>\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\:{t}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{6}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}{x}+\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{10} \\ $$
Answered by lyubita last updated on 25/Apr/21

$$\mathrm{10} \\ $$
Answered by liberty last updated on 25/Apr/21

$$\:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:=\:\mathrm{x}+\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{x}}} \\ $$$$\:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:=\:\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{x}}} \\ $$$$\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:=\:\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{x}}} \\ $$$$\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{1}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{x}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{6x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{12x}+\mathrm{6}\:=\:\mathrm{x} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{6x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{13x}+\mathrm{6}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{x}−\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{6}}\right)\left(\mathrm{x}−\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{6}}\right)=\mathrm{0}\:\rightarrow\begin{cases}{\mathrm{x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}}\\{\mathrm{x}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\:\mathrm{6x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5x}+\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{6}\left(\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{15}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{16}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\mathrm{54}−\mathrm{30}+\mathrm{16}}{\mathrm{4}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{40}}{\mathrm{4}}=\mathrm{10} \\ $$$$\mathrm{or}\:\mathrm{6x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5x}+\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{6}\left(\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{9}}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{3}}+\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{8}}{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{12}}{\mathrm{3}}=\frac{\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
Commented by lyubita last updated on 25/Apr/21

$${x}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\:{tidak}\:{memenuhi} \\ $$
Answered by qaz last updated on 25/Apr/21

$$\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}={x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}={x}+\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}}} \\ $$$$\ll\mathrm{1}\gg:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}=\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{6}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{13}{x}+\mathrm{6}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\:{or}\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{6}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}{x}+\mathrm{4}=\left(\mathrm{13}{x}−\mathrm{6}\right)−\mathrm{5}{x}+\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{8}{x}−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{8}×\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{2}\:{or}\:\mathrm{8}×\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{10}\:{or}\:\frac{\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\ll\mathrm{2}\gg:{x}=\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}}}\:\:\wedge\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}^{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{6}\:\wedge\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\nLeftrightarrow{x}=\sqrt[{\mathrm{3}}]{\mathrm{6}}\:\:\:\:\wedge\:\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}\:……………\:{Impossible} \\ $$$$\ll\mathrm{1}\gg\&\ll\mathrm{2}\gg \\ $$$$\mathrm{6}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}{x}+\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{10}\:{or}\:\frac{\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
Commented by lyubita last updated on 25/Apr/21
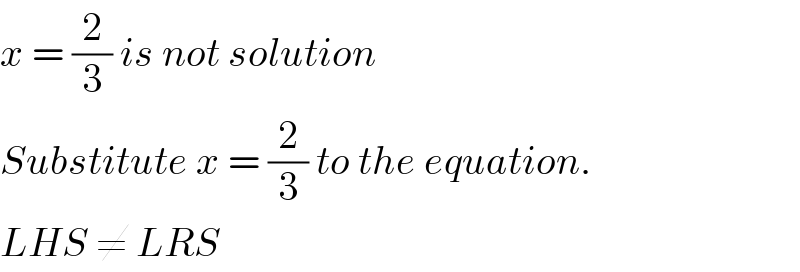
$${x}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\:{is}\:{not}\:{solution} \\ $$$${Substitute}\:{x}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\:{to}\:{the}\:{equation}.\: \\ $$$${LHS}\:\neq\:{LRS} \\ $$
Commented by qaz last updated on 26/Apr/21
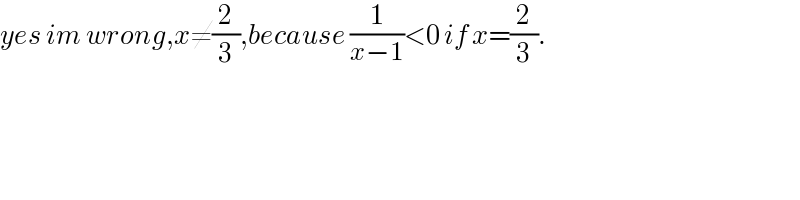
$${yes}\:{im}\:{wrong},{x}\neq\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}},{because}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}<\mathrm{0}\:{if}\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}. \\ $$
