Question Number 75986 by Ajao yinka last updated on 21/Dec/19
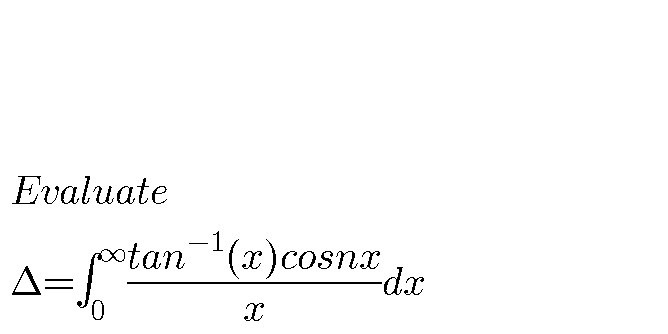
Commented by abdomathmax last updated on 24/Dec/19

$${let}\:{f}\left({t}\right)\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{{arctan}\left({xt}\right){cos}\left({nx}\right)}{{x}}{dx}\:\:{with}\:{t}\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${f}^{'} \left({t}\right)=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\frac{{cos}\left({nx}\right)}{{x}}{dx}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{{cos}\left({nx}\right)}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {t}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}{dx} \\ $$$$=_{{xt}={u}} \:\:\:\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{{cos}\left({n}\frac{{u}}{{t}}\right)}{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}\frac{{du}}{{t}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{t}}\:\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\frac{{cos}\left(\frac{{nu}}{{t}}\right)}{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}\:{du}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{t}}\:{Re}\left(\:\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\frac{{e}^{{i}\left(\frac{{nu}}{{t}}\right)} }{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}{du}\right) \\ $$$${let}\:{W}\left({z}\right)\:=\frac{{e}^{{i}\left(\frac{{nz}}{{t}}\right)} }{{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}\:\:{we}\:{hsve}? \\ $$$$\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:{W}\left({z}\right){dz}\:=\mathrm{2}{i}\pi\:{Res}\left({W},{i}\right)\:=\mathrm{2}{i}\pi\:×\frac{{e}^{−\frac{{n}}{{t}}} }{\mathrm{2}{i}} \\ $$$$=\pi\:{e}^{−\frac{{n}}{{t}}} \:\Rightarrow{f}^{'} \left({t}\right)\:=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}{t}}\:{e}^{−\frac{{n}}{{t}}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${f}\left({t}\right)\:=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{{t}} \:\:\:\frac{{e}^{−\frac{{n}}{{z}}} }{{z}}{dz}\:+{c}\:….{be}\:{continued}… \\ $$
Answered by mind is power last updated on 23/Dec/19

$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} \frac{\mathrm{tan}^{−} \left(\mathrm{xt}\right)\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{nx}\right)}{\mathrm{x}}\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}'\left(\mathrm{t}\right)=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} \frac{\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{nx}\right)}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{n}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} \frac{\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{z}\right)}{\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }.\mathrm{dz} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \frac{\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{z}\right)}{\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\mathrm{dz}\:=\mathrm{Re}\left(\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{iz}} \:}{\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\mathrm{dz}\right)\:\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{residu}\:\mathrm{th} \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{z}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{iz}} }{\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\left.=\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{2}}.\mathrm{2i}\pi\left\{\mathrm{Res}\left(\mathrm{f},\frac{\mathrm{ni}}{\mathrm{t}}\right)\right)\right\} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{in}\pi\frac{\mathrm{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{t}}} }{\mathrm{2int}}\right\}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2t}}\mathrm{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{t}}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} \frac{\mathrm{arvtan}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{nx}\right)\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{x}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\Delta=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{f}'\left(\mathrm{t}\right)\mathrm{dt}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2t}}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\frac{−\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{t}}} \right)\mathrm{dt}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{t}}} }{\mathrm{t}}\mathrm{dt} \\ $$$$\mathrm{w}=\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{t}}\Rightarrow\mathrm{dt}=−\mathrm{n}\frac{\mathrm{dw}}{\mathrm{w}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Delta=−\frac{\mathrm{n}\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{+\infty} \frac{\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{w}} }{\mathrm{w}}\mathrm{dw} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Ei}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=−\int_{−\mathrm{x}} ^{+\infty} \frac{\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{t}} }{\mathrm{t}}\mathrm{dt}\:\:\:\:\:,\mathrm{x}<\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Delta=−\frac{\mathrm{n}\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{i}} \left(−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Ajao yinka last updated on 31/Dec/19
Perfect
