Question Number 74284 by arthur.kangdani@gmail.com last updated on 21/Nov/19

Commented by mr W last updated on 21/Nov/19

$${a}_{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{4} \\ $$$${a}_{\mathrm{21}} =\mathrm{99} \\ $$$$\Sigma=\frac{\left(\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{99}\right)×\mathrm{20}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{1030} \\ $$
Commented by TawaTawa last updated on 21/Nov/19
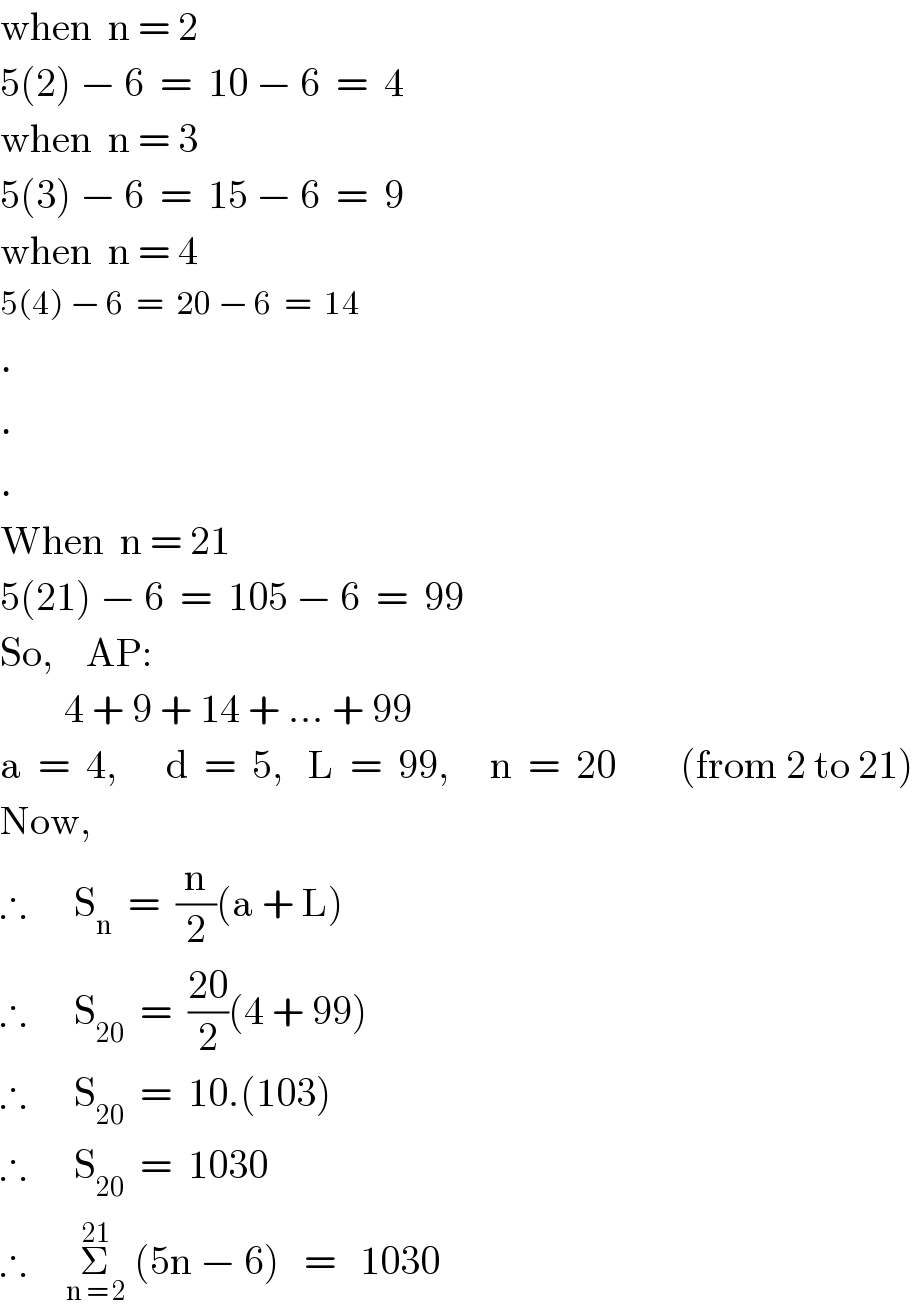
$$\mathrm{when}\:\:\mathrm{n}\:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:−\:\mathrm{6}\:\:=\:\:\mathrm{10}\:−\:\mathrm{6}\:\:=\:\:\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\mathrm{when}\:\:\mathrm{n}\:=\:\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}\left(\mathrm{3}\right)\:−\:\mathrm{6}\:\:=\:\:\mathrm{15}\:−\:\mathrm{6}\:\:=\:\:\mathrm{9} \\ $$$$\mathrm{when}\:\:\mathrm{n}\:=\:\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}\left(\mathrm{4}\right)\:−\:\mathrm{6}\:\:=\:\:\mathrm{20}\:−\:\mathrm{6}\:\:=\:\:\mathrm{14} \\ $$$$. \\ $$$$. \\ $$$$. \\ $$$$\mathrm{When}\:\:\mathrm{n}\:=\:\mathrm{21} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}\left(\mathrm{21}\right)\:−\:\mathrm{6}\:\:=\:\:\mathrm{105}\:−\:\mathrm{6}\:\:=\:\:\mathrm{99} \\ $$$$\mathrm{So},\:\:\:\:\mathrm{AP}:\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{4}\:+\:\mathrm{9}\:+\:\mathrm{14}\:+\:…\:+\:\mathrm{99} \\ $$$$\mathrm{a}\:\:=\:\:\mathrm{4},\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{d}\:\:=\:\:\mathrm{5},\:\:\:\mathrm{L}\:\:=\:\:\mathrm{99},\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{n}\:\:=\:\:\mathrm{20}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{from}\:\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{21}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{Now}, \\ $$$$\therefore\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{S}_{\mathrm{n}} \:\:=\:\:\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{a}\:+\:\mathrm{L}\right) \\ $$$$\therefore\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{S}_{\mathrm{20}} \:\:=\:\:\frac{\mathrm{20}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{4}\:+\:\mathrm{99}\right) \\ $$$$\therefore\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{S}_{\mathrm{20}} \:\:=\:\:\mathrm{10}.\left(\mathrm{103}\right) \\ $$$$\therefore\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{S}_{\mathrm{20}} \:\:=\:\:\mathrm{1030} \\ $$$$\therefore\:\:\:\:\:\underset{\mathrm{n}\:=\:\mathrm{2}} {\overset{\mathrm{21}} {\sum}}\:\left(\mathrm{5n}\:−\:\mathrm{6}\right)\:\:\:=\:\:\:\mathrm{1030} \\ $$
Commented by TawaTawa last updated on 21/Nov/19

