Question Number 304 by 123456 last updated on 20/Dec/14
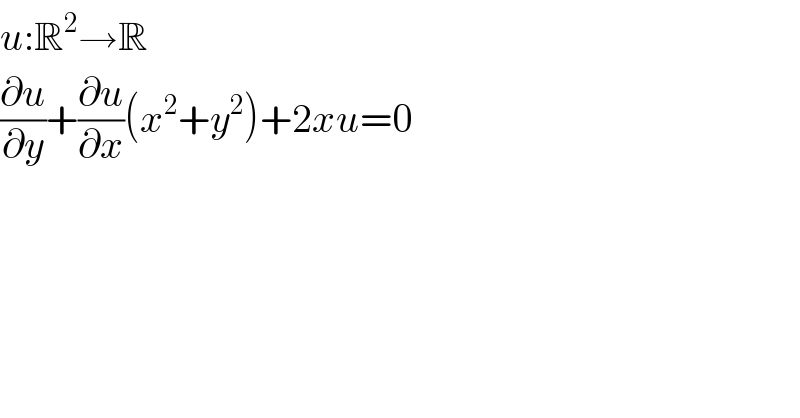
$${u}:\mathbb{R}^{\mathrm{2}} \rightarrow\mathbb{R} \\ $$$$\frac{\partial{u}}{\partial{y}}+\frac{\partial{u}}{\partial{x}}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)+\mathrm{2}{xu}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 20/Dec/14

$$\mathrm{Let}\:\mathrm{us}\:\mathrm{consider}\:\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{equation} \\ $$$${dx}−\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){dy}=\mathrm{0}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{i}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{This}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{an}\:\mathrm{exact}\:\mathrm{equation}.\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{M}=\mathrm{1},{N}=−\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{This}\:\mathrm{equation}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{converted}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{exact},\:\mathrm{if} \\ $$$$\frac{\partial{M}}{\partial{y}}.{u}+\frac{\partial{u}}{\partial{y}}\centerdot{M}=\frac{\partial{N}}{\partial{x}}\centerdot{u}+\frac{\partial{u}}{\partial{x}}{N} \\ $$$$\frac{\partial{u}}{\partial{y}}=−\mathrm{2}{xu}−\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\frac{\partial{u}}{\partial{x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Which}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{given}\:\mathrm{differential}\:\mathrm{equation}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{In}\:\mathrm{other}\:\mathrm{words}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{given}\:\mathrm{differential} \\ $$$$\mathrm{equation}\:\mathrm{gives}\:\mathrm{integrating}\:\mathrm{factor}\:\mathrm{for}\:\left(\mathrm{i}\right). \\ $$$$\frac{\partial{M}}{\partial{y}}=\mathrm{0},\:\frac{\partial{N}}{\partial{x}}=−\mathrm{2}{x} \\ $$$$\frac{\frac{\partial{M}}{\partial{y}}−\frac{\partial{N}}{\partial{x}}}{{N}}=\frac{−\mathrm{2}{x}}{−\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\:\mathrm{This}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{function}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{only}\:{x}. \\ $$$$\frac{\frac{\partial{M}}{\partial{y}}−\frac{\partial{N}}{\partial{x}}}{{M}}=\frac{−\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{1}}\:\mathrm{This}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{function}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{only}\:{y}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{So}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{does}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{look}\:\mathrm{like}\:{u}\left({x},{y}\right)\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{an}\:\mathrm{elementry} \\ $$$$\mathrm{function}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{will}\:\mathrm{see}\:\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{he}\:\mathrm{solved}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{terms}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{other} \\ $$$$\mathrm{functions}. \\ $$
