Question Number 163789 by amin96 last updated on 10/Jan/22
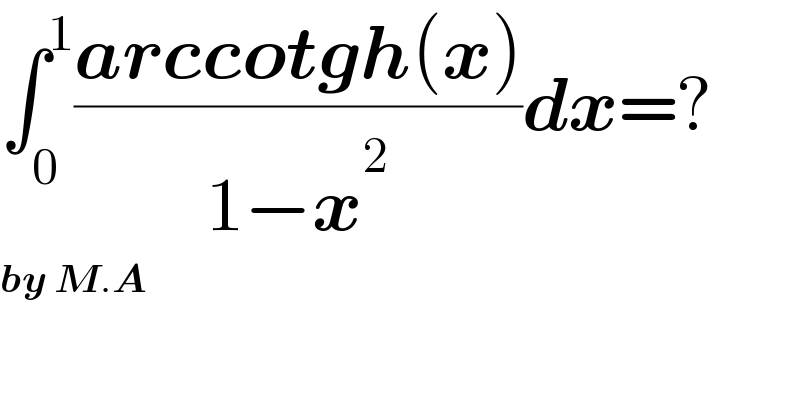
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\boldsymbol{{arccotgh}}\left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)}{\mathrm{1}−\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }\boldsymbol{{dx}}=? \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{by}}\:\boldsymbol{{M}}.\boldsymbol{{A}} \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 10/Jan/22

$$\mathrm{tanh}\:{x}\:=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} −\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} +\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{coth}\:{x}\:=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} +\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} −\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{arcoth}\:{x}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}}{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}\left(\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +{C} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\frac{\mathrm{arcoth}\:{x}}{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}\:\mathrm{doesn}'\mathrm{t}\:\mathrm{converge} \\ $$
