Question Number 66350 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 12/Aug/19
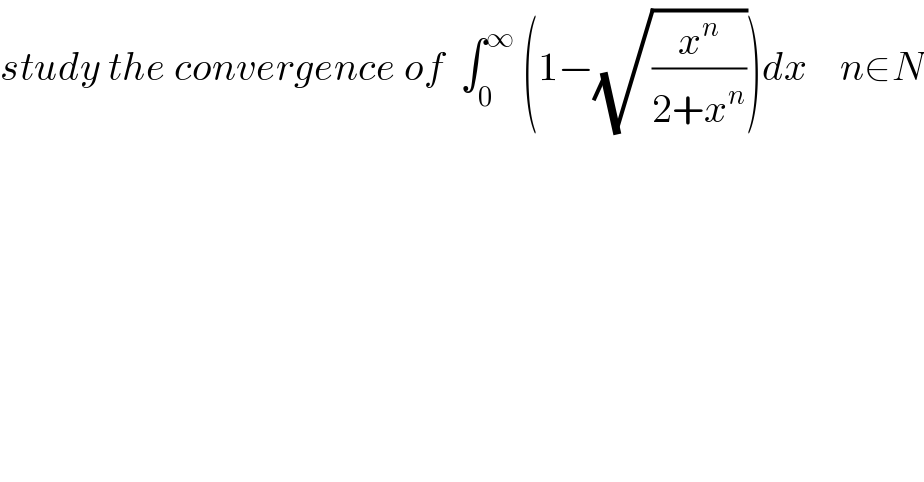
$${study}\:{the}\:{convergence}\:{of}\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\left(\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{\mathrm{2}+{x}^{{n}} }}\right){dx}\:\:\:\:{n}\in{N} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 14/Aug/19
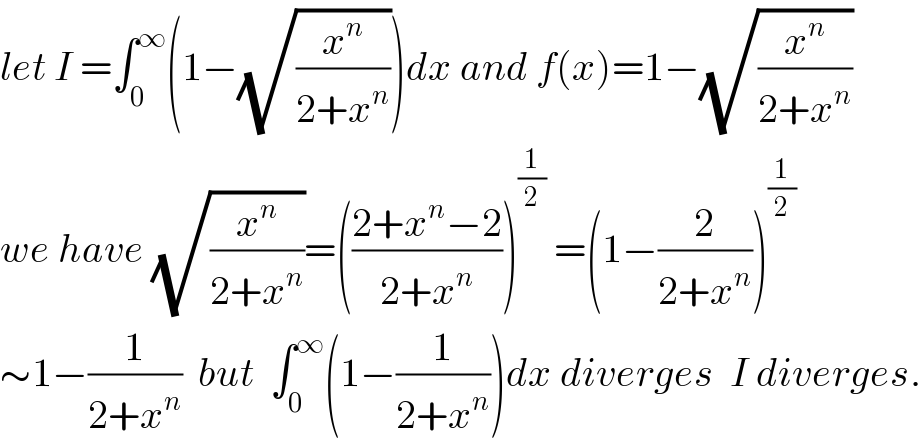
$${let}\:{I}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left(\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{\mathrm{2}+{x}^{{n}} }}\right){dx}\:{and}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{\mathrm{2}+{x}^{{n}} }} \\ $$$${we}\:{have}\:\sqrt{\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{\mathrm{2}+{x}^{{n}} }}=\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}+{x}^{{n}} −\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}+{x}^{{n}} }\right)^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} \:=\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}+{x}^{{n}} }\right)^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\sim\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}+{x}^{{n}} }\:\:{but}\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}+{x}^{{n}} }\right){dx}\:{diverges}\:\:{I}\:{diverges}. \\ $$
