Question Number 182 by sudhanshur last updated on 25/Jan/15
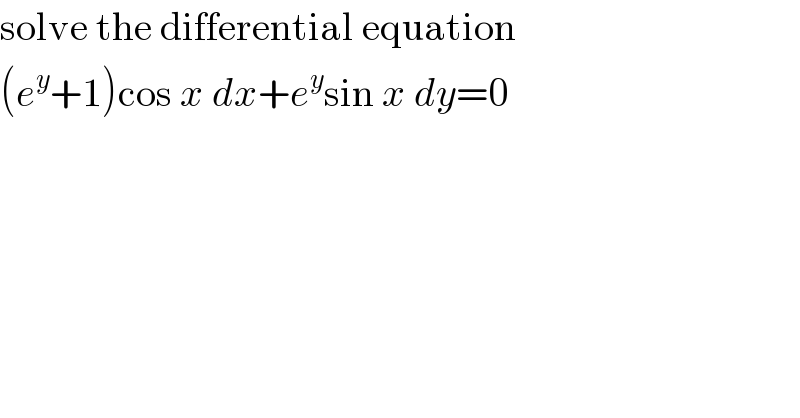
$$\mathrm{solve}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{differential}\:\mathrm{equation} \\ $$$$\left({e}^{{y}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:{dx}+{e}^{{y}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:{dy}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by 123456 last updated on 14/Dec/14
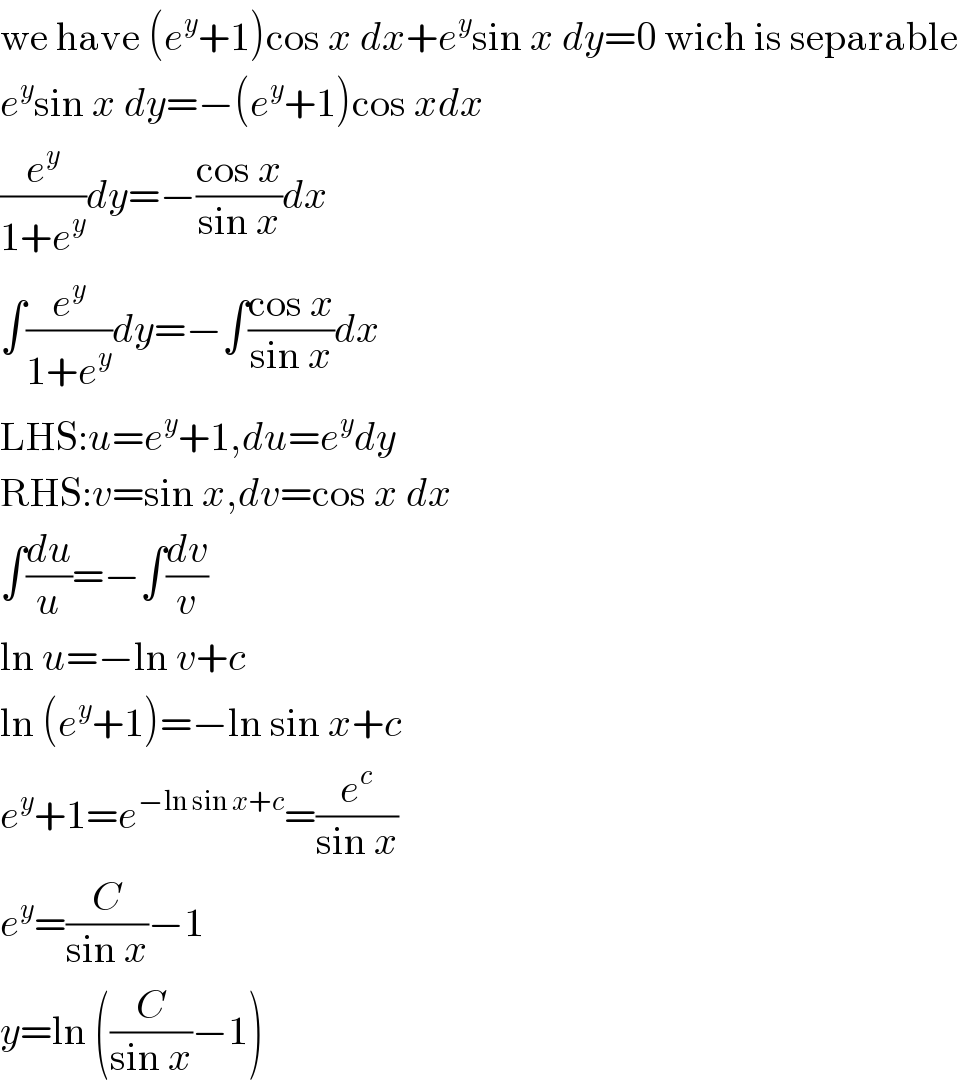
$$\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have}\:\left({e}^{{y}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:{dx}+{e}^{{y}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:{dy}=\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{wich}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{separable} \\ $$$${e}^{{y}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:{dy}=−\left({e}^{{y}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{cos}\:{xdx} \\ $$$$\frac{{e}^{{y}} }{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{y}} }{dy}=−\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}{dx} \\ $$$$\int\frac{{e}^{{y}} }{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{y}} }{dy}=−\int\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{LHS}:{u}={e}^{{y}} +\mathrm{1},{du}={e}^{{y}} {dy} \\ $$$$\mathrm{RHS}:{v}=\mathrm{sin}\:{x},{dv}=\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:{dx} \\ $$$$\int\frac{{du}}{{u}}=−\int\frac{{dv}}{{v}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{ln}\:{u}=−\mathrm{ln}\:{v}+{c} \\ $$$$\mathrm{ln}\:\left({e}^{{y}} +\mathrm{1}\right)=−\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}+{c} \\ $$$${e}^{{y}} +\mathrm{1}={e}^{−\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}+{c}} =\frac{{e}^{{c}} }{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}} \\ $$$${e}^{{y}} =\frac{{C}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${y}=\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\frac{{C}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$
