Question Number 4230 by prakash jain last updated on 03/Jan/16
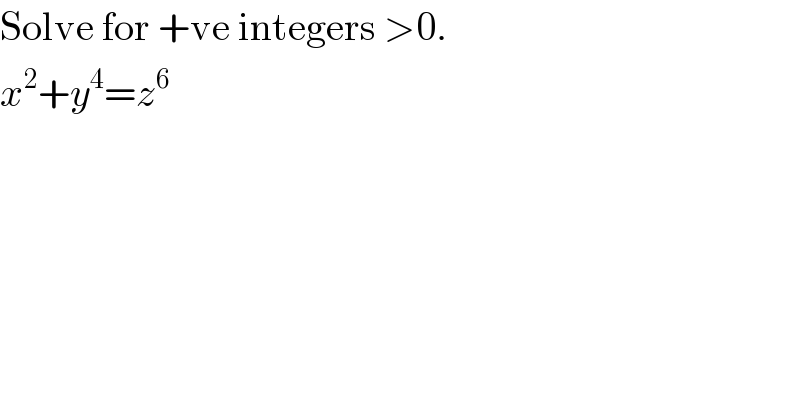
$$\mathrm{Solve}\:\mathrm{for}\:+\mathrm{ve}\:\mathrm{integers}\:>\mathrm{0}. \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{4}} ={z}^{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 04/Jan/16
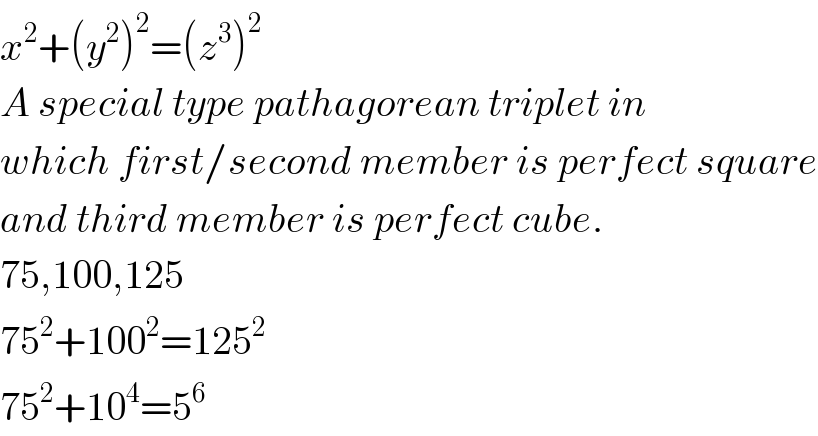
$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\left({z}^{\mathrm{3}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${A}\:{special}\:{type}\:{pathagorean}\:{triplet}\:{in} \\ $$$${which}\:{first}/{second}\:{member}\:{is}\:{perfect}\:{square} \\ $$$${and}\:{third}\:{member}\:{is}\:{perfect}\:{cube}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{75},\mathrm{100},\mathrm{125} \\ $$$$\mathrm{75}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{100}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{125}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{75}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{10}^{\mathrm{4}} =\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 05/Jan/16
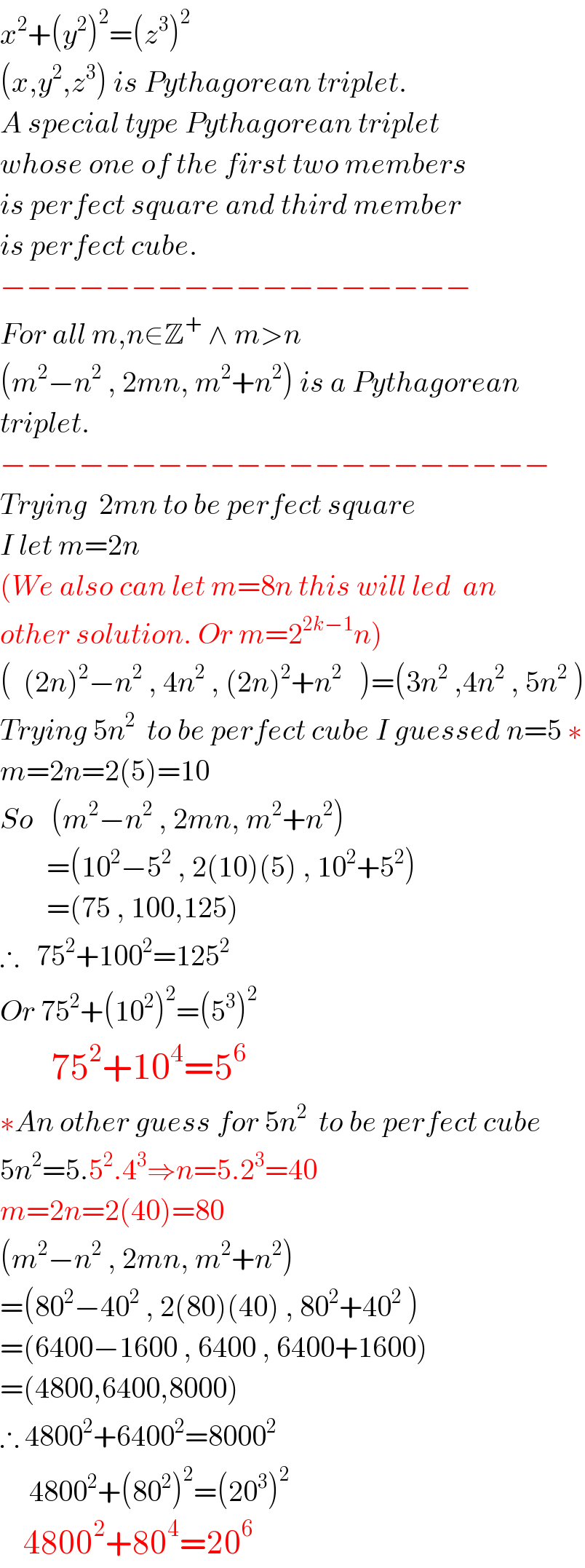
$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\left({z}^{\mathrm{3}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left({x},{y}^{\mathrm{2}} ,{z}^{\mathrm{3}} \right)\:{is}\:{Pythagorean}\:{triplet}. \\ $$$${A}\:{special}\:{type}\:{Pythagorean}\:{triplet} \\ $$$${whose}\:{one}\:{of}\:{the}\:{first}\:{two}\:{members} \\ $$$${is}\:{perfect}\:{square}\:{and}\:{third}\:{member} \\ $$$${is}\:{perfect}\:{cube}. \\ $$$$−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− \\ $$$${For}\:{all}\:{m},{n}\in\mathbb{Z}^{+} \:\wedge\:{m}>{n} \\ $$$$\left({m}^{\mathrm{2}} −{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \:,\:\mathrm{2}{mn},\:{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:{is}\:{a}\:{Pythagorean} \\ $$$${triplet}. \\ $$$$−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− \\ $$$${Trying}\:\:\mathrm{2}{mn}\:{to}\:{be}\:{perfect}\:{square} \\ $$$${I}\:{let}\:{m}=\mathrm{2}{n} \\ $$$$\left({We}\:{also}\:{can}\:{let}\:{m}=\mathrm{8}{n}\:{this}\:{will}\:{led}\:\:{an}\right. \\ $$$$\left.{other}\:{solution}.\:{Or}\:{m}=\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{k}−\mathrm{1}} {n}\right) \\ $$$$\left(\:\:\left(\mathrm{2}{n}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \:,\:\mathrm{4}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \:,\:\left(\mathrm{2}{n}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\:\:\right)=\left(\mathrm{3}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \:,\mathrm{4}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \:,\:\mathrm{5}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\right) \\ $$$${Trying}\:\mathrm{5}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\:{to}\:{be}\:{perfect}\:{cube}\:{I}\:{guessed}\:{n}=\mathrm{5}\:\ast \\ $$$${m}=\mathrm{2}{n}=\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{5}\right)=\mathrm{10} \\ $$$${So}\:\:\:\left({m}^{\mathrm{2}} −{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \:,\:\mathrm{2}{mn},\:{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\left(\mathrm{10}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}} \:,\:\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{10}\right)\left(\mathrm{5}\right)\:,\:\mathrm{10}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\left(\mathrm{75}\:,\:\mathrm{100},\mathrm{125}\right) \\ $$$$\therefore\:\:\:\mathrm{75}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{100}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{125}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${Or}\:\mathrm{75}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(\mathrm{10}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\left(\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{3}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{75}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{10}^{\mathrm{4}} =\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$$\ast{An}\:{other}\:{guess}\:{for}\:\mathrm{5}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\:{to}\:{be}\:{perfect}\:{cube} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{5}.\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}} .\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{3}} \Rightarrow{n}=\mathrm{5}.\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{40} \\ $$$${m}=\mathrm{2}{n}=\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{40}\right)=\mathrm{80} \\ $$$$\left({m}^{\mathrm{2}} −{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \:,\:\mathrm{2}{mn},\:{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$=\left(\mathrm{80}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{40}^{\mathrm{2}} \:,\:\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{80}\right)\left(\mathrm{40}\right)\:,\:\mathrm{80}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{40}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\right) \\ $$$$=\left(\mathrm{6400}−\mathrm{1600}\:,\:\mathrm{6400}\:,\:\mathrm{6400}+\mathrm{1600}\right) \\ $$$$=\left(\mathrm{4800},\mathrm{6400},\mathrm{8000}\right) \\ $$$$\therefore\:\mathrm{4800}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{6400}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{8000}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{4800}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(\mathrm{80}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\left(\mathrm{20}^{\mathrm{3}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\mathrm{4800}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{80}^{\mathrm{4}} =\mathrm{20}^{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 05/Jan/16

$$\mathrm{General}\:\mathrm{Solution} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({y}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\left({z}^{\mathrm{3}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left({x},{y}^{\mathrm{2}} ,{z}^{\mathrm{3}} \right)\:{is}\:{Pythagorean}\:{triplet}. \\ $$$$−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− \\ $$$${For}\:{m}>{n}\:{and}\:{m},{n}\in\mathbb{N}\:{one}\:{general} \\ $$$${Pythagorean}\:{triplet}\:{is} \\ $$$$\left({m}^{\mathrm{2}} −{n}^{\mathrm{2}} ,\mathrm{2}{mn},{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− \\ $$$${To}\:{make}\:\mathrm{2}{mn}\:{perfect}\:{square} \\ $$$${Let}\:{m}=\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{k}−\mathrm{1}} {n} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{mn}=\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{k}−\mathrm{1}} {n}\right){n}=\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{k}} {n}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${m}^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} =\left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{k}−\mathrm{1}} {n}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} =\left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right){n}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${In}\:{order}\:{to}\:{make}\:{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{perfect}\:{cube} \\ $$$${Let}\:{n}=\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\therefore\:{m}=\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{k}−\mathrm{1}} {n}=\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{k}−\mathrm{1}} ×\left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{6}{k}−\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{k}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$−−−−−−− \\ $$$${m}^{\mathrm{2}} −{n}^{\mathrm{2}} =\left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{6}{k}−\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{k}−\mathrm{1}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:=\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{12}{k}−\mathrm{6}} +\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{8}{k}−\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{8}{k}−\mathrm{4}} −\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{mn}=\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{k}} \left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\left\{\mathrm{2}^{{k}} \left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\right\}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${m}^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} =\left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\left\{\left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{6}{k}−\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{k}−\mathrm{1}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \right\}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left\{\:\mathrm{2}^{{k}} \left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\right\}^{\mathrm{4}} \:\:\:\:\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{6}} \:\:\:\forall\:{k}\in\mathbb{N} \\ $$$$\left({x},{y},{z}\right)=\left(\left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{6}{k}−\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{k}−\mathrm{1}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:,\:\mathrm{2}^{{k}} \left(\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right),\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$${For}\:{k}=\mathrm{1}\:\:\mathrm{75}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{10}^{\mathrm{4}} =\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 05/Jan/16
