Question Number 6268 by sanusihammed last updated on 21/Jun/16
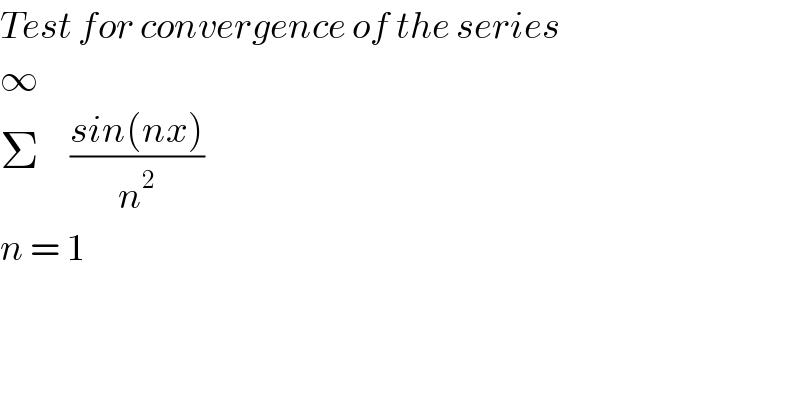
$${Test}\:{for}\:{convergence}\:{of}\:{the}\:{series}\: \\ $$$$\infty \\ $$$$\Sigma\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{sin}\left({nx}\right)}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${n}\:=\:\mathrm{1}\: \\ $$
Commented by FilupSmith last updated on 21/Jun/16
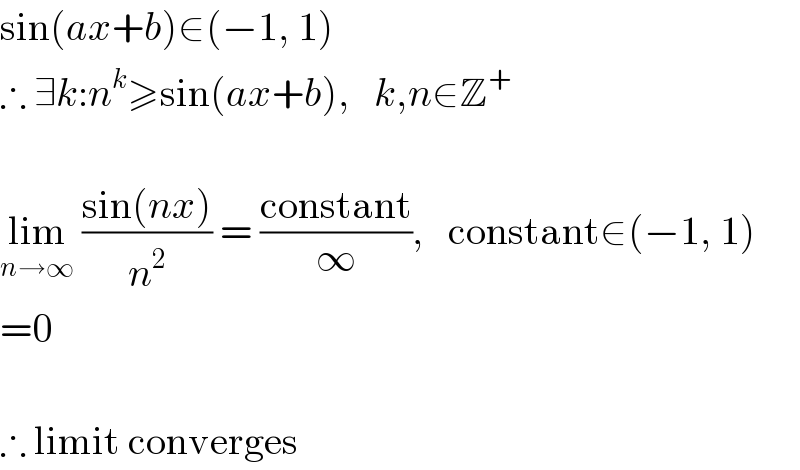
$$\mathrm{sin}\left({ax}+{b}\right)\in\left(−\mathrm{1},\:\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\therefore\:\exists{k}:{n}^{{k}} \geqslant\mathrm{sin}\left({ax}+{b}\right),\:\:\:{k},{n}\in\mathbb{Z}^{+} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{sin}\left({nx}\right)}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{constant}}{\infty},\:\:\:\mathrm{constant}\in\left(−\mathrm{1},\:\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\therefore\:\mathrm{limit}\:\mathrm{converges} \\ $$
Commented by sanusihammed last updated on 21/Jun/16

$${Thanks} \\ $$
Answered by Yozzii last updated on 21/Jun/16
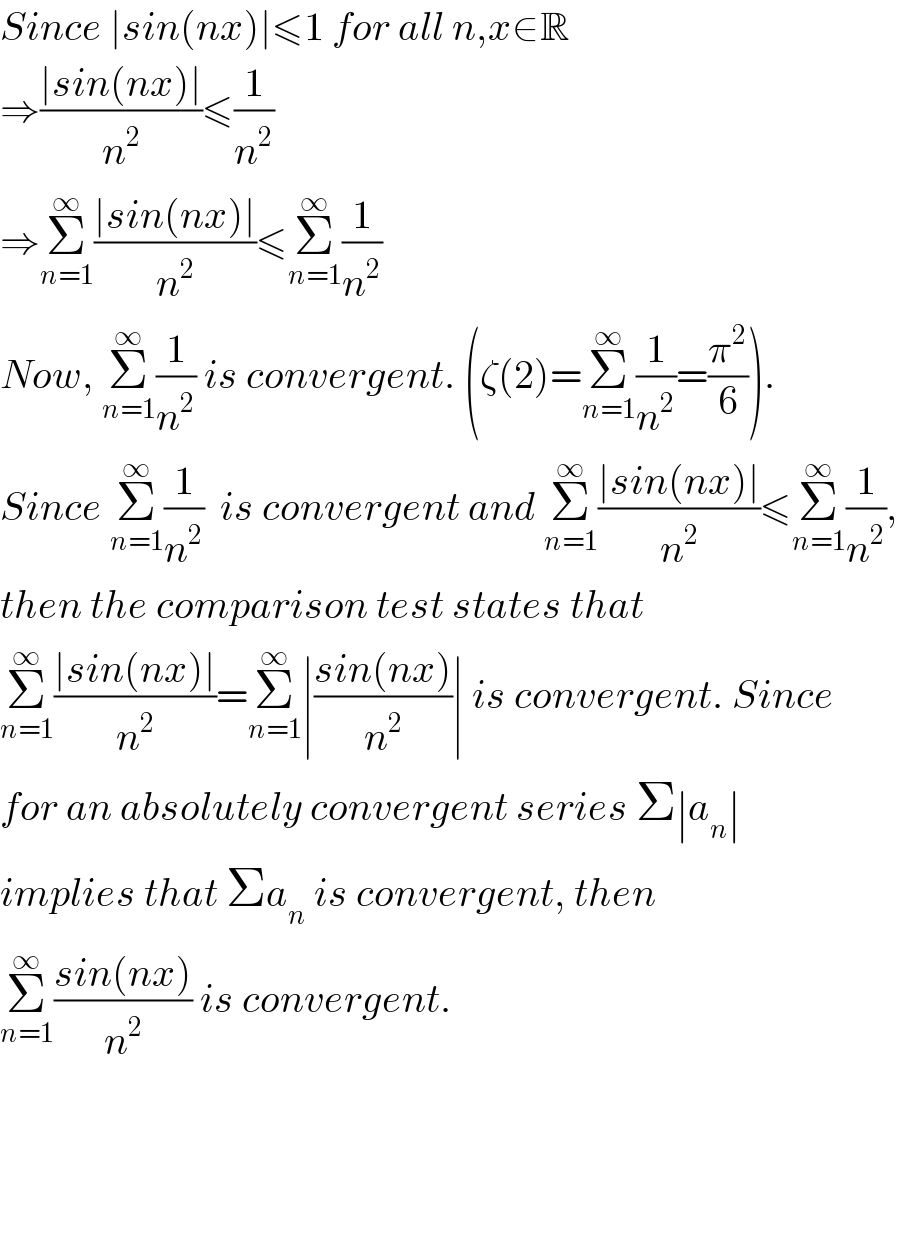
$${Since}\:\mid{sin}\left({nx}\right)\mid\leqslant\mathrm{1}\:{for}\:{all}\:{n},{x}\in\mathbb{R} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\mid{sin}\left({nx}\right)\mid}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mid{sin}\left({nx}\right)\mid}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\leqslant\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${Now},\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{is}\:{convergent}.\:\left(\zeta\left(\mathrm{2}\right)=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{6}}\right). \\ $$$${Since}\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:{is}\:{convergent}\:{and}\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mid{sin}\left({nx}\right)\mid}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\leqslant\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }, \\ $$$${then}\:{the}\:{comparison}\:{test}\:{states}\:{that}\: \\ $$$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mid{sin}\left({nx}\right)\mid}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\mid\frac{{sin}\left({nx}\right)}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\mid\:{is}\:{convergent}.\:{Since} \\ $$$${for}\:{an}\:{absolutely}\:{convergent}\:{series}\:\Sigma\mid{a}_{{n}} \mid \\ $$$${implies}\:{that}\:\Sigma{a}_{{n}} \:{is}\:{convergent},\:{then} \\ $$$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{sin}\left({nx}\right)}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{is}\:{convergent}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by sanusihammed last updated on 21/Jun/16

$${Thanks}\:{for}\:{help} \\ $$
