Question Number 135254 by 0731619177 last updated on 11/Mar/21
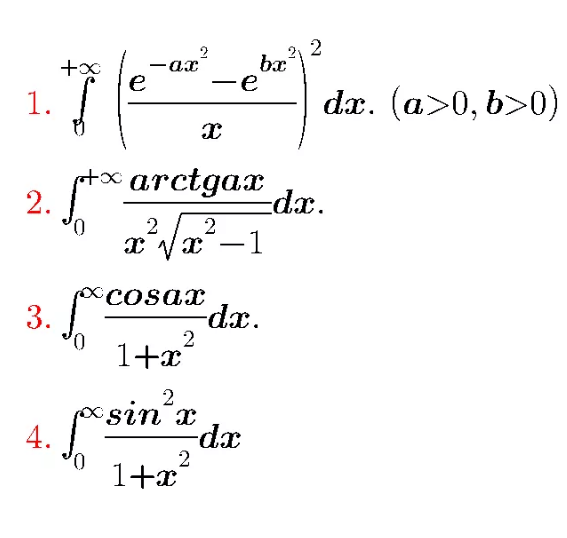
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 11/Mar/21
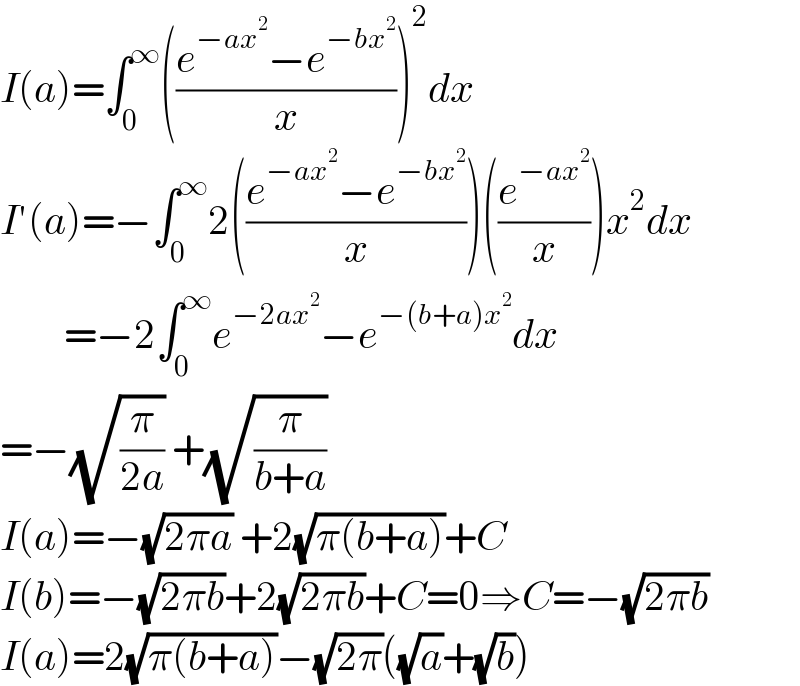
$${I}\left({a}\right)=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left(\frac{{e}^{−{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} } −{e}^{−{bx}^{\mathrm{2}} } }{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} {dx} \\ $$$${I}'\left({a}\right)=−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \mathrm{2}\left(\frac{{e}^{−{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} } −{e}^{−{bx}^{\mathrm{2}} } }{{x}}\right)\left(\frac{{e}^{−{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} } }{{x}}\right){x}^{\mathrm{2}} {dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=−\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−\mathrm{2}{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} } −{e}^{−\left({b}+{a}\right){x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {dx} \\ $$$$=−\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}{a}}}\:+\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{{b}+{a}}} \\ $$$${I}\left({a}\right)=−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}\pi{a}}\:+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\pi\left({b}+{a}\right)}+{C} \\ $$$${I}\left({b}\right)=−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}\pi{b}}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}\pi{b}}+{C}=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow{C}=−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}\pi{b}} \\ $$$${I}\left({a}\right)=\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\pi\left({b}+{a}\right)}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}\pi}\left(\sqrt{{a}}+\sqrt{{b}}\right) \\ $$
Commented by 0731619177 last updated on 11/Mar/21

$${tanks} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by 0731619177 last updated on 11/Mar/21

$${mor}\:{qustion} \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 11/Mar/21
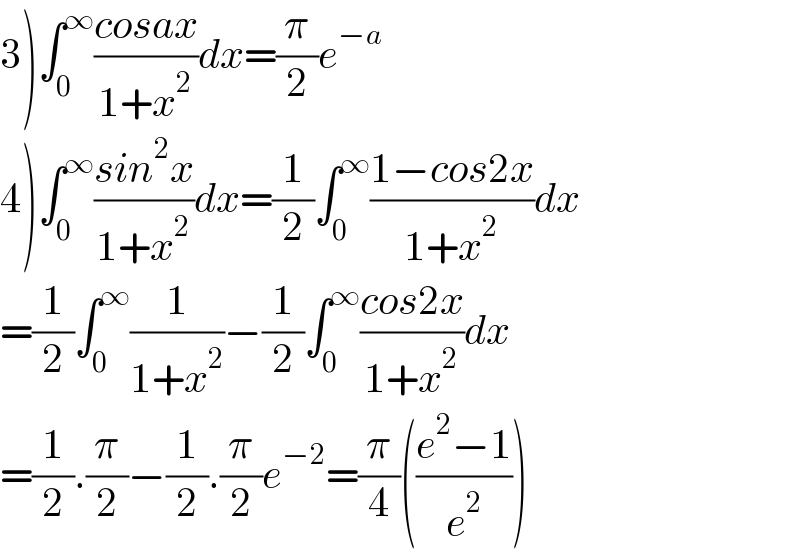
$$\left.\mathrm{3}\right)\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{{cosax}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}{e}^{−{a}} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{4}\right)\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{\mathrm{1}−{cos}\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{{cos}\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}.\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}.\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}{e}^{−\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\left(\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}{{e}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right) \\ $$
Commented by 0731619177 last updated on 11/Mar/21
$${two}\:{nomber}\:{question} \\ $$
