Question Number 141333 by cesarL last updated on 17/May/21
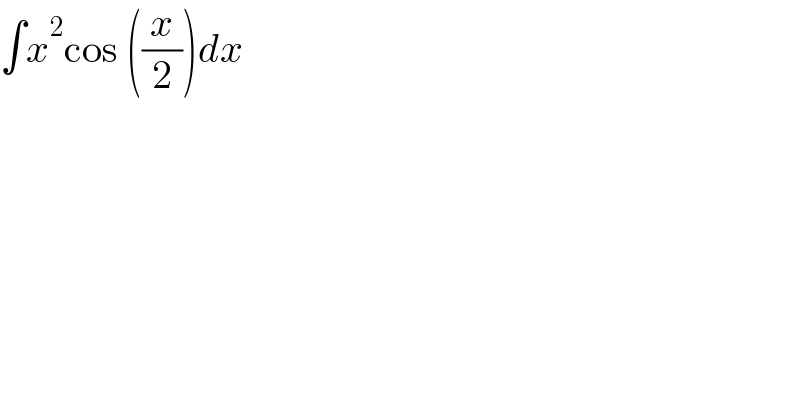
$$\int{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}\:\left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right){dx} \\ $$
Answered by qaz last updated on 17/May/21
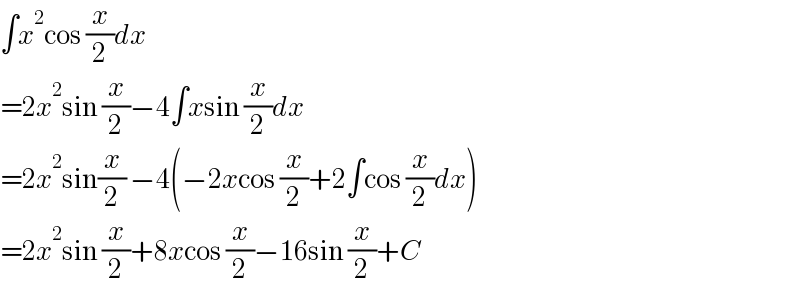
$$\int{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}{dx} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{4}\int{x}\mathrm{sin}\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}{dx} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\:−\mathrm{4}\left(−\mathrm{2}{x}\mathrm{cos}\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{2}\int\mathrm{cos}\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}{dx}\right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{8}{x}\mathrm{cos}\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{16sin}\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+{C} \\ $$
Commented by cesarL last updated on 17/May/21

$${Thank}\:{you}\:{bro} \\ $$
