Question Number 136225 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 19/Mar/21
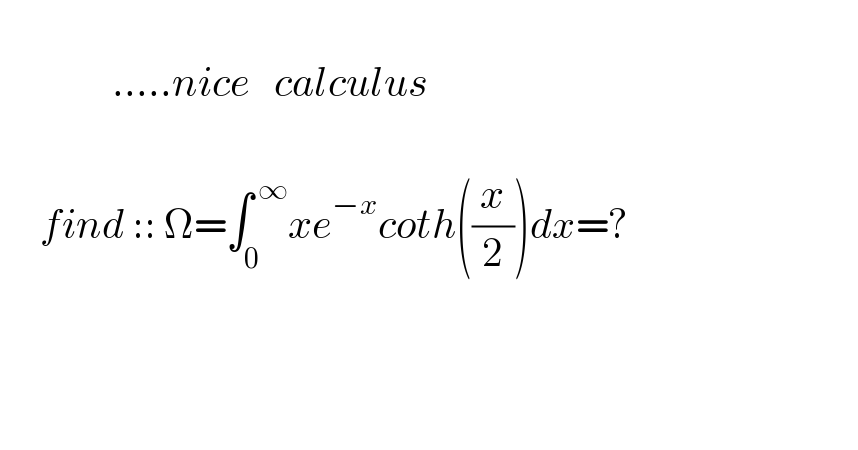
$$\:\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:…..{nice}\:\:\:{calculus}\:\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{find}\:::\:\Omega=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\infty} {xe}^{−{x}} {coth}\left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right){dx}=? \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 19/Mar/21
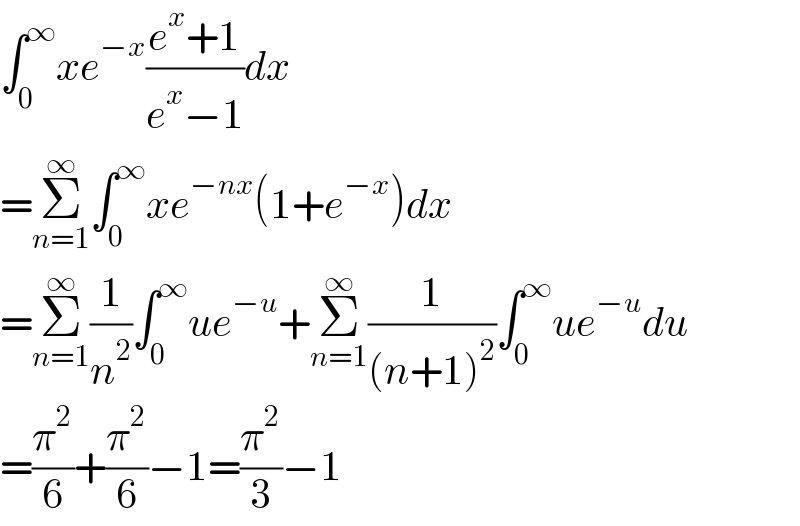
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {xe}^{−{x}} \frac{{e}^{{x}} +\mathrm{1}}{{e}^{{x}} −\mathrm{1}}{dx} \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {xe}^{−{nx}} \left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−{x}} \right){dx} \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {ue}^{−{u}} +\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {ue}^{−{u}} {du} \\ $$$$=\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{6}}+\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{6}}−\mathrm{1}=\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 19/Mar/21
$$\:{grateful}\:{and}\:{thank}\:{you}… \\ $$
