Question Number 136582 by physicstutes last updated on 23/Mar/21

$$\mathrm{Use}\:\mathrm{De}'\mathrm{Moivre}'\mathrm{s}\:\mathrm{theorem}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{prove}\:\mathrm{that} \\ $$$$\:\underset{{r}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\mathrm{cos}\:{rx}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{value}\left(\mathrm{or}\:\mathrm{expression}\right)\:\mathrm{for}\:\underset{{r}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\mathrm{sin}\:{rx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{assume}\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{two}\:\mathrm{series}\:\mathrm{were}\:\mathrm{convergent}. \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 23/Mar/21
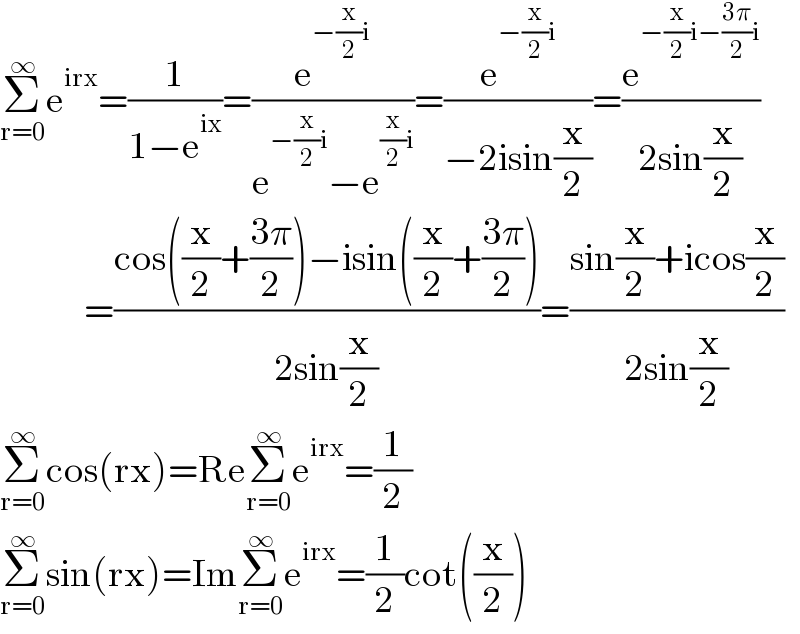
$$\underset{\mathrm{r}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{irx}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{ix}} }=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{i}} }{\mathrm{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{i}} −\mathrm{e}^{\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{i}} }=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{i}} }{−\mathrm{2isin}\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}}=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{i}−\frac{\mathrm{3}\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{i}} }{\mathrm{2sin}\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\frac{\mathrm{cos}\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{3}\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)−\mathrm{isin}\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{3}\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\mathrm{2sin}\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}}=\frac{\mathrm{sin}\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{icos}\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2sin}\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{r}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{rx}\right)=\mathrm{Re}\underset{\mathrm{r}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{irx}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{r}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{rx}\right)=\mathrm{Im}\underset{\mathrm{r}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{irx}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{cot}\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right) \\ $$
Commented by physicstutes last updated on 23/Mar/21

$$\mathrm{perfect} \\ $$
