Question Number 143332 by bramlexs22 last updated on 13/Jun/21
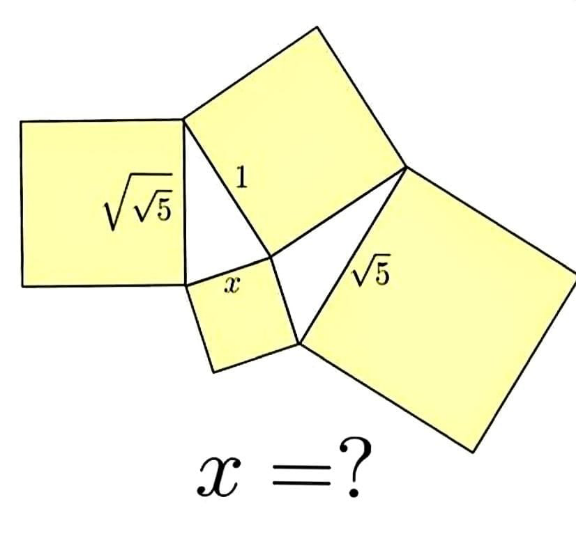
Commented by soumyasaha last updated on 13/Jun/21

$$\:\mathrm{x}\:=\:\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{3}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 13/Jun/21
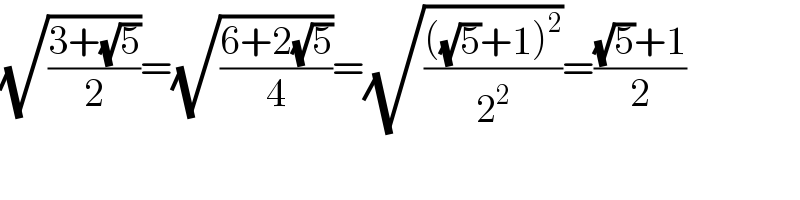
$$\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{3}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}}=\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{4}}}=\sqrt{\frac{\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} }}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by nimnim last updated on 13/Jun/21
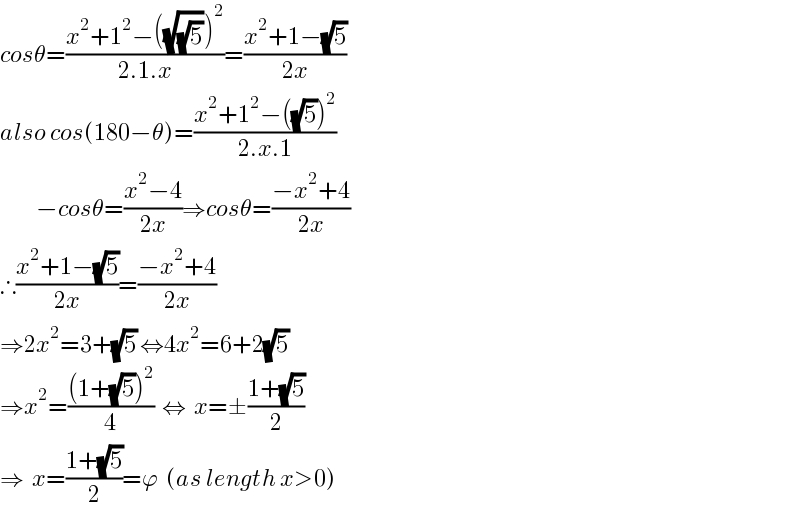
$${cos}\theta=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}^{\mathrm{2}} −\left(\sqrt{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{1}.{x}}=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}{x}} \\ $$$${also}\:{cos}\left(\mathrm{180}−\theta\right)=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}^{\mathrm{2}} −\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}.{x}.\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−{cos}\theta=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{2}{x}}\Rightarrow{cos}\theta=\frac{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{2}{x}} \\ $$$$\therefore\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}{x}}=\frac{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{2}{x}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{3}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\:\Leftrightarrow\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{6}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}}\:\:\Leftrightarrow\:\:{x}=\pm\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}=\varphi\:\:\left({as}\:{length}\:{x}>\mathrm{0}\right) \\ $$
Commented by nimnim last updated on 13/Jun/21

Answered by mr W last updated on 13/Jun/21

Commented by mr W last updated on 13/Jun/21
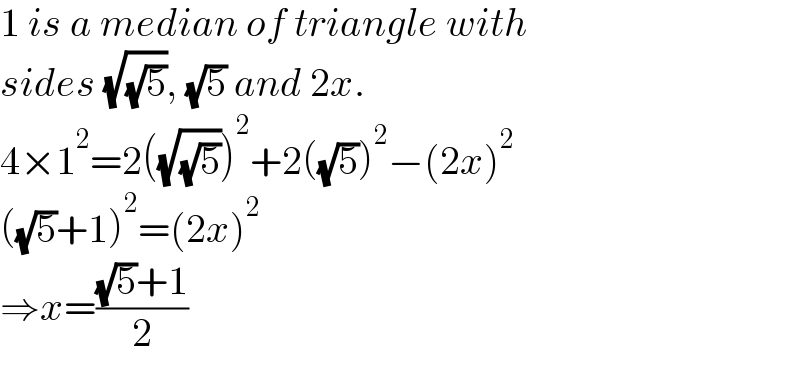
$$\mathrm{1}\:{is}\:{a}\:{median}\:{of}\:{triangle}\:{with} \\ $$$${sides}\:\sqrt{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}},\:\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\:{and}\:\mathrm{2}{x}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{4}×\mathrm{1}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{2}\left(\sqrt{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
