Question Number 137290 by JulioCesar last updated on 31/Mar/21

Answered by EDWIN88 last updated on 01/Apr/21
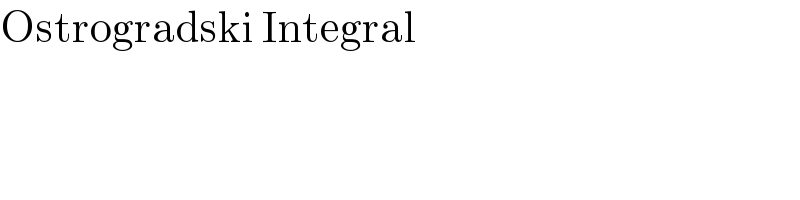
$$\mathrm{Ostrogradski}\:\mathrm{Integral}\: \\ $$
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 01/Apr/21
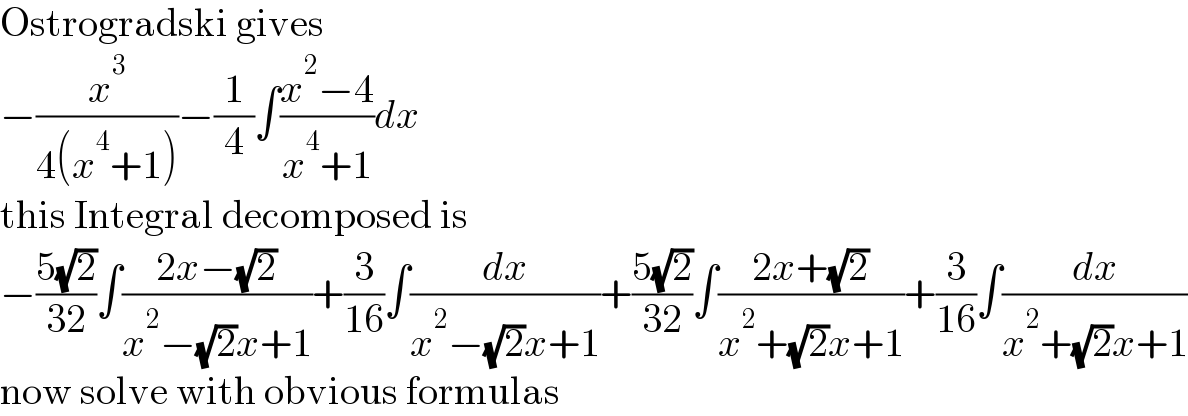
$$\mathrm{Ostrogradski}\:\mathrm{gives} \\ $$$$−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{4}\left({x}^{\mathrm{4}} +\mathrm{1}\right)}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\int\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +\mathrm{1}}{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{Integral}\:\mathrm{decomposed}\:\mathrm{is} \\ $$$$−\frac{\mathrm{5}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{32}}\int\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}{x}+\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{16}}\int\frac{{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}{x}+\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{5}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{32}}\int\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}{x}+\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{16}}\int\frac{{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}{x}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{now}\:\mathrm{solve}\:\mathrm{with}\:\mathrm{obvious}\:\mathrm{formulas} \\ $$