$$\mathrm{Wow},\:\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{got}\:\mathrm{it}.\:\:\mathrm{sir}\:\mathrm{mrW}\:\:\mathrm{thanks}\:\mathrm{sir}.\:\:\mathrm{God}\:\mathrm{bless}\:\mathrm{you}. \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 21/Nov/19

$${let}\:{S}\:=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{21}} \left(\mathrm{5}{n}−\mathrm{6}\right)\:{changement}\:{of}\:{indice}\:{n}−\mathrm{1}={k}\:{give} \\ $$$${S}\:=\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{20}} \left(\mathrm{5}\left({k}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{6}\right)\:=\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{20}} \left(\mathrm{5}{k}−\mathrm{1}\right)\:{the}\:{sequenc}\:{u}_{{k}} =\mathrm{5}{k}−\mathrm{1}\:{is} \\ $$$${srithmetic}\:{with}\:{r}=\mathrm{5}\:{and}\:{u}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{4}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${S}\:={u}_{\mathrm{1}} +{u}_{\mathrm{2}} +…+{u}_{\mathrm{20}} =\frac{\mathrm{20}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({u}_{\mathrm{1}} +{u}_{\mathrm{20}} \right)\:=\mathrm{10}\left(\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{99}\right)\:=\mathrm{10}×\mathrm{103}=\mathrm{1030}\:. \\ $$
Answered by $@ty@m123 last updated on 21/Nov/19

$$=\left\{\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{21}} {\sum}}\left(\mathrm{5}{n}−\mathrm{6}\right)\right\}−\left(\mathrm{5}×\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{6}\right) \\ $$$$=\left\{\mathrm{5}\Sigma{n}−\Sigma\mathrm{6}\right\}−\left(−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{5}×\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{6}{n}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{5}×\frac{\mathrm{21}×\mathrm{22}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{6}×\mathrm{21}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{1155}−\mathrm{126}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{1030} \\ $$
Answered by malwaan last updated on 22/Nov/19
![<4 ; 9 ; 14 ; 19 ;....; 94 ; 99 > n = 20 ; u_1 = 4 ; r = 5 ⇒S = (n/2)[2u_1 + (n−1)r] = ((20)/2)[2×4 + (20−1)×5] = 10(8 + 95 )=10×103=1030](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q74319.png)
$$<\mathrm{4}\:;\:\mathrm{9}\:;\:\mathrm{14}\:;\:\mathrm{19}\:;….;\:\mathrm{94}\:;\:\mathrm{99}\:> \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{n}}\:=\:\mathrm{20}\:;\:\boldsymbol{{u}}_{\mathrm{1}} \:=\:\mathrm{4}\:;\:\boldsymbol{{r}}\:=\:\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\boldsymbol{{S}}\:=\:\frac{\boldsymbol{{n}}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{{u}}_{\mathrm{1}} \:+\:\left(\boldsymbol{{n}}−\mathrm{1}\right)\boldsymbol{{r}}\right] \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{20}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\mathrm{2}×\mathrm{4}\:+\:\left(\mathrm{20}−\mathrm{1}\right)×\mathrm{5}\right] \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\:\mathrm{10}\left(\mathrm{8}\:+\:\mathrm{95}\:\right)=\mathrm{10}×\mathrm{103}=\mathrm{1030} \\ $$
Commented by $@ty@m123 last updated on 22/Nov/19

$${When}\:{last}\:{term}\:{is}\:{known}, \\ $$$${it}\:{is}\:{easier}\:{to}\:{use}\:{following}\:{formula}: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\boldsymbol{{S}}=\frac{\boldsymbol{{n}}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\boldsymbol{{a}}+\boldsymbol{{l}}\right) \\ $$$${where}\:{n}=\:{no}.{of}\:{terms} \\ $$$${a}=\:{first}\:{term} \\ $$$${l}={last}\:{term} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\boldsymbol{{S}}=\frac{\mathrm{20}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{99}\right)=\mathrm{1030} \\ $$
