Question Number 74615 by chess1 last updated on 27/Nov/19

Answered by mind is power last updated on 27/Nov/19
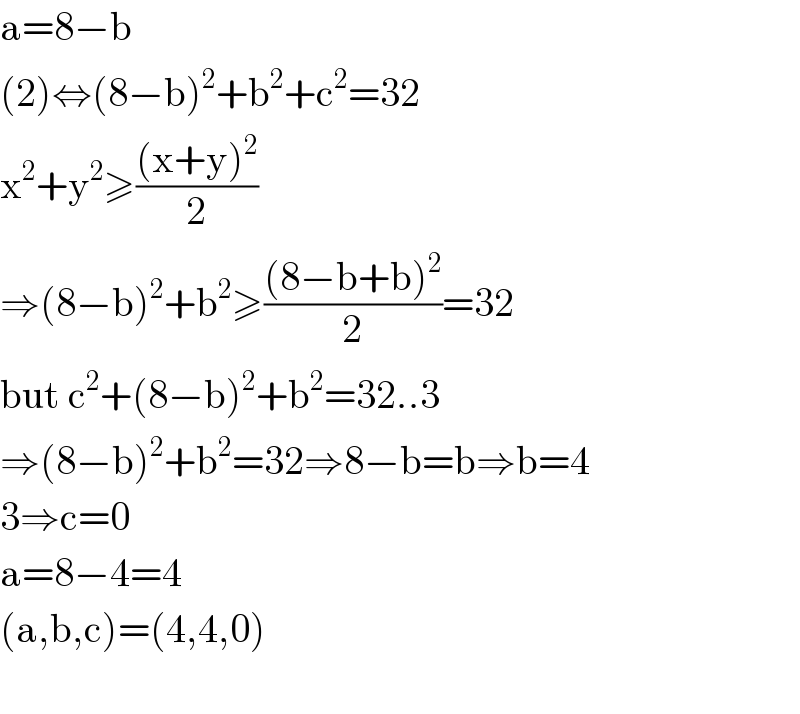
$$\mathrm{a}=\mathrm{8}−\mathrm{b} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\Leftrightarrow\left(\mathrm{8}−\mathrm{b}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{b}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{c}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{32} \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \geqslant\frac{\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{y}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left(\mathrm{8}−\mathrm{b}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{b}^{\mathrm{2}} \geqslant\frac{\left(\mathrm{8}−\mathrm{b}+\mathrm{b}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{32} \\ $$$$\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{c}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(\mathrm{8}−\mathrm{b}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{b}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{32}..\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left(\mathrm{8}−\mathrm{b}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{b}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{32}\Rightarrow\mathrm{8}−\mathrm{b}=\mathrm{b}\Rightarrow\mathrm{b}=\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}\Rightarrow\mathrm{c}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{a}=\mathrm{8}−\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{a},\mathrm{b},\mathrm{c}\right)=\left(\mathrm{4},\mathrm{4},\mathrm{0}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by JDamian last updated on 28/Nov/19
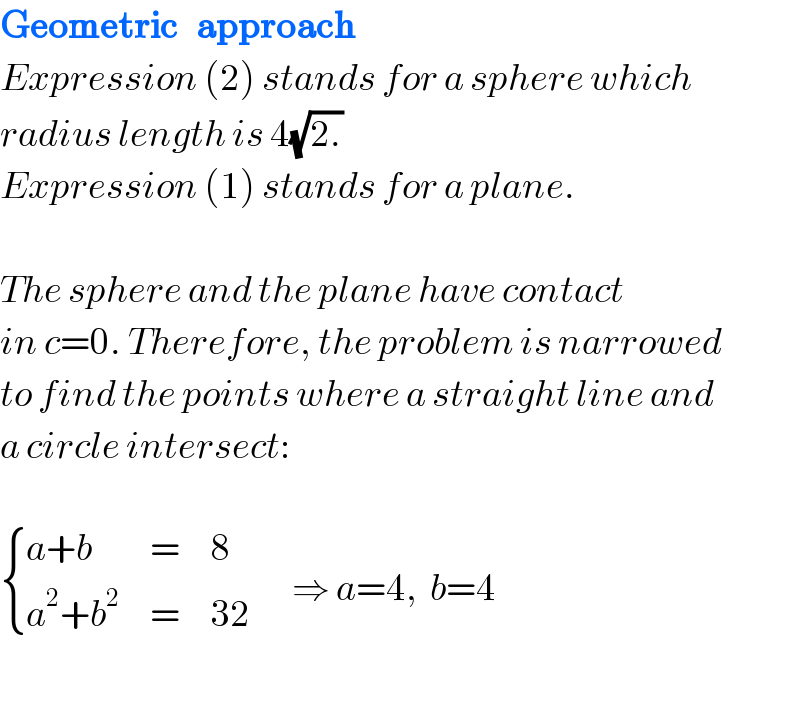
$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{Geometric}}\:\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{approach}} \\ $$$${Expression}\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:{stands}\:{for}\:{a}\:{sphere}\:{which} \\ $$$${radius}\:{length}\:{is}\:\mathrm{4}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}.} \\ $$$${Expression}\:\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:{stands}\:{for}\:{a}\:{plane}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${The}\:{sphere}\:{and}\:{the}\:{plane}\:{have}\:{contact} \\ $$$${in}\:{c}=\mathrm{0}.\:{Therefore},\:{the}\:{problem}\:{is}\:{narrowed} \\ $$$${to}\:{find}\:{the}\:{points}\:{where}\:{a}\:{straight}\:{line}\:{and} \\ $$$${a}\:{circle}\:{intersect}: \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{{a}+{b}}&{=}&{\mathrm{8}}\\{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} +{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }&{=}&{\mathrm{32}}\end{cases}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\Rightarrow\:{a}=\mathrm{4},\:\:{b}=\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
