Question Number 143561 by ZiYangLee last updated on 15/Jun/21
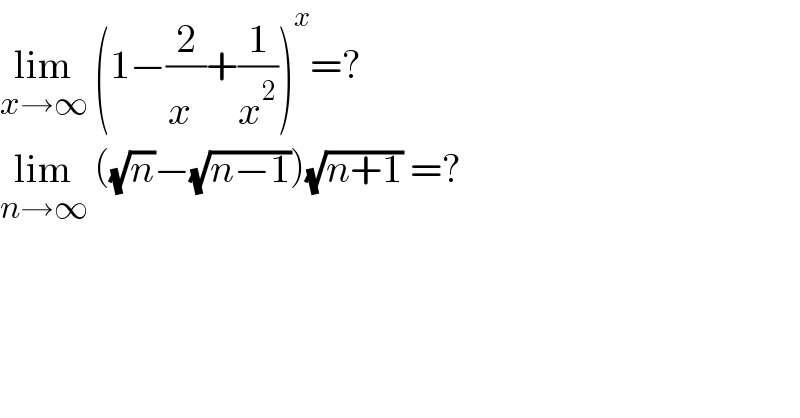
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}^{} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)^{{x}} =? \\ $$$$\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\left(\sqrt{{n}}−\sqrt{{n}−\mathrm{1}}\right)\sqrt{{n}+\mathrm{1}}\:=? \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 15/Jun/21
![a=lim_(x→∞) [(1−(1/x))^2 ]^x =lim_(x→∞) [(1−(1/x))^(−x) ]^(−2) =e^(−2) =(1/e^2 ) b=lim_(n→∞) ((√(n+1))/( (√n)+(√(n−1)))) =lim_(n→∞) ((√(1+(1/n)))/( 1+(√(1−(1/n)))))=(1/2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q143564.png)
$${a}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \right]^{{x}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)^{−{x}} \right]^{−\mathrm{2}} ={e}^{−\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{e}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${b}=\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\sqrt{{n}+\mathrm{1}}}{\:\sqrt{{n}}+\sqrt{{n}−\mathrm{1}}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}}}{\:\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by ZiYangLee last updated on 15/Jun/21
$${wow}…\:{thanks}\:{sir}\:{W}! \\ $$
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 15/Jun/21
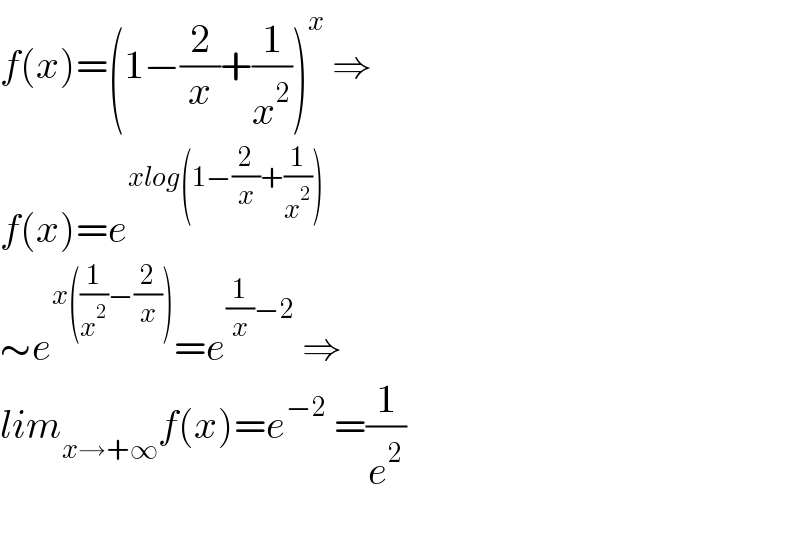
$${f}\left({x}\right)=\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)^{{x}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)={e}^{{xlog}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)} \\ $$$$\sim{e}^{{x}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}\right)} ={e}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}−\mathrm{2}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${lim}_{{x}\rightarrow+\infty} {f}\left({x}\right)={e}^{−\mathrm{2}} \:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{e}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by bobhans last updated on 15/Jun/21
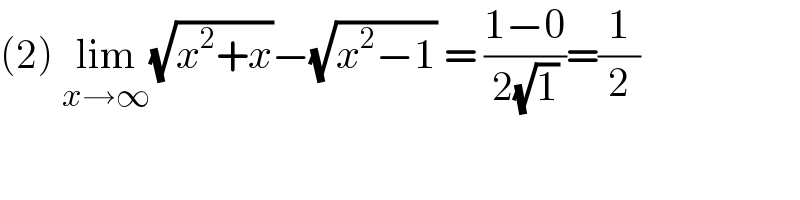
$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}}−\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{0}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
