Question Number 2478 by Syaka last updated on 21/Nov/15
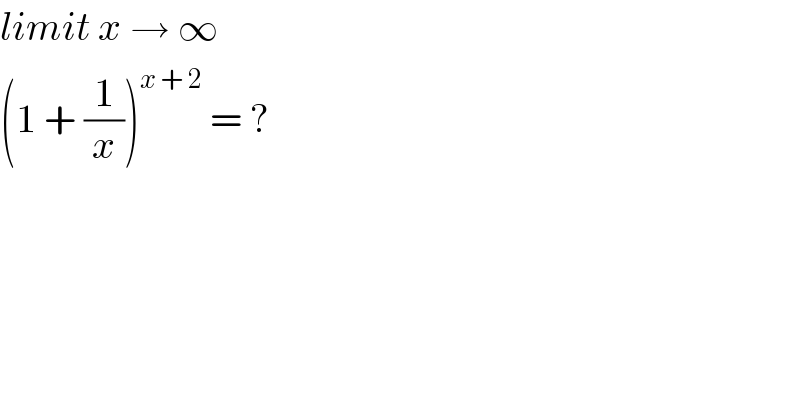
$${limit}\:{x}\:\rightarrow\:\infty \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)^{{x}\:+\:\mathrm{2}} \:=\:? \\ $$
Commented by John_Haha last updated on 21/Nov/15

$${e} \\ $$
Answered by Yozzi last updated on 21/Nov/15

$${L}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)^{{x}+\mathrm{2}} =\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)^{{x}} \\ $$$${L}=\left(\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left(\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)^{{x}} \right) \\ $$$${L}=\left(\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\infty}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left({e}\right) \\ $$$${L}=\mathrm{1}^{\mathrm{2}} ×{e}={e} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${Proof}\:{for}\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}/{x}\right)^{{x}} ={e} \\ $$$${Let}\:{l}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}/{x}\right)^{{x}} \:\:\left(\ast\right). \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}/{x}\right)^{{x}} >\mathrm{0}\:\forall{x}>\mathrm{0}\:{so}\:{if}\:{l}\:{exists},\:{l}>\mathrm{0}. \\ $$$${Taking}\:{logs}\:{to}\:{base}\:{e}\:{on}\:{both}\:{sides}\:{of}\:\left(\ast\right). \\ $$$${lnl}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}/{x}\right)^{{x}} \\ $$$${lnl}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}{xln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right) \\ $$$${Let}\:{u}=\mathrm{1}/{x}\Rightarrow{as}\:{x}\rightarrow\infty,{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}. \\ $$$$\therefore{lnl}=\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\right) \\ $$$${Using}\:{the}\:{Maclaurin}\:{expansion}\:{for} \\ $$$${ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\right)={u}−\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{5}} }{\mathrm{5}}−…\:\:\:−\mathrm{1}<{u}\leqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{lnl}=\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}\left({u}−\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{5}} }{\mathrm{5}}−…\right) \\ $$$${lnl}=\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{{u}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{5}}−…\right) \\ $$$${lnl}=\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{0}+\mathrm{0}−\mathrm{0}+\mathrm{0}−… \\ $$$${lnl}=\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow{l}={e} \\ $$$$\therefore\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)^{{x}} ={e} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