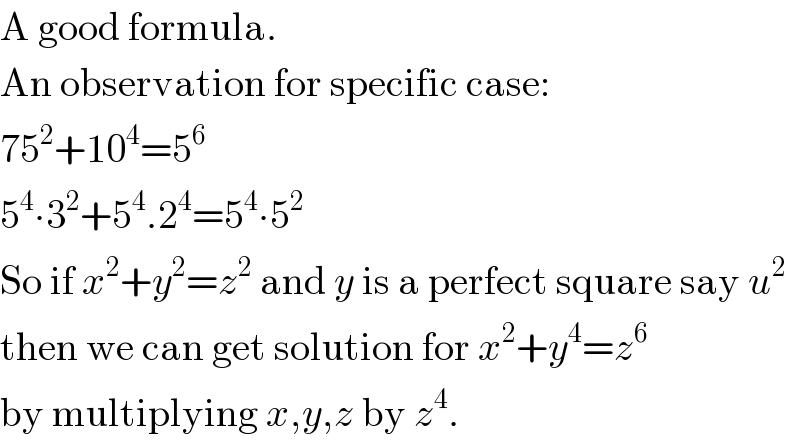
$$\mathrm{A}\:\mathrm{good}\:\mathrm{formula}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{An}\:\mathrm{observation}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{specific}\:\mathrm{case}: \\ $$$$\mathrm{75}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{10}^{\mathrm{4}} =\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{4}} \centerdot\mathrm{3}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{4}} .\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}} =\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{4}} \centerdot\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{So}\:\mathrm{if}\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} ={z}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{and}\:{y}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{perfect}\:\mathrm{square}\:\mathrm{say}\:{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{get}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{for}\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{4}} ={z}^{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{multiplying}\:{x},{y},{z}\:\mathrm{by}\:{z}^{\mathrm{4}} . \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 06/Jan/16

$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{G}}^{\mathcal{OO}} \boldsymbol{\mathrm{D}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{T}}\mathrm{echnique}!\:\:\mathcal{T}\:\mathcal{H}\alpha{n}\Bbbk\mathcal{S}! \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 08/Jan/16

$${Pythagorean}\:{Triple} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\bigtriangledown \\ $$$$\:{Triple}\:{satisfying}\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{4}} ={z}^{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Your}\:\mathrm{technique}\:\mathrm{applying}\:\:\mathrm{twice} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} ={z}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}^{\mathrm{2}} ={z}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left({xy}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{4}} =\left({zy}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left({xy}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left({zy}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} +{y}^{\mathrm{4}} \left({zy}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} =\left({zy}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left({zy}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\left({xy}^{\mathrm{3}} {z}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({y}^{\mathrm{2}} {z}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} =\left({zy}\right)^{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$$\left({x},{y},{z}\right)\:{is}\:{Pythagorean}\:{triplet} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\Rightarrow\left({xy}^{\mathrm{3}} {z}^{\mathrm{2}} \:,\:{y}^{\mathrm{2}} {z}\:,\:{zy}\right)\:{is}\:{tripletfor}\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{4}} ={z}^{\mathrm{6}} . \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{3},\mathrm{4},\mathrm{5}\right)\Rightarrow\left(\:\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{4}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} \left(\mathrm{5}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} ,\:\left(\mathrm{4}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{5}\right),\left(\mathrm{5}\right)\left(\mathrm{4}\right)\:\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\left(\:\:\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{64}\right)\left(\mathrm{25}\right),\mathrm{16}\left(\mathrm{5}\right),\mathrm{20}\:\:\right)=\left(\mathrm{4800},\mathrm{80},\mathrm{20}\right) \\ $$$$\:\left(\mathrm{4},\mathrm{3},\mathrm{5}\right)\Rightarrow\left(\:\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{3}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} \left(\mathrm{5}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} ,\left(\mathrm{3}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{5}\right),\left(\mathrm{3}\right)\left(\mathrm{5}\right)\:\right)=\left(\mathrm{2700},\mathrm{45},\mathrm{15}\right) \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 07/Jan/16
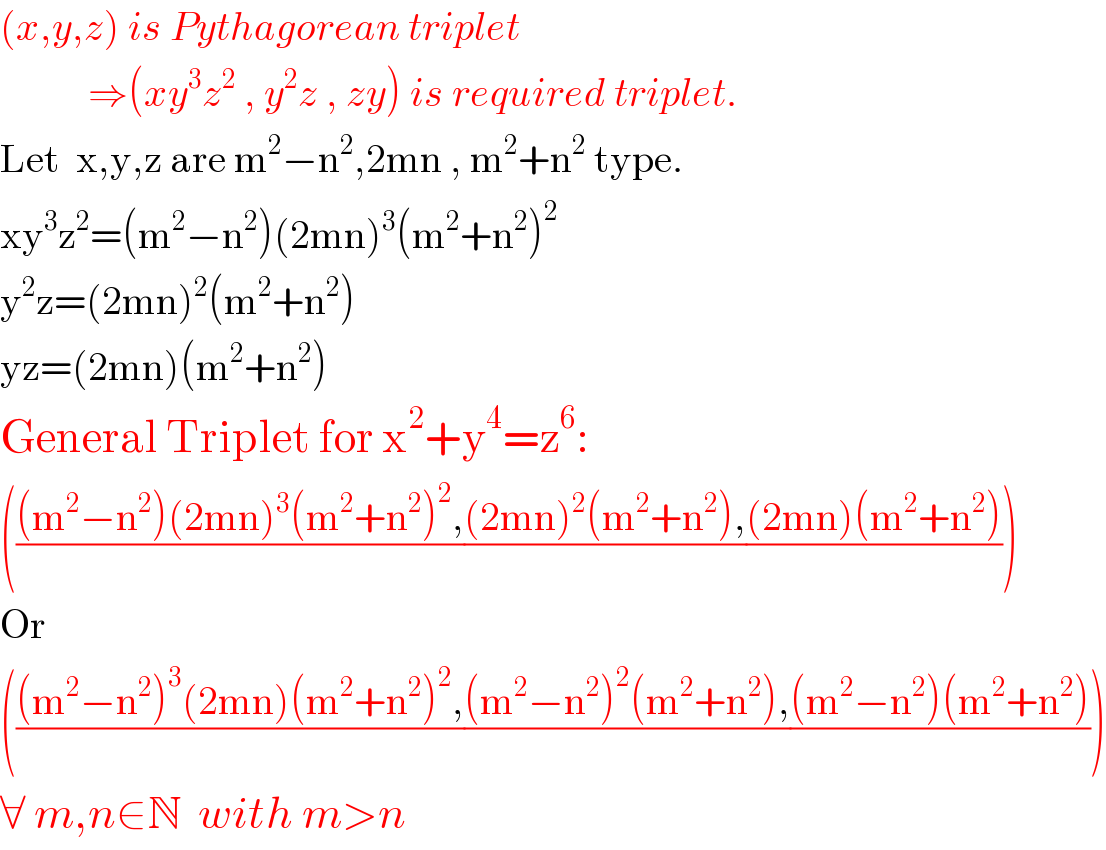
$$\left({x},{y},{z}\right)\:{is}\:{Pythagorean}\:{triplet} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\Rightarrow\left({xy}^{\mathrm{3}} {z}^{\mathrm{2}} \:,\:{y}^{\mathrm{2}} {z}\:,\:{zy}\right)\:{is}\:{required}\:{triplet}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{Let}\:\:\mathrm{x},\mathrm{y},\mathrm{z}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} ,\mathrm{2mn}\:,\:\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{type}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{xy}^{\mathrm{3}} \mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} =\left(\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left(\mathrm{2mn}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} \left(\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{z}=\left(\mathrm{2mn}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{yz}=\left(\mathrm{2mn}\right)\left(\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{General}\:\mathrm{Triplet}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{4}} =\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{6}} : \\ $$$$\left(\frac{\left(\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left(\mathrm{2mn}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} \left(\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} ,}{}\frac{\left(\mathrm{2mn}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right),}{}\frac{\left(\mathrm{2mn}\right)\left(\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}{}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{Or} \\ $$$$\left(\frac{\left(\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{3}} \left(\mathrm{2mn}\right)\left(\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} ,}{}\frac{\left(\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right),}{}\frac{\left(\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left(\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}{}\right) \\ $$$$\forall\:{m},{n}\in\mathbb{N}\:\:{with}\:{m}>{n} \\ $$
