Question Number 133859 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 24/Feb/21
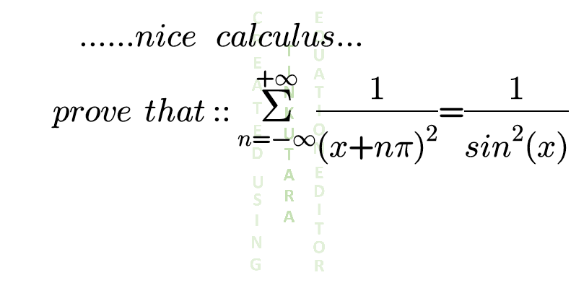
Answered by Ñï= last updated on 24/Feb/21
![Σ_(n=−∞) ^(+∞) (1/((x+nπ)^2 )) =Σ_(n=1) ^∞ [(1/((x+nπ)^2 ))+(1/((x−nπ)^2 ))+(1/x^2 )] =−(d/dx)Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ((1/(x+nπ))+(1/(x−nπ))+(1/x)) =−(d/dx)[(1/x)+Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ((2x)/(x^2 −n^2 π^2 ))] =−(d^2 /dx^2 )[lnx+Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ln(x^2 −n^2 π^2 )] =−(d^2 /dx^2 ){ln[Π_(n=1) ^∞ x(x^2 −n^2 π^2 )]} =−(d^2 /dx^2 )(lnsinx) =csc^2 x](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q133880.png)
$$\underset{{n}=−\infty} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({x}+{n}\pi\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({x}+{n}\pi\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({x}−{n}\pi\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right] \\ $$$$=−\frac{{d}}{{dx}}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}+{n}\pi}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−{n}\pi}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right) \\ $$$$=−\frac{{d}}{{dx}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}+\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \pi^{\mathrm{2}} }\right] \\ $$$$=−\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\left[{lnx}+\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{ln}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \pi^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\right] \\ $$$$=−\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\left\{{ln}\left[\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\prod}}{x}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \pi^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\right]\right\} \\ $$$$=−\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\left({lnsinx}\right) \\ $$$$={csc}^{\mathrm{2}} {x} \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 24/Feb/21
$${thanks}\:{alot}\:{sir}… \\ $$
