Question Number 9020 by tawakalitu last updated on 14/Nov/16
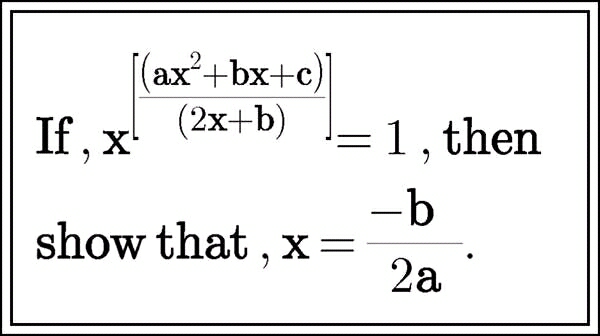
Commented by RasheedSoomro last updated on 20/Nov/16
![By [((ax^2 +bx+c)/(2x+b))] do you mean bracket function?](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q9131.png)
$$\mathrm{By}\:\left[\frac{\mathrm{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{bx}+\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{b}}\right]\:\mathrm{do}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{mean}\:\mathrm{bracket}\:\mathrm{function}? \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 14/Nov/16
![x^([((ax^2 +bx+c)/(2x+b))]) =1 x^([((ax^2 +bx+c)/(2x+b))]) =x^0 [((ax^2 +bx+c)/(2x+b))]=0 0≤((ax^2 +bx+c)/(2x+b))<1 Continue](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q9022.png)
$$\mathrm{x}^{\left[\frac{\mathrm{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{bx}+\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{b}}\right]} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}^{\left[\frac{\mathrm{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{bx}+\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{b}}\right]} =\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{0}} \\ $$$$\left[\frac{\mathrm{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{bx}+\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{b}}\right]=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{0}\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{bx}+\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{b}}<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Continue} \\ $$
Commented by tawakalitu last updated on 14/Nov/16

$$\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{sir}. \\ $$
Answered by mrW last updated on 15/Nov/16
![x^([(((ax^2 +bx+c))/((2x+b)))]) =1 x=1 or ((ax^2 +bx+c)/(2x+b))=0 i.e. ax^2 +bx+c=0 x=((−b±(√(b^2 −4ac)))/(2a)) condition: 2x+b≠0 ((−b±(√(b^2 −4ac)))/a)+b≠0 c≠((b^2 (2−a))/4)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q9036.png)
$$\mathrm{x}^{\left[\frac{\left(\mathrm{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{bx}+\mathrm{c}\right)}{\left(\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{b}\right)}\right]} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{1}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{or} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{bx}+\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{b}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{i}.\mathrm{e}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{bx}+\mathrm{c}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}=\frac{−\mathrm{b}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{b}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4ac}}}{\mathrm{2a}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{condition}:\:\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{b}\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\frac{−\mathrm{b}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{b}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4ac}}}{\mathrm{a}}+\mathrm{b}\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{c}\neq\frac{\mathrm{b}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{a}\right)}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
Commented by tawakalitu last updated on 15/Nov/16

$$\mathrm{Thanks}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 16/Nov/16
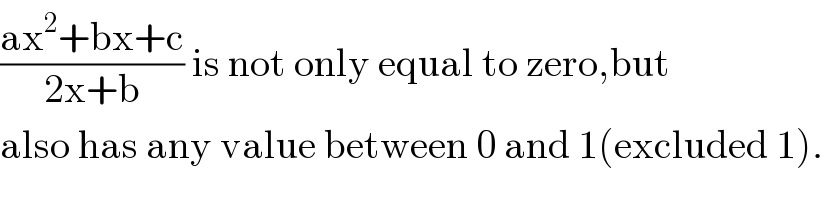
$$\frac{\mathrm{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{bx}+\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{b}}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{only}\:\mathrm{equal}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{zero},\mathrm{but} \\ $$$$\mathrm{also}\:\mathrm{has}\:\mathrm{any}\:\mathrm{value}\:\mathrm{between}\:\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{1}\left(\mathrm{excluded}\:\mathrm{1}\right). \\ $$