Answered by 123456 last updated on 14/Dec/14
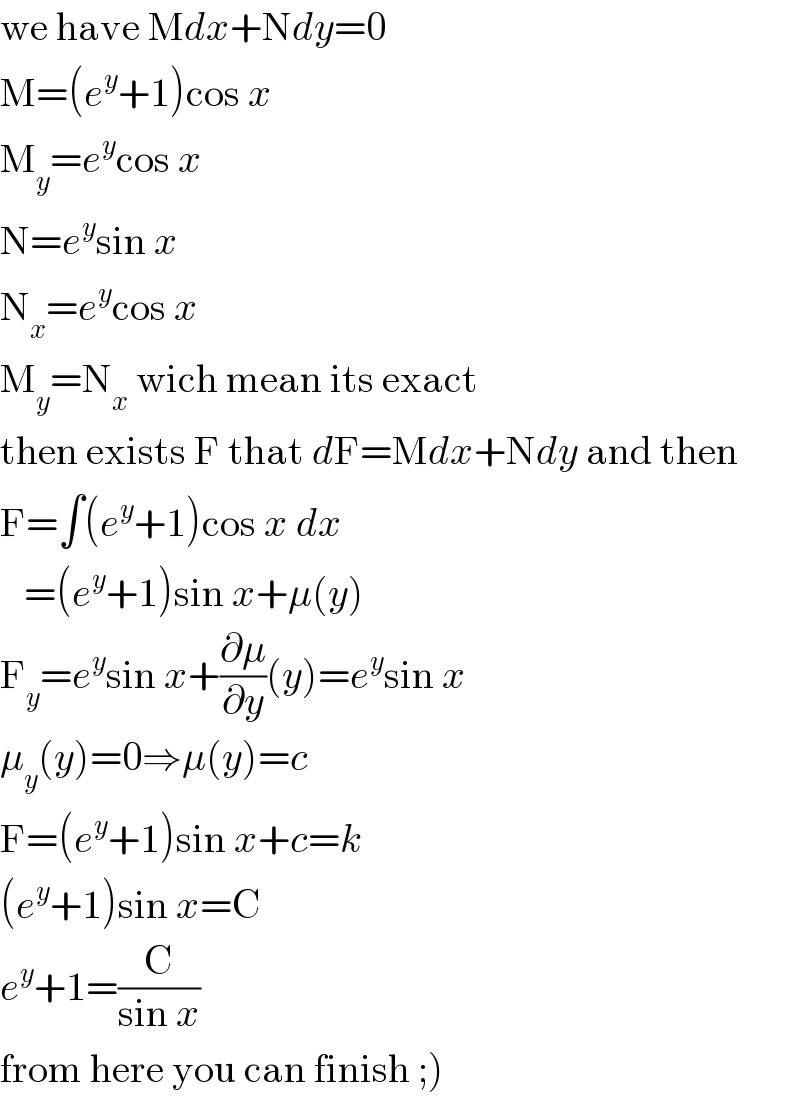
$$\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{M}{dx}+\mathrm{N}{dy}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{M}=\left({e}^{{y}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{cos}\:{x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{M}_{{y}} ={e}^{{y}} \mathrm{cos}\:{x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{N}={e}^{{y}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{N}_{{x}} ={e}^{{y}} \mathrm{cos}\:{x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{M}_{{y}} =\mathrm{N}_{{x}} \:\mathrm{wich}\:\mathrm{mean}\:\mathrm{its}\:\mathrm{exact} \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{exists}\:\mathrm{F}\:\mathrm{that}\:{d}\mathrm{F}=\mathrm{M}{dx}+\mathrm{N}{dy}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{then} \\ $$$$\mathrm{F}=\int\left({e}^{{y}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:{dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\left({e}^{{y}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{sin}\:{x}+\mu\left({y}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{F}_{{y}} ={e}^{{y}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}+\frac{\partial\mu}{\partial{y}}\left({y}\right)={e}^{{y}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x} \\ $$$$\mu_{{y}} \left({y}\right)=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow\mu\left({y}\right)={c} \\ $$$$\mathrm{F}=\left({e}^{{y}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{sin}\:{x}+{c}={k} \\ $$$$\left({e}^{{y}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{sin}\:{x}=\mathrm{C} \\ $$$${e}^{{y}} +\mathrm{1}=\frac{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{from}\:\mathrm{here}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{finish}\:;\right) \\ $$
