Question Number 135178 by bemath last updated on 11/Mar/21

$$ \\ $$The top of a 29 feet ladder, leaning against a vertical wall is slipping at a rate of 7 feet per second. how fast is the bottom of the ladder slipping along the ground when the bottom of the ladder is 13 feet away from the base of the wall?
Answered by liberty last updated on 11/Mar/21
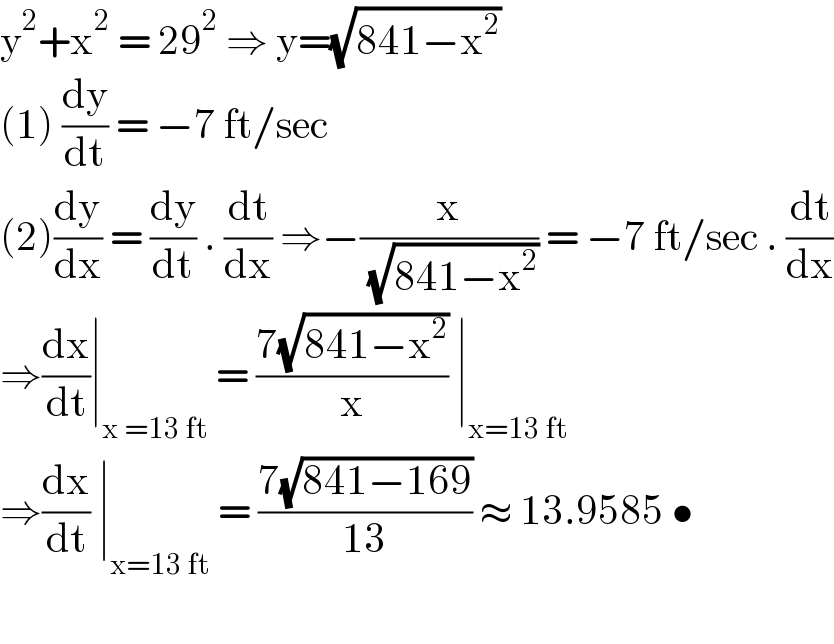
$$\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:=\:\mathrm{29}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{y}=\sqrt{\mathrm{841}−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dt}}\:=\:−\mathrm{7}\:\mathrm{ft}/\mathrm{sec} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dt}}\:.\:\frac{\mathrm{dt}}{\mathrm{dx}}\:\Rightarrow−\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{841}−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\:=\:−\mathrm{7}\:\mathrm{ft}/\mathrm{sec}\:.\:\frac{\mathrm{dt}}{\mathrm{dx}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{dt}}\mid_{\mathrm{x}\:=\mathrm{13}\:\mathrm{ft}} \:=\:\frac{\mathrm{7}\sqrt{\mathrm{841}−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{\mathrm{x}}\:\mid_{\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{13}\:\mathrm{ft}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{dt}}\:\mid_{\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{13}\:\mathrm{ft}} \:=\:\frac{\mathrm{7}\sqrt{\mathrm{841}−\mathrm{169}}}{\mathrm{13}}\:\approx\:\mathrm{13}.\mathrm{9585}\:\bullet \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 11/Mar/21
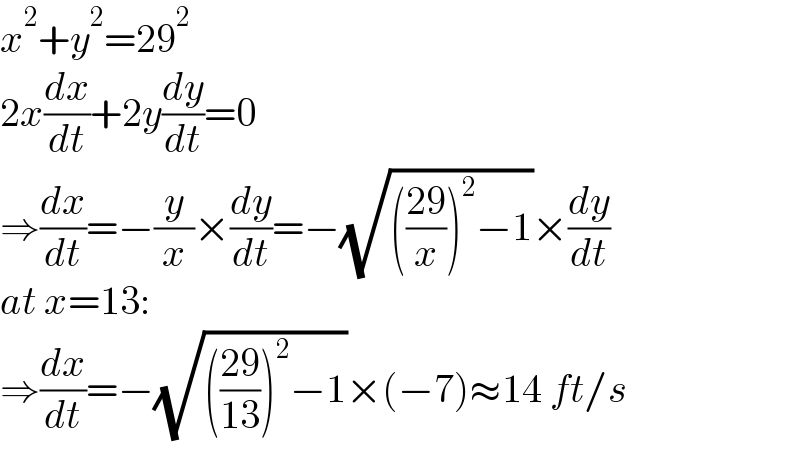
$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{29}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{x}\frac{{dx}}{{dt}}+\mathrm{2}{y}\frac{{dy}}{{dt}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{dx}}{{dt}}=−\frac{{y}}{{x}}×\frac{{dy}}{{dt}}=−\sqrt{\left(\frac{\mathrm{29}}{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}×\frac{{dy}}{{dt}} \\ $$$${at}\:{x}=\mathrm{13}: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{dx}}{{dt}}=−\sqrt{\left(\frac{\mathrm{29}}{\mathrm{13}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}×\left(−\mathrm{7}\right)\approx\mathrm{14}\:{ft}/{s} \\ $$
