Question Number 73518 by aliesam last updated on 13/Nov/19

Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 13/Nov/19
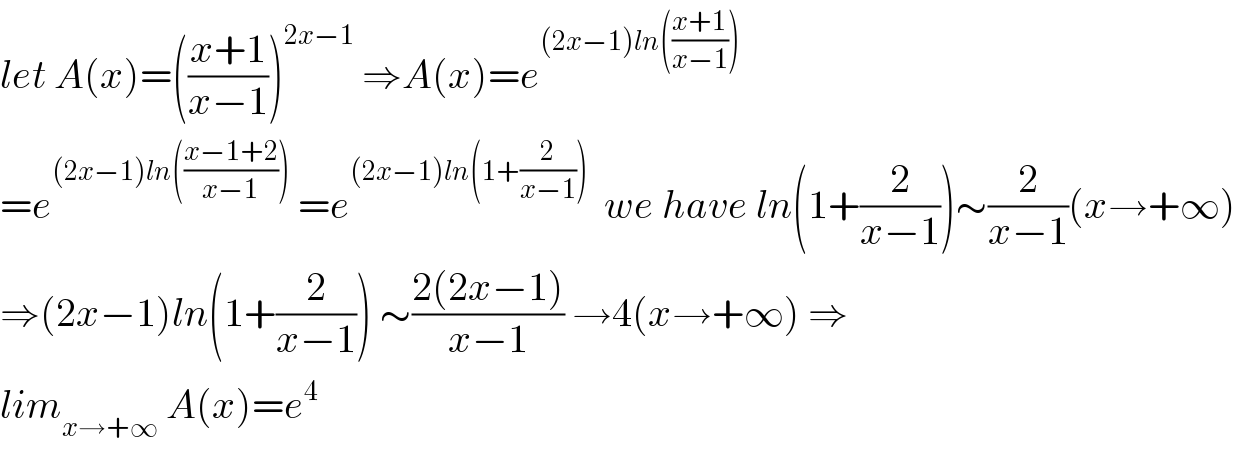
$${let}\:{A}\left({x}\right)=\left(\frac{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}} \:\Rightarrow{A}\left({x}\right)={e}^{\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right){ln}\left(\frac{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right)} \\ $$$$={e}^{\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right){ln}\left(\frac{{x}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right)} \:={e}^{\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right){ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right)} \:\:{we}\:{have}\:{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right)\sim\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\left({x}\rightarrow+\infty\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right){ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right)\:\sim\frac{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:\rightarrow\mathrm{4}\left({x}\rightarrow+\infty\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${lim}_{{x}\rightarrow+\infty} \:{A}\left({x}\right)={e}^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
Answered by ajfour last updated on 13/Nov/19
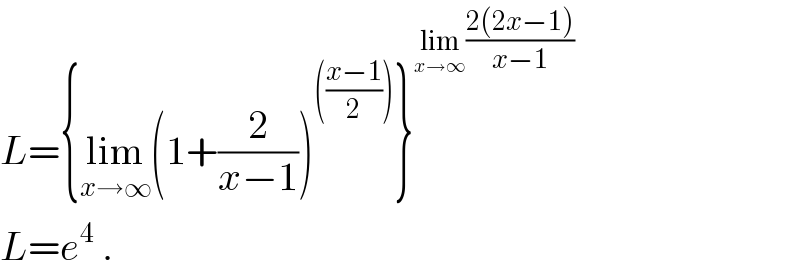
$${L}=\left\{\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right)^{\left(\frac{{x}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)} \right\}^{\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}} \\ $$$${L}={e}^{\mathrm{4}} \:. \\ $$
