Question Number 76586 by Master last updated on 28/Dec/19

Commented by Master last updated on 28/Dec/19

$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{solve}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{please}} \\ $$
Commented by Tony Lin last updated on 28/Dec/19

$$\left(\mathrm{5}\right) \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} {sin}^{{n}} {xcos}^{{n}} {xdx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{{n}} }\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} {sin}^{{n}} \left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right){dx} \\ $$$${let}\:\mathrm{2}{x}={u},\:{du}=\mathrm{2}{dx} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} }\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} {sin}^{{n}} {udu} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{{n}−\mathrm{2}} }\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} {sin}^{{n}} {xdx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{{n}−\mathrm{2}} }×\begin{cases}{\frac{\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({n}−\mathrm{3}\right)\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot\mathrm{1}}{{n}\left({n}−\mathrm{2}\right)\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot\mathrm{2}}×\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}},\:{if}\:{n}\:{is}\:{even}}\\{\frac{\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({n}−\mathrm{3}\right)\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot\mathrm{2}}{{n}\left({n}−\mathrm{2}\right)\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot\mathrm{1}},\:{if}\:{n}\:{is}\:{odd}}\end{cases} \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 28/Dec/19
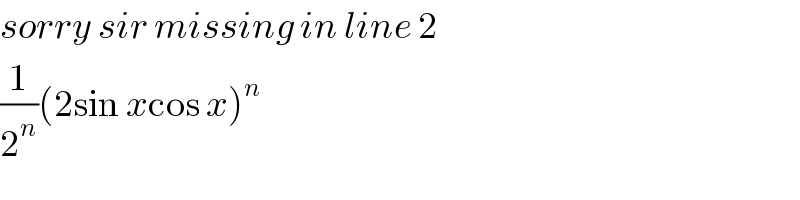
$${sorry}\:{sir}\:{missing}\:{in}\:{line}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{{n}} }\left(\mathrm{2sin}\:{x}\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\right)^{{n}} \\ $$
Commented by Tony Lin last updated on 28/Dec/19

$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$${a}_{{n}+\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{a}_{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }+{a}_{{n}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{a}_{{n}+\mathrm{2}} {a}_{{n}+\mathrm{1}} ={a}_{{n}+\mathrm{1}} {a}_{{n}} +\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{a}_{\mathrm{2019}} {a}_{\mathrm{2018}} \\ $$$$={a}_{\mathrm{2018}} {a}_{\mathrm{2017}} +\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$={a}_{\mathrm{2017}} {a}_{\mathrm{2016}} +\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$={a}_{\mathrm{1}} {a}_{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2017} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2018} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{a}_{{n}+\mathrm{1}} {a}_{{n}} ={n} \\ $$$$\frac{{a}_{\mathrm{2019}} }{{a}_{\mathrm{2017}} }=\frac{\mathrm{2018}}{\mathrm{2017}} \\ $$$$\frac{{a}_{\mathrm{2017}} }{{a}_{\mathrm{2015}} }=\frac{\mathrm{2016}}{\mathrm{2015}} \\ $$$$\frac{{a}_{\mathrm{5}} }{{a}_{\mathrm{3}} }=\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\frac{{a}_{\mathrm{3}} }{{a}_{\mathrm{1}} }=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{a}_{\mathrm{2019}} ={a}_{\mathrm{1}} ×\frac{\mathrm{2}×\mathrm{4}×\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot×\mathrm{2018}}{\mathrm{1}×\mathrm{3}×\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot×\mathrm{2017}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{2018}!!}{\mathrm{2017}!!} \\ $$
Commented by Master last updated on 28/Dec/19
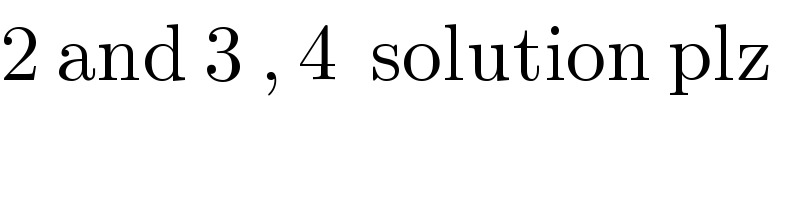
$$\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{3}\:,\:\mathrm{4}\:\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{plz} \\ $$
Commented by Master last updated on 28/Dec/19

$$\mathrm{thanks} \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 28/Dec/19
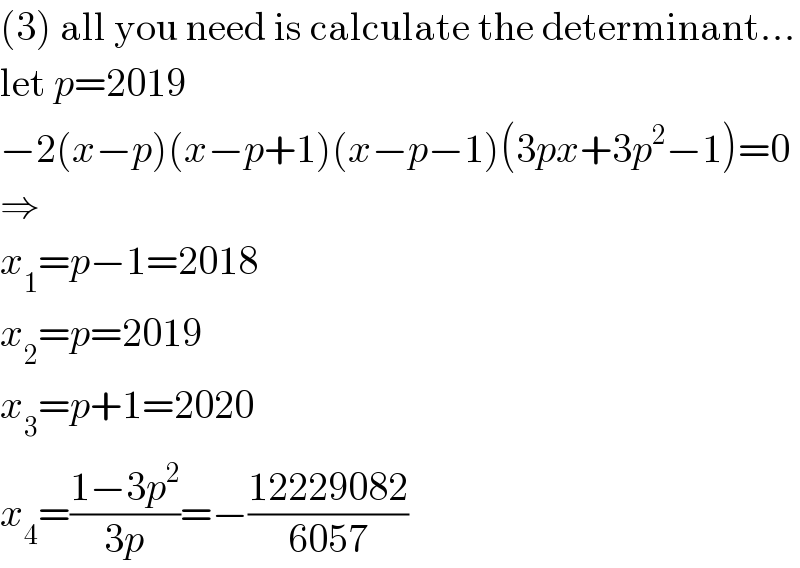
$$\left(\mathrm{3}\right)\:\mathrm{all}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{need}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{calculate}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{determinant}… \\ $$$$\mathrm{let}\:{p}=\mathrm{2019} \\ $$$$−\mathrm{2}\left({x}−{p}\right)\left({x}−{p}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}−{p}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{3}{px}+\mathrm{3}{p}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{1}} ={p}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{2018} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{2}} ={p}=\mathrm{2019} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{3}} ={p}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{2020} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{4}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{3}{p}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}{p}}=−\frac{\mathrm{12229082}}{\mathrm{6057}} \\ $$
Answered by benjo 1/2 santuyy last updated on 29/Dec/19

$$\left(\mathrm{4}\right)\:{f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{4}\:\rightarrow{c}=\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\mathrm{0}\leqslant{f}\left({x}\right)\leqslant\mathrm{4}\:{for}\:\mathrm{0}\leqslant{x}\leqslant\mathrm{3}\:\rightarrow \\ $$$${ax}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{bx}+\mathrm{4}\leqslant\mathrm{4}\:,\: \\ $$$${x}\left({ax}+{b}\right)\leqslant\mathrm{0}\:,\:{b}\:{must}\:{be}\:{negatif} \\ $$$${so}\:{we}\:{has}\:\mathrm{0}\leqslant{x}\leqslant−\left({b}/{a}\right)\:.\: \\ $$$${we}\:{getting}\:−\left({b}/{a}\right)=\mathrm{3}\:\rightarrow\:{b}\:=−\mathrm{3}{a}\:,\:{a}\:>\mathrm{0}\:\blacksquare \\ $$$$ \\ $$
