Question Number 69715 by Mikaell last updated on 26/Sep/19
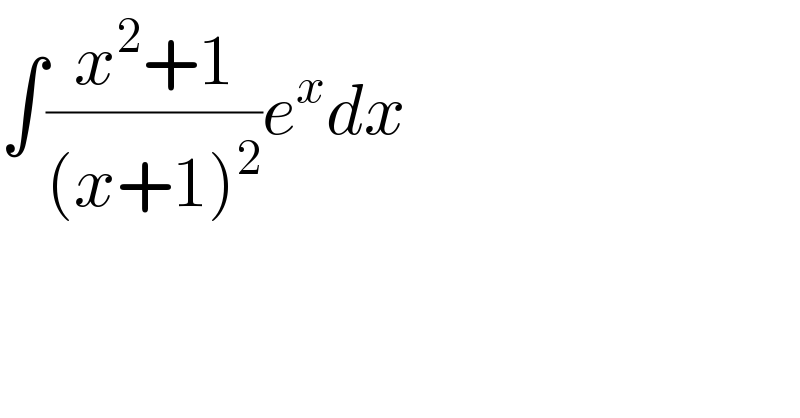
$$\int\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}{\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{e}^{{x}} {dx} \\ $$
Answered by mind is power last updated on 27/Sep/19
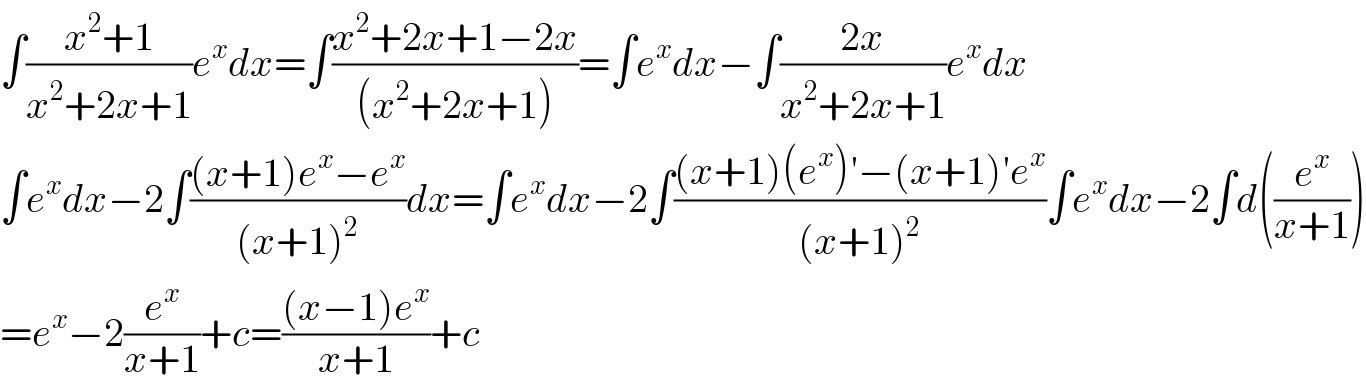
$$\int\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}{e}^{{x}} {dx}=\int\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2}{x}}{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)}=\int{e}^{{x}} {dx}−\int\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}{e}^{{x}} {dx} \\ $$$$\int{e}^{{x}} {dx}−\mathrm{2}\int\frac{\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right){e}^{{x}} −{e}^{{x}} }{\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}=\int{e}^{{x}} {dx}−\mathrm{2}\int\frac{\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({e}^{{x}} \right)'−\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)'{e}^{{x}} }{\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\int{e}^{{x}} {dx}−\mathrm{2}\int{d}\left(\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{x}+\mathrm{1}}\right) \\ $$$$={e}^{{x}} −\mathrm{2}\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{x}+\mathrm{1}}+{c}=\frac{\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right){e}^{{x}} }{{x}+\mathrm{1}}+{c} \\ $$
Commented by Mikaell last updated on 27/Sep/19

$${thank}\:{you}\:{Sir} \\ $$
